Disease ⎻ Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII
When it comes to Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII, it is crucial to understand the impact on the liver due to enzyme deficiency. This autosomal recessive disorder results from gene mutations affecting metabolism. Stay tuned for insights on symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and more.
Introduction
Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII, also known as hepatic phosphorylase kinase deficiency, is a rare inherited metabolic disorder that affects glycogenolysis, the process by which glycogen is broken down into glucose. This specific type predominantly involves the liver. The condition is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme phosphorylase kinase, which plays a crucial role in glycogen metabolism. Individuals with Type VIII have an autosomal recessive gene mutation that impairs the function of this enzyme.
Understanding this disease is essential as it can lead to various symptoms and complications. In this article, we will delve deeper into the characteristics of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII, including its impact on the liver, inheritance pattern, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment approaches, dietary modifications, monitoring, genetic counseling, as well as current research and future directions in managing this condition. Stay informed to better navigate the complexities of this rare disorder.
Understanding Glycogen Storage Diseases
Before delving into Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII, it’s important to have a broad understanding of glycogen storage diseases (GSDs) in general. GSDs are a group of inherited metabolic disorders characterized by enzyme deficiencies impacting glycogen metabolism. Glycogen is a form of stored glucose that serves as an essential energy source, especially in the liver and muscles.
Individuals with GSDs experience difficulties in storing, breaking down, or releasing glycogen, leading to various health complications. There are different types of GSDs, each caused by deficiencies in specific enzymes involved in glycogen metabolism. These disorders can affect various organs and tissues, depending on the enzyme deficiency.
By understanding the mechanisms behind GSDs, including factors influencing glycogenolysis and glycogenesis, individuals can grasp the complexities of these rare genetic conditions. Research in this field continues to expand our knowledge of GSDs, leading to improved diagnostic techniques and treatment strategies.
Stay informed about GSDs to better comprehend the intricacies of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII and other related disorders. Education and awareness play a vital role in managing these conditions effectively, promoting early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and a better quality of life for affected individuals.
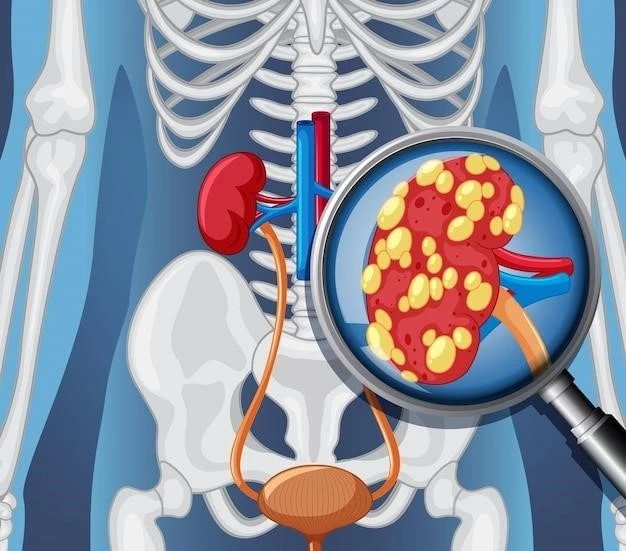
Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII⁚ Liver Involvement
Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII primarily affects the liver due to the deficiency of the enzyme phosphorylase kinase. This enzyme plays a crucial role in glycogenolysis, the breakdown of glycogen into glucose. Without sufficient phosphorylase kinase activity, the liver struggles to release glucose when needed, leading to various metabolic challenges.
The liver’s involvement in Type VIII manifests through symptoms such as hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), and elevated liver enzymes. Hypoglycemia can cause weakness, fatigue, and dizziness, while hepatomegaly may result in abdominal discomfort and complications over time.
Understanding how Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII impacts the liver is essential for proper management and treatment. Individuals with this condition require specialized care to address liver function, maintain stable blood sugar levels, and prevent long-term complications associated with liver involvement.
By staying informed about the specific challenges related to liver function in Type VIII, patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers can work together to develop comprehensive management strategies tailored to the individual’s needs. Awareness of liver-related symptoms and regular monitoring are key aspects of effectively managing Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII.
Cause⁚ Enzyme Deficiency
The root cause of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII lies in the deficiency of the enzyme phosphorylase kinase. This enzyme is essential for glycogenolysis, the process by which glycogen is converted into glucose for energy production. In Type VIII, the insufficient activity of phosphorylase kinase disrupts this metabolic pathway, leading to impaired glucose release from glycogen stores within the liver.
This enzyme deficiency in Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII is the result of genetic mutations affecting the PHKA2 gene٫ which encodes the alpha subunit of phosphorylase kinase. These mutations are inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern٫ meaning that an affected individual must inherit a copy of the mutated gene from both parents.
Understanding the specific enzyme deficiency driving Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies. By recognizing the genetic basis of the condition, healthcare providers can offer personalized care to address the underlying cause of the disorder and manage its symptoms more effectively.
Individuals diagnosed with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII and their families can benefit from genetic counseling to understand the inheritance pattern, assess the risk of passing the condition to future generations, and make informed decisions regarding family planning. By addressing the cause of the enzyme deficiency through genetic insights, healthcare professionals can provide comprehensive care and support to individuals affected by Type VIII.
Inheritance Pattern⁚ Autosomal Recessive
Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, meaning that an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) to develop the disorder. In the case of Type VIII, the mutations occur in the PHKA2 gene, which is responsible for encoding the alpha subunit of phosphorylase kinase.
Individuals who inherit one mutated copy of the PHKA2 gene are considered carriers of the condition but typically do not show symptoms of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII. When two carriers of the mutated gene have children, there is a 25% chance with each pregnancy that the child will inherit two copies of the mutated gene and develop the disease.
Understanding the autosomal recessive nature of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII is essential for genetic counseling, family planning, and risk assessment. By being aware of the inheritance pattern, individuals and families affected by Type VIII can make informed decisions regarding genetic testing, prenatal screening, and the likelihood of passing the condition to future generations.
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in explaining the implications of autosomal recessive inheritance and guiding families through the complexities of genetic conditions like Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII. By promoting awareness and education about inheritance patterns, healthcare professionals empower individuals to make informed choices regarding their health and family planning decisions.
Symptoms of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII
Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII presents with a range of symptoms related to liver dysfunction and impaired glycogen metabolism. Common symptoms include recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), elevated liver enzymes, fatigue, weakness, and abdominal discomfort.
Individuals with Type VIII may experience dizziness, confusion, and sweating during hypoglycemic episodes, which can be triggered by fasting or strenuous exercise. Hepatomegaly may cause abdominal pain, fullness, and a feeling of heaviness in the upper right abdomen. Elevated liver enzymes can be indicative of liver inflammation or damage.
It is important to recognize and monitor these symptoms to ensure timely intervention and management of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII. Seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment is crucial in addressing the underlying metabolic challenges and liver-related issues associated with this disorder.
By understanding the common signs and symptoms of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII, individuals, caregivers, and healthcare providers can work together to develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses the unique needs of each patient. Regular monitoring, adherence to treatment protocols, and lifestyle modifications can help optimize health outcomes and improve quality of life for individuals living with Type VIII.
Diagnosis of Type VIII
Diagnosing Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may conduct blood tests to assess glucose levels, liver function, and specific enzyme activity related to glycogen metabolism. Elevated liver enzymes, hypoglycemia, and hepatomegaly are common indicators that prompt further investigation for Type VIII.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of Type VIII by identifying mutations in the PHKA2 gene associated with the deficiency of phosphorylase kinase. Molecular genetic analysis can provide definitive results and help differentiate Type VIII from other glycogen storage diseases or liver disorders with similar presentations.
It is essential for individuals exhibiting symptoms of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII to seek medical attention and undergo a thorough diagnostic process to accurately identify the underlying cause of their metabolic imbalance. Early and precise diagnosis allows for the implementation of targeted treatment strategies and proper management of the condition.
Healthcare professionals specializing in genetic disorders, metabolism, and hepatology can guide patients through the diagnostic journey, interpret test results, and develop tailored care plans to address the specific needs of individuals with Type VIII. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team can ensure a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management, enhancing the quality of care and outcomes for those affected by Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII.
Treatment Approaches
The management of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII aims to address the underlying enzyme deficiency, control symptoms, and optimize metabolic function. Treatment approaches for Type VIII typically involve a combination of dietary modifications, medications, and lifestyle adjustments tailored to the individual’s needs.
**Dietary Management⁚** A key aspect of treating Type VIII involves following a carefully controlled diet to regulate blood sugar levels and support liver function. Patients may benefit from frequent meals with a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, along with avoiding prolonged fasting and high-sugar foods that can exacerbate hypoglycemia.
**Medications⁚** Some individuals with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII may require medications to help manage symptoms such as hypoglycemia or hyperlipidemia. Specific drugs may be prescribed to stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of metabolic complications, or support liver health.
**Monitoring and Support⁚** Regular monitoring of liver function, glucose levels, and overall metabolic health is essential in the long-term management of Type VIII. Close follow-up with healthcare providers, including specialists in metabolism and genetics, can help ensure proper disease management and timely intervention when needed.
Individuals with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII should work closely with a healthcare team knowledgeable about metabolic disorders to develop a personalized treatment plan. By adhering to prescribed therapies, making healthy lifestyle choices, and staying proactive in managing their condition, patients can better control symptoms, prevent complications, and improve their quality of life while living with Type VIII.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications play a critical role in managing Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII and supporting liver health. Individuals with Type VIII should work closely with a healthcare provider or a dietitian specializing in metabolic disorders to develop a nutrition plan tailored to their specific needs.
**Balanced Nutrition⁚** A well-rounded diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables is essential for individuals with Type VIII. Balancing macronutrients helps regulate blood sugar levels and provides sustained energy throughout the day.
**Frequent Meals⁚** Eating frequent small meals and snacks can help prevent episodes of hypoglycemia by maintaining a steady supply of glucose to the body. Avoiding long periods without eating and incorporating healthy snacks can support metabolic stability in individuals with Type VIII.
**Avoiding Trigger Foods⁚** Foods high in simple sugars or refined carbohydrates can quickly spike blood sugar levels and trigger hypoglycemia in individuals with Type VIII. Limiting the intake of sugary beverages, candies, pastries, and other high-glycemic foods is crucial for preventing metabolic fluctuations.
**Supplementation⁚** In some cases, individuals with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII may benefit from specific nutrient supplements to address potential deficiencies or support liver function. Discussing supplementation options with a healthcare provider can ensure comprehensive nutritional support.
By prioritizing a nutrition plan that emphasizes balanced meals, regular eating schedules, and mindful food choices, individuals with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII can better manage their symptoms and support overall metabolic health. Engaging in ongoing dietary modifications as part of a comprehensive treatment approach can enhance the quality of life for those living with Type VIII.
Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring and proactive management are essential components of caring for individuals with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII to ensure optimal health outcomes and prevent complications. Healthcare providers, including specialists in metabolism, hepatology, and genetics, play a crucial role in overseeing the ongoing care and treatment of individuals with Type VIII.
**Liver Function Monitoring⁚** Routine assessments of liver function, including liver enzyme levels and imaging studies, help track the progression of liver involvement in individuals with Type VIII. Monitoring liver health is vital in preventing complications such as cirrhosis or liver failure.
**Blood Glucose Control⁚** Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is key in managing hypoglycemia and preventing metabolic fluctuations in individuals with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII. Continuous glucose monitoring or periodic blood sugar tests can provide valuable insights for optimizing treatment.
**Medication Management⁚** For individuals with Type VIII who require medications to address symptoms or complications, adherence to prescribed treatments and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential. Proper medication management plays a significant role in controlling symptoms and supporting overall well-being.
**Lifestyle Adjustments⁚** Making healthy lifestyle choices, including regular physical activity, sufficient sleep, stress management, and avoiding alcohol and smoking, can complement medical treatments and support metabolic health in individuals with Type VIII. Lifestyle adjustments can help improve overall health outcomes and quality of life.
By prioritizing regular monitoring of liver function, blood glucose levels, and overall metabolic health, individuals with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII can work towards effectively managing their condition and reducing the risk of complications. Collaboration with a knowledgeable healthcare team and consistent adherence to monitoring protocols are essential in promoting optimal health and well-being for individuals living with Type VIII.
Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling plays a crucial role in supporting individuals and families affected by Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII by providing education, guidance, and personalized risk assessment regarding the inheritance pattern and genetic implications of the condition. Genetic counselors, specialized healthcare professionals trained in medical genetics, can offer valuable support and information to individuals with Type VIII.
**Understanding Inheritance⁚** Genetic counselors can explain the autosomal recessive inheritance pattern of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII, clarifying the likelihood of passing the mutated gene to future generations and the risk of having a child with the condition. Understanding the genetic basis of Type VIII is essential for informed decision-making regarding family planning.
**Risk Assessment⁚** Through genetic testing and family history evaluation, genetic counselors can assess the risk of Type VIII in individuals and their families. Identifying carriers of the mutated gene and determining recurrence risks in future pregnancies enable families to make informed choices about genetic testing, prenatal screening, and reproductive options.
**Emotional Support⁚** Genetic counseling provides a safe space for individuals and families to process the emotional impact of a genetic diagnosis, navigate complex medical information, and address concerns about living with or passing on Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII. Emotional support and resources can help individuals cope with the challenges associated with genetic conditions.
**Education and Advocacy⁚** By offering educational resources, advocacy support, and empowering individuals to take an active role in their healthcare journey, genetic counselors contribute to enhanced knowledge and self-advocacy among those affected by Type VIII. Empowering individuals with information fosters informed decision-making and proactive management of genetic conditions.
Engaging in genetic counseling provides individuals and families affected by Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII with essential support, information, and resources to navigate the complexities of genetic conditions. By working collaboratively with genetic counselors, individuals can gain knowledge, receive emotional support, and make informed decisions about their healthcare, ultimately promoting holistic well-being and effective management of Type VIII.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research in Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII paves the way for advancements in understanding the disease mechanisms, developing novel treatments, and improving patient outcomes. Researchers and healthcare professionals are exploring innovative approaches to better diagnose, manage, and potentially cure Type VIII in the future.
**Genetic Therapies⁚** Current research focuses on gene therapy and gene editing technologies as potential treatments for genetic disorders like Type VIII. These emerging therapies aim to correct gene mutations, restore enzyme function, and address the underlying cause of the disease at a molecular level.
**Enzyme Replacement⁚** Investigational studies are evaluating the feasibility of enzyme replacement therapies for individuals with Type VIII to supplement deficient phosphorylase kinase activity. Enzyme replacement strategies may offer a targeted approach to restore glycogen metabolism and improve metabolic function in affected individuals;
**Nutritional Interventions⁚** Research into optimized dietary interventions, personalized nutrition plans, and metabolic profiling aims to enhance the management of Type VIII and support liver health in affected individuals. Tailored nutritional strategies may complement existing treatments and promote better outcomes for patients.
**Clinical Trials⁚** Participation in clinical trials and research studies on Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII provides individuals with access to innovative therapies, specialized care, and the opportunity to contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge. Collaborating with research institutions and healthcare providers can open doors to cutting-edge treatments and potential breakthroughs for Type VIII.
Staying informed about the latest research findings, participating in clinical trials, and advocating for continued investment in Type VIII research can accelerate progress towards improved therapies and management strategies for individuals affected by the condition. By supporting research initiatives and engaging with the scientific community, individuals, families, and healthcare providers can contribute to a brighter future for those living with Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII.
In conclusion, Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII poses unique challenges related to liver involvement and enzyme deficiency, impacting glycogen metabolism and overall health. Understanding the genetic basis, inheritance pattern, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment approaches is essential for effectively managing this rare metabolic disorder.
By prioritizing regular monitoring, genetic counseling, personalized treatment plans, and dietary modifications, individuals with Type VIII can navigate the complexities of the condition with support from healthcare professionals and genetic experts. Embracing lifestyle adjustments, participating in research initiatives, and staying informed about advancements in Type VIII management can empower individuals to take an active role in their care.
As research continues to expand our knowledge of Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII, promising therapies, genetic interventions, and personalized approaches offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected by the condition. By fostering awareness, advocating for research funding, and promoting genetic education, we can work towards a future where individuals with Type VIII can thrive with comprehensive care and support.
Together, we can create a path towards better understanding, enhanced treatments, and ultimately, a brighter future for individuals and families impacted by Glycogen Storage Disease Type VIII. By raising awareness, fostering collaboration, and championing advancements in care, we can strive to improve the lives of those living with this rare metabolic disorder.