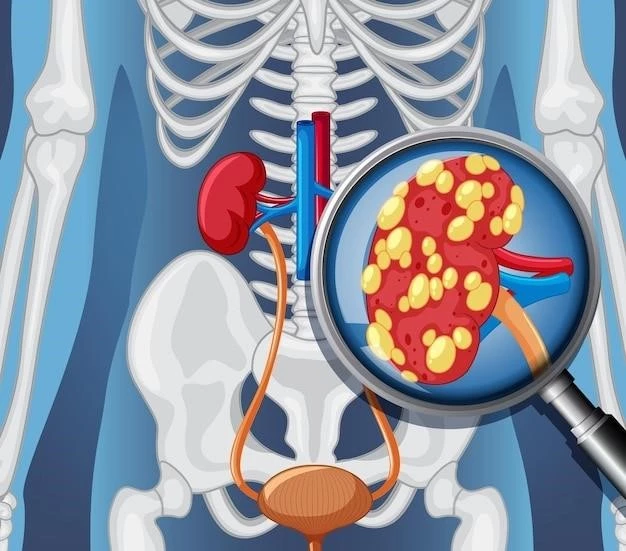
Understanding and Managing Fanconi Syndrome with Renal Nephrocalcinosis and Renal Stones
– Treatment for these conditions aims to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
– Medications may be prescribed to address mineral imbalances.
– Dietary changes like reducing salt and protein intake can help.
– Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is essential.
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Fanconi syndrome, renal nephrocalcinosis, and renal stones. These conditions affect the kidneys and can impact overall health and quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing these complex renal disorders.
Fanconi syndrome is a rare kidney disorder that affects the normal functioning of the renal tubules. Renal nephrocalcinosis involves the deposition of calcium salts in the kidney tissue, while renal stones are hard deposits that can form in the kidneys and cause pain and other complications.
By exploring the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment approaches for Fanconi syndrome, renal nephrocalcinosis, and renal stones, you will gain valuable insights into managing these conditions effectively. Stay informed, seek medical advice, and take proactive steps towards better kidney health.
What is Fanconi Syndrome?
Fanconi syndrome is a rare disorder that affects the renal tubules in the kidneys, leading to impaired reabsorption of certain substances such as glucose, amino acids, bicarbonate, and electrolytes. This results in the excessive excretion of these vital nutrients into the urine.
Patients with Fanconi syndrome may experience symptoms like frequent urination, dehydration, weakness, stunted growth in children, and bone issues due to mineral deficiencies. It is essential to seek medical advice if you suspect you or a loved one may have Fanconi syndrome.
Diagnosis involves urine and blood tests to assess levels of specific substances. Treatment typically focuses on managing symptoms, addressing underlying causes, and preventing complications. A healthcare provider will tailor a treatment plan to meet individual needs and improve kidney function.
Understanding Fanconi syndrome is crucial for effective management. By working closely with healthcare professionals, adhering to treatment plans, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, individuals with Fanconi syndrome can enhance their quality of life and promote kidney health.
Causes of Fanconi Syndrome
Fanconi syndrome can be caused by various factors, including genetic mutations, exposure to certain toxins, and specific medications. Genetic causes include inherited conditions that affect renal tubule function.
Toxin-induced Fanconi syndrome can result from exposure to heavy metals like lead, outdated tetracycline antibiotics, or other nephrotoxic substances. Additionally, certain medications such as antiretrovirals, chemotherapeutic drugs, and some antibiotics can trigger Fanconi syndrome.
Other underlying conditions like multiple myeloma, cystinosis, or Wilson’s disease can also contribute to the development of Fanconi syndrome. It is essential to identify and address the root cause of Fanconi syndrome to effectively manage the condition and prevent further kidney damage.
If you suspect you have Fanconi syndrome or are at risk due to genetic factors, environmental exposures, or medication use, consult a healthcare provider for thorough evaluation and personalized management strategies. Early detection and intervention can help control symptoms and preserve kidney function.
Symptoms of Fanconi Syndrome
Fanconi syndrome can present with a variety of symptoms that indicate impaired kidney function. Common signs include excessive thirst and urination, weakness, bone pain, muscle cramps, and fatigue. Children with Fanconi syndrome may exhibit growth delays.
Other symptoms to watch for include glucose in the urine (glycosuria), protein in the urine (proteinuria), low levels of phosphate in the blood (hypophosphatemia), and electrolyte imbalances. These abnormalities can lead to complications like bone deformities and electrolyte disturbances.
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect you may have Fanconi syndrome, it is crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and management of Fanconi syndrome can help prevent further kidney damage and improve overall health outcomes.
Consult a healthcare provider if you notice persistent symptoms or have risk factors for Fanconi syndrome. By addressing symptoms promptly and following a personalized treatment plan, individuals with Fanconi syndrome can better manage their condition and promote kidney health.
Diagnosis of Fanconi Syndrome
Diagnosing Fanconi syndrome involves a series of tests to evaluate kidney function and assess the excretion of specific substances in the urine; Initial steps typically include urine analysis to detect abnormalities such as glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes.
Blood tests may be conducted to measure levels of electrolytes, phosphate, calcium, and other relevant markers. Additionally, imaging studies like kidney ultrasound or CT scans can help identify structural changes in the kidneys that may indicate Fanconi syndrome.
A doctor may also perform a renal biopsy to examine kidney tissue for signs of tubular dysfunction. Genetic testing can be recommended to identify inherited forms of Fanconi syndrome. Collaborating closely with healthcare providers is essential for a comprehensive and accurate diagnosis.
If you suspect you have Fanconi syndrome or are experiencing symptoms like frequent urination or muscle weakness, seek medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis of Fanconi syndrome enables timely intervention and personalized treatment plans to manage the condition effectively and preserve kidney function.
Understanding Renal Nephrocalcinosis
Renal nephrocalcinosis is a condition characterized by the accumulation of calcium salts in the renal tubules and interstitium of the kidneys. This deposition can lead to the formation of calcifications, impacting kidney function and potentially causing complications.
The development of renal nephrocalcinosis may result from various factors, including genetic disorders like primary hyperoxaluria or Dent disease, metabolic imbalances, vitamin D toxicity, hyperparathyroidism, or certain medications that affect calcium metabolism.
Common symptoms of renal nephrocalcinosis include flank pain, blood in the urine (hematuria), frequent urinary tract infections, and kidney stones. Diagnosis involves imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize the calcium deposits in the kidneys.
If you suspect you may have renal nephrocalcinosis or are experiencing symptoms like kidney pain or blood in the urine, consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and personalized management strategies. Effective treatment and lifestyle modifications can help mitigate the impact of renal nephrocalcinosis on kidney health.
Causes and Risk Factors of Renal Nephrocalcinosis
Renal nephrocalcinosis can have multiple causes and risk factors that contribute to the accumulation of calcium deposits in the kidneys. Various underlying conditions and lifestyle factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition.
Primary causes of renal nephrocalcinosis include genetic disorders like Bartter syndrome, distal renal tubular acidosis, and medullary sponge kidney. Metabolic disorders such as hyperparathyroidism and hyperoxaluria can also lead to calcium deposition in the renal tissue.
Some medications, particularly those containing calcium or vitamin D supplements, can elevate calcium levels in the blood and contribute to nephrocalcinosis. Chronic dehydration, excessive calcium intake, and a diet high in oxalate-rich foods can further increase the risk of developing renal nephrocalcinosis.
Individuals with a history of kidney stones, renal tubular defects, or certain systemic diseases are at a higher risk of developing renal nephrocalcinosis. It is essential to address modifiable risk factors through dietary modifications, hydration strategies, and medication adjustments to minimize the risk of kidney calcifications.
Symptoms of Renal Nephrocalcinosis
Renal nephrocalcinosis can manifest with various symptoms that indicate calcium deposition in the kidneys. Common signs include flank pain, blood in the urine (hematuria), frequent urinary tract infections, and recurrent kidney stones. In some cases, individuals may experience no symptoms initially.
As the condition progresses, symptoms may worsen, leading to persistent pain in the lower back or abdomen, discomfort during urination, and changes in urinary habits. Complications like kidney damage or impaired renal function can arise if renal nephrocalcinosis is left untreated.
If you notice any symptoms of renal nephrocalcinosis or have a history of kidney issues, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and appropriate management. Early detection and intervention can help mitigate symptoms, prevent complications, and preserve kidney health.
By addressing symptoms promptly and adhering to treatment plans recommended by healthcare professionals, individuals with renal nephrocalcinosis can better manage their condition and minimize the impact on overall well-being. Regular follow-ups and lifestyle modifications are key to maintaining kidney health.
Diagnosis of Renal Nephrocalcinosis
Diagnosing renal nephrocalcinosis involves a series of tests and imaging studies to identify calcium deposits in the kidneys and assess kidney function. Healthcare providers use various diagnostic approaches to confirm the presence of renal calcifications and determine the underlying cause.
Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can visualize the calcium deposits in the kidneys. These imaging studies help healthcare professionals evaluate the extent of nephrocalcinosis and its impact on kidney structure.
Additional tests like blood and urine analyses may be conducted to assess electrolyte levels, kidney function markers, and the presence of other abnormalities indicative of renal nephrocalcinosis. A thorough diagnostic evaluation is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
If you suspect you have renal nephrocalcinosis or are experiencing symptoms like flank pain or hematuria, seek medical attention for proper evaluation and management. Early diagnosis of renal nephrocalcinosis allows for timely intervention to prevent complications and preserve kidney function.
Renal Stones⁚ Types and Formation
Renal stones, also known as kidney stones, can form due to the accumulation of minerals in the kidneys. There are several types of renal stones, each with different compositions and causes. The most common types include calcium stones, uric acid stones, struvite stones, and cystine stones.
Calcium stones are the most prevalent and are usually composed of calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate. Uric acid stones form when urine becomes too acidic, leading to the crystallization of uric acid. Struvite stones typically develop in response to urinary tract infections caused by certain bacteria.
Cystine stones are rare and result from a genetic disorder that leads to high levels of cystine in the urine. The formation of renal stones can be influenced by various factors, including dehydration, dietary habits high in salt or oxalate, and metabolic conditions like hyperparathyroidism.
To prevent renal stones, staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing underlying medical conditions are essential. Understanding the types of renal stones and their formation can help individuals make informed choices to reduce the risk of stone development and promote kidney health.
Treatment Approaches for Fanconi Syndrome, Renal Nephrocalcinosis, and Renal Stones
Treatment for Fanconi syndrome aims to manage symptoms and address underlying causes. Medications may be prescribed to help regulate electrolyte imbalances and mineral deficiencies. Monitoring kidney function and bone health is crucial in the management of Fanconi syndrome.
For renal nephrocalcinosis, treatment focuses on reducing calcium deposits in the kidneys and preventing complications. Lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medications to manage underlying conditions can help improve kidney function and slow the progression of nephrocalcinosis.
Managing renal stones involves various approaches depending on the type and size of the stones. Treatments may include increased fluid intake, dietary adjustments, medications to dissolve stones, or procedures like lithotripsy to break down larger stones. Surgery may be necessary for complex cases.
Collaborating with healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans is essential for effectively managing Fanconi syndrome, renal nephrocalcinosis, and renal stones. Adhering to treatment recommendations, maintaining regular follow-ups, and making necessary lifestyle changes can help individuals improve their kidney health and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Implementing lifestyle changes and home remedies can complement medical treatment for Fanconi syndrome, renal nephrocalcinosis, and renal stones. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage symptoms and support overall kidney health.
– Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water daily to prevent dehydration and promote kidney function.
– Follow a balanced diet that is low in salt, sugar, and processed foods to reduce the risk of mineral imbalances.
– Increase intake of fruits and vegetables rich in essential nutrients to support kidney health and overall well-being.
– Avoid foods high in oxalate if prone to kidney stones and monitor calcium intake to prevent stone formation.
– Engage in regular physical activity to improve circulation, maintain a healthy weight, and support kidney function.
– Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga to promote overall wellness.
Consult healthcare providers before making significant lifestyle changes, as they can provide guidance tailored to individual needs. By incorporating these lifestyle modifications and home remedies into daily routines, individuals can enhance their quality of life and better manage kidney-related conditions.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Managing Fanconi syndrome, renal nephrocalcinosis, and renal stones requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these kidney-related conditions, individuals can take proactive steps towards better kidney health.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals, following treatment plans, and making necessary lifestyle changes are essential for effectively managing these disorders. It is important to seek medical advice promptly if experiencing symptoms or at risk of developing kidney-related issues.
By staying informed, practicing healthy habits, and prioritizing kidney health, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of Fanconi syndrome, renal nephrocalcinosis, and renal stones. Remember that early detection, proactive management, and self-care play key roles in maintaining optimal kidney function and overall well-being.
Take charge of your kidney health by seeking regular check-ups, adhering to treatment recommendations, and adopting a kidney-friendly lifestyle. With dedication to self-care and ongoing support from healthcare providers, you can navigate these kidney-related conditions with resilience and improved quality of life.