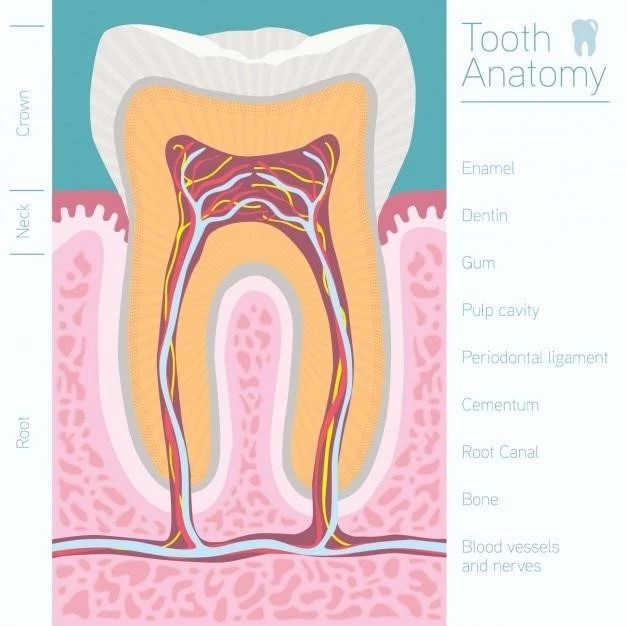
Disease ౼ Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones
Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones is a rare genetic defect affecting dental development. It leads to dental abnormalities, brittle bones, and issues with dental enamel. This condition, related to bone formation and connective tissue, requires specialized dental care.
Introduction to Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones
Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones is a rare dental disorder characterized by abnormal development of dentin, the tissue beneath the enamel of teeth. This genetic defect affects the formation of dentin and can impact the jaw bone as well. Individuals with this inherited condition may experience issues with dental health due to the abnormal development of dentin. Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones is linked to a defect in connective tissue, leading to weakened dental enamel and increased susceptibility to tooth decay.
People with this condition may also exhibit brittle bones due to the impact on bone formation. The abnormal dentin formation can affect the dental pulp, the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels, leading to dental complications. Diagnosis of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones is crucial for appropriate dental treatment and management. Understanding the mechanisms underlying this condition is essential for providing effective care and improving the dental health of affected individuals.
Understanding Dental Abnormalities
Dental abnormalities associated with Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones encompass a range of issues impacting the teeth and jaw bone. These abnormalities stem from genetic defects affecting the development of dentin, leading to structural changes in the teeth. The abnormal dentin formation can result in weakened dental enamel, predisposing individuals to tooth decay and other oral health problems.
Individuals with this condition may also experience brittleness in their bones due to the impact on bone formation. The abnormal development of dentin can affect the dental pulp, which can cause complications such as tooth sensitivity and pain. Understanding the spectrum of dental abnormalities that arise from Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment of affected individuals.
By recognizing and addressing these dental abnormalities early on, dental professionals can provide appropriate care to manage the impact of this genetic defect on oral health. Through tailored dental treatments and preventive strategies, individuals with Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones can maintain better dental health and overall well-being.
Causes of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones
The primary cause of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones lies in genetic abnormalities that affect the formation of dentin and bone tissue. This rare condition is linked to inherited factors that disrupt the normal development of dentin, leading to structural anomalies in the teeth. The genetic defect influences the process of bone formation and connective tissue, resulting in dental abnormalities and brittle bones.
Individuals may inherit this condition from their parents, with the genetic defect manifesting in the abnormal development of dentin and impacting the overall dental health. The disruption in connective tissue can compromise the strength of dental enamel, making teeth more susceptible to decay. The genetic factors contributing to Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones play a significant role in shaping the dental characteristics and predisposition to oral health issues in affected individuals.
Understanding the genetic basis of this condition is crucial for early identification and intervention to address the dental abnormalities associated with Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones. By unraveling the genetic components involved in this disorder, healthcare providers can tailor dental care and treatment strategies to manage the impact of the genetic defect on oral health effectively.
Mechanisms of Bone Formation and Connective Tissue in Dental Health
The mechanisms of bone formation and connective tissue play a critical role in maintaining optimal dental health. In the context of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones, these mechanisms are disrupted due to genetic defects affecting dentin and bone tissue development. Bone formation is intricately linked to the formation of dentin, the tissue that comprises the bulk of the tooth beneath the enamel.
Connective tissue, which includes collagen and other proteins, is essential for providing structural support to teeth and bones. In individuals with Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones, abnormalities in connective tissue can lead to weakened dental enamel and compromised bone strength. The interplay between bone formation and connective tissue function is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the teeth and jaw bone.
Understanding how these mechanisms are affected by genetic defects in Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones is fundamental to developing targeted interventions to address the dental abnormalities associated with this condition. By comprehending the intricate relationship between bone formation and connective tissue in dental health, healthcare professionals can devise specialized treatment approaches to manage the impact of this rare genetic defect on oral health effectively.
Effects of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones on Dental Enamel and Dental Pulp
Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones can have significant effects on both dental enamel and dental pulp. The abnormal development of dentin, a key component of teeth, can impact the structure and strength of dental enamel, leading to increased susceptibility to tooth decay. Weakened dental enamel in individuals with this condition can result in compromised oral health and an elevated risk of dental caries.
Furthermore, Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones can affect the dental pulp, the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels. Changes in dentin formation can disrupt the integrity of the dental pulp, causing sensitivity, pain, and potential complications. The impact on dental pulp health underscores the intricate relationship between dentin abnormalities and the overall well-being of the tooth structure.
Recognizing the effects of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones on dental enamel and dental pulp is essential for devising comprehensive treatment plans to address these specific challenges. By addressing both the structural changes in dental enamel and the implications for dental pulp health, dental professionals can provide targeted care to mitigate the impact of this rare genetic defect on the oral health of affected individuals.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones
Diagnosing Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones involves a comprehensive assessment of dental abnormalities, genetic history, and clinical symptoms. Dental professionals may conduct imaging studies, genetic testing, and dental examinations to confirm the presence of this rare condition. Early diagnosis is crucial for initiating timely interventions to manage the impact of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones on oral health.
Once diagnosed, the treatment of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones focuses on addressing the specific challenges associated with this condition. Dental care for individuals with this disorder may involve strategies to strengthen dental enamel, prevent tooth decay, and manage any complications related to dental pulp health; Specialized dental treatments, such as custom restorations and preventive measures, can help individuals maintain optimal oral health.
Collaboration between dental professionals, genetic specialists, and other healthcare providers is essential in developing a holistic treatment plan for individuals with Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones. By leveraging a multidisciplinary approach, healthcare teams can optimize the management of this rare genetic defect and improve the overall dental well-being of affected individuals.
Management and Prevention Strategies
Managing Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones involves a combination of dental interventions and preventive measures to uphold oral health. Individuals with this condition may benefit from regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and proactive cavity prevention strategies. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly, can help prevent dental decay.
For individuals with Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones, personalized management strategies may include the use of dental sealants to protect vulnerable teeth, dietary modifications to reduce sugar intake, and fluoride treatments to strengthen dental enamel. Dental professionals may recommend tailored approaches to address the unique challenges posed by this genetic defect and promote optimal oral health outcomes.
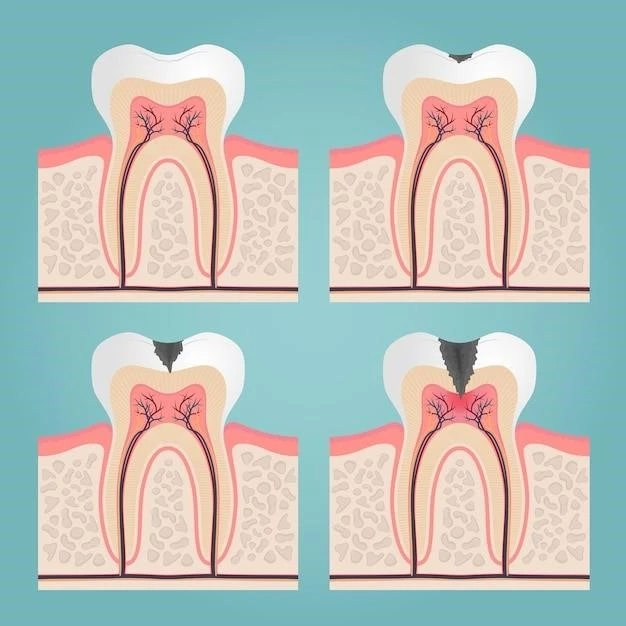
Prevention strategies for individuals with Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones may also involve lifestyle adjustments to support overall well-being, including a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients for dental health. By adopting a proactive approach to oral care and implementing preventive measures early on, individuals with this condition can minimize the impact of dental abnormalities and maintain healthy teeth and gums.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones is a rare genetic defect that affects dental development and bone formation. This condition manifests in dental abnormalities, weakened dental enamel, and potential complications related to dental pulp health. Understanding the causes, effects, and management strategies for Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones is essential for providing effective dental care to individuals with this rare disorder.
By recognizing the impact of genetic defects on dentin and connective tissue, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment approaches to address the specific challenges faced by individuals with Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones. Early diagnosis, specialized dental treatments, and preventive strategies can play a crucial role in managing the oral health implications of this condition and promoting better dental well-being.
Collaboration between dental specialists, genetic experts, and healthcare teams is key to optimizing the management of Dentin Dysplasia Sclerotic Bones and enhancing the quality of life for affected individuals. Through a multidisciplinary approach and a focus on personalized care, it is possible to mitigate the impact of this rare genetic defect on dental health and support overall oral well-being.