Understanding Dermatitis Herpetiformis (Duhring–Brocq Disease)
When exploring Duhring–Brocq disease, it’s crucial to dive into the connection with Celiac disease and the impact of wheat products. Understanding these aspects is key to effectively managing this autoimmune disorder. Stay tuned for insightful information!
Overview of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis, also known as Duhring–Brocq disease, is an autoimmune disorder linked to gluten sensitivity. It manifests as a chronic skin rash characterized by itchy blisters. The condition is closely associated with intestinal inflammation and the production of specific antibodies in response to gluten. To confirm a diagnosis, both a dermatologist and a gastroenterologist may be consulted. A skin biopsy is often the definitive method for diagnosis.
Individuals with this condition typically benefit from a gluten-free diet, which helps alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups. It’s important to understand that even small amounts of gluten can trigger the inflammatory response in the skin and intestine, leading to exacerbation of symptoms. By diligently following a gluten-free diet, patients can effectively manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications associated with untreated dermatitis herpetiformis.
Living with dermatitis herpetiformis may require adjustments to lifestyle, particularly regarding dietary choices and skincare routines. Seeking support from patient education resources and support groups can offer valuable information and emotional aid. Collaboration with healthcare providers, including dermatologists, gastroenterologists, and dietitians, is essential for comprehensive care. Through ongoing research and advancements in treatment options, the outlook for individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis continues to improve.
Causes and Mechanism
Dermatitis herpetiformis, or Duhring–Brocq disease, is caused by an autoimmune response triggered by gluten ingestion in susceptible individuals. This autoimmune reaction leads to the formation of inflammatory itchy blisters on the skin. The mechanism involves the immune system producing antibodies targeting gluten, leading to the deposition of these antibodies in the skin and intestines.
When gluten is ingested, individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis experience an immune response that results in skin rash and intestinal inflammation. This inflammatory process can cause damage to the small intestine’s lining, impairing nutrient absorption. The presence of gluten in the diet exacerbates the symptoms and perpetuates the autoimmune response.
Understanding the causes and mechanisms of dermatitis herpetiformis is crucial for individuals diagnosed with this condition. By adhering to a strict gluten-free diet, patients can mitigate autoimmune reactions, reduce skin rash flare-ups, and alleviate intestinal inflammation. Collaborating with healthcare providers, such as dermatologists and gastroenterologists, can help manage the autoimmune response effectively.
Symptoms and Presentation
Individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis may experience a range of symptoms, with the hallmark being a skin rash characterized by itchy blisters. These blisters are often found on the elbows, knees, back, or buttocks. The rash tends to be chronic and may come and go in cycles.
Other common symptoms include burning or stinging sensation in the affected areas, as well as skin lesions that can be red, raised, and filled with clear fluid. In some cases, the rash may be accompanied by skin discoloration or hyperpigmentation after healing.
It is essential to recognize the symptoms early to seek a proper diagnosis and initiate treatment promptly. Consulting a dermatologist for a comprehensive evaluation of the skin rash and a gastroenterologist for further investigation of underlying gastrointestinal inflammation is crucial in managing dermatitis herpetiformis effectively.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing dermatitis herpetiformis often involves a collaborative approach between dermatologists and gastroenterologists. A skin biopsy is a key diagnostic tool, where a small sample of skin is taken and examined for specific changes characteristic of the condition.
In addition to the skin biopsy, blood tests may be conducted to detect the presence of antibodies associated with gluten sensitivity and autoimmune responses. Gastrointestinal evaluation, including endoscopy and biopsy of the small intestine, can provide further insights into the extent of inflammation and damage caused by the autoimmune reaction.
It is important to undergo a thorough diagnostic process to confirm the presence of dermatitis herpetiformis accurately. With a definitive diagnosis in hand, individuals can start appropriate treatment, such as adhering to a strict gluten-free diet and possibly medication to manage symptoms and inflammation.
Connection to Celiac Disease
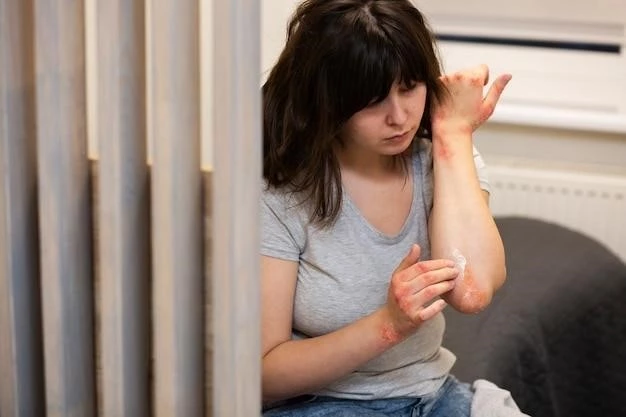

Dermatitis herpetiformis shares a strong connection with celiac disease, a well-known autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten ingestion. Both conditions involve an immune response to gluten, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. Dermatitis herpetiformis is considered the skin manifestation of gluten sensitivity, while celiac disease primarily affects the small intestine.
Individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis often have underlying celiac disease, with studies suggesting that a significant percentage of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis also exhibit intestinal damage characteristic of celiac disease. Therefore, it is essential for individuals diagnosed with dermatitis herpetiformis to undergo screening for celiac disease to ensure comprehensive management and treatment.
Understanding the connection between dermatitis herpetiformis and celiac disease is crucial for healthcare providers to develop a holistic approach to care. By addressing both the skin manifestations and the underlying intestinal inflammation associated with celiac disease, patients can effectively manage their conditions and improve their quality of life. Adhering to a strict gluten-free diet is key in managing both dermatitis herpetiformis and celiac disease.
Treatment Options
Managing dermatitis herpetiformis involves various treatment approaches tailored to alleviate symptoms and address the underlying autoimmune response. The primary treatment for dermatitis herpetiformis is adherence to a strict gluten-free diet. Eliminating gluten from the diet helps prevent the immune response triggered by gluten ingestion, reducing skin rash flare-ups and intestinal inflammation.
In addition to dietary modifications, medications such as dapsone may be prescribed to manage symptoms and skin rash. Dapsone is an oral medication that can provide relief from itching and help heal the skin lesions associated with dermatitis herpetiformis. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust the management plan as needed.
Other treatment options may include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching, as well as medications that modulate the immune response. It is crucial for individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis to work closely with their dermatologist, gastroenterologist, and dietitian to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the skin manifestations and any underlying gastrointestinal issues.
Impact of Wheat Products
Wheat products play a crucial role in the development and management of dermatitis herpetiformis due to gluten sensitivity. Gluten, a protein found in wheat and related grains, triggers the autoimmune response that leads to skin rash and intestinal inflammation in individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis.
Consumption of wheat products containing gluten can exacerbate symptoms of dermatitis herpetiformis, leading to itchy blisters and potential damage to the small intestine. It is essential for individuals with this condition to avoid all sources of gluten, including bread, pasta, cereals, and baked goods, to prevent flare-ups and maintain symptom control.
Understanding the impact of wheat products on dermatitis herpetiformis is key to effectively managing the condition. Adopting a gluten-free diet is the cornerstone of treatment and plays a critical role in reducing the inflammatory response, promoting skin healing, and improving overall quality of life for individuals living with dermatitis herpetiformis.
Managing the Inflammatory Response
Effectively managing the inflammatory response in dermatitis herpetiformis is crucial for symptom control and overall well-being. Adopting a gluten-free diet is the primary strategy to reduce the autoimmune reaction triggered by gluten ingestion, which is central to the inflammatory process in this condition.
In addition to dietary modifications, medications such as dapsone or corticosteroids may be prescribed to help alleviate inflammation and itching associated with dermatitis herpetiformis. These medications work to suppress the immune response and reduce skin rash flare-ups, providing relief from symptoms.
Skincare routines that focus on gentle cleansing and moisturizing can also help manage the inflammatory response in the skin and promote healing of lesions. Avoiding harsh chemicals or irritants in skincare products is important to prevent further irritation and maintain skin health.
Regular monitoring by healthcare providers, including dermatologists and gastroenterologists, is essential to track the inflammatory response and adjust treatment as needed. By actively managing the inflammatory process through a combination of dietary, medication, and skincare interventions, individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis can enhance symptom control and improve their quality of life.
Patient Education and Support
Empowering patients with dermatitis herpetiformis through education and support is key to effectively managing this chronic autoimmune disorder. Providing comprehensive information about the condition, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Support groups and online resources dedicated to dermatitis herpetiformis offer valuable emotional support, practical tips, and a sense of community for individuals navigating the challenges of living with this condition. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide encouragement and a platform for sharing coping strategies.
Education on the importance of adhering to a gluten-free diet, skincare practices, medication management, and regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential for long-term symptom control and overall well-being. Patients are encouraged to actively participate in their care by asking questions, seeking clarification, and expressing their concerns to their healthcare team.
By fostering a supportive and educational environment, healthcare providers can assist patients in developing effective self-management strategies for dermatitis herpetiformis. Encouraging open communication, providing reliable information, and offering emotional support can significantly impact patients’ treatment adherence and quality of life.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research into dermatitis herpetiformis continues to drive advancements in understanding the underlying mechanisms of this autoimmune disorder and improving treatment strategies. Scientists are exploring novel diagnostic tools, such as advanced imaging techniques and biomarker identification, to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis.
Clinical trials focusing on new medications, targeted therapies, and immunomodulatory approaches offer promising avenues for more effective management of dermatitis herpetiformis while minimizing side effects. Researchers are investigating personalized treatment regimens tailored to individuals’ specific immune profiles and genetic factors.
Advancements in dermatological and gastroenterological research are shedding light on the intricate interplay between skin manifestations and gastrointestinal symptoms in dermatitis herpetiformis. By unraveling the complex pathophysiology of this condition, researchers aim to develop innovative treatment modalities that target the autoimmune response at its source.
Staying informed about the latest research findings and treatment developments in dermatitis herpetiformis is essential for healthcare providers and patients alike. Engaging with clinical trials, educational seminars, and reputable medical journals can broaden knowledge and offer insights into emerging therapies that may impact the management and outcomes of this autoimmune disorder.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Living with dermatitis herpetiformis may necessitate certain lifestyle adjustments to effectively manage the condition and improve quality of life. Adhering to a gluten-free diet is paramount, requiring individuals to carefully read food labels, identify hidden sources of gluten, and opt for gluten-free alternatives.
Creating a skincare regimen that focuses on gentle products devoid of harsh chemicals or irritants can help alleviate skin symptoms and promote healing of lesions. Regular moisturization and sun protection are key aspects of skincare for individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis.
Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or hobbies, can aid in managing flare-ups and supporting overall well-being. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, adequate sleep, and balanced nutrition contributes to immune system support and optimal health for individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis.
Educating family members, friends, and coworkers about the challenges associated with dermatitis herpetiformis can foster a supportive environment and enhance understanding of the dietary restrictions and lifestyle adaptations required for managing the condition. Open communication and proactive self-care practices are essential components of effectively navigating life with dermatitis herpetiformis.
Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
Collaborating closely with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers is essential for comprehensive management of dermatitis herpetiformis. Consulting with a dermatologist for skin evaluations, treatment recommendations, and monitoring of skin rash progression is crucial in addressing the dermatological aspects of the condition.
Working in tandem with a gastroenterologist can provide insights into the impact of dermatitis herpetiformis on the gastrointestinal system and facilitate diagnostic testing to assess intestinal inflammation and damage. Gastroenterologists play a key role in confirming a diagnosis of celiac disease and guiding treatment strategies related to dietary management.
Engaging with a registered dietitian experienced in gluten-free nutrition can offer personalized dietary guidance, meal planning support, and tips for navigating social situations while adhering to a gluten-free diet. Dietitians can help individuals optimize their nutrition intake, address potential nutrient deficiencies, and ensure dietary compliance.
Establishing a collaborative relationship with healthcare providers empowers individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis to actively participate in their care, ask questions, voice concerns, and work towards shared treatment goals. Through effective communication and coordination among healthcare team members, patients can receive comprehensive support for managing their condition and improving their quality of life.
Risks of Untreated Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Leaving dermatitis herpetiformis untreated poses various risks and complications that can impact both skin health and overall well-being. Without proper management, the autoimmune inflammatory response triggered by gluten ingestion can result in persistent skin rash flare-ups, intensifying itchiness, discomfort, and skin damage.
Untreated dermatitis herpetiformis is associated with an increased risk of long-term skin complications, such as scarring, hyperpigmentation, and potential secondary skin infections. Chronic inflammation in the skin can lead to reduced healing capacity and impaired skin barrier function, making individuals more susceptible to skin issues.
Moreover, untreated dermatitis herpetiformis is often linked to ongoing intestinal inflammation and damage characteristic of celiac disease. Prolonged exposure to gluten without dietary intervention can exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms, compromise nutrient absorption in the small intestine, and increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies and related health conditions.
By neglecting to address dermatitis herpetiformis through appropriate treatment, individuals may experience a diminished quality of life, challenges in managing symptoms, and potential complications that can impact both dermatological and gastrointestinal health. Seeking timely diagnosis and implementing a comprehensive treatment plan are crucial steps in mitigating the risks associated with untreated dermatitis herpetiformis.
Support Groups and Resources
Joining support groups and accessing resources dedicated to dermatitis herpetiformis can provide invaluable assistance, guidance, and solidarity for individuals managing this autoimmune condition. Support groups offer a platform for sharing experiences, exchanging information, and fostering a sense of community among those affected by dermatitis herpetiformis.
Online forums, social media groups, and in-person meetings allow individuals to connect with others facing similar challenges, seek advice on coping strategies, and find emotional support during their dermatitis herpetiformis journey. Engaging with a supportive community can alleviate feelings of isolation, provide encouragement, and offer practical tips for navigating daily life with the condition.
Accessing reputable resources, such as educational websites, patient advocacy organizations, and informational materials from healthcare providers, can enhance understanding of dermatitis herpetiformis, its management strategies, and available treatment options. Reliable sources of information empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and self-care.
By actively participating in support groups and utilizing resources tailored to dermatitis herpetiformis, individuals can augment their knowledge, strengthen their support network, and gain a sense of empowerment in managing their condition. Building a support system and leveraging educational tools are essential components of holistic care for individuals living with dermatitis herpetiformis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and effectively managing dermatitis herpetiformis, also known as Duhring–Brocq disease, require a comprehensive approach addressing both the skin manifestations and the underlying autoimmune response triggered by gluten sensitivity. By adhering to a strict gluten-free diet, individuals can minimize inflammatory reactions, reduce skin rash flare-ups, and promote healing.
Collaboration with healthcare providers, including dermatologists, gastroenterologists, and dietitians, is essential for personalized treatment plans and ongoing support in managing dermatitis herpetiformis. Engaging in patient education, connecting with support groups, and staying informed about research advancements can further empower individuals in navigating the challenges posed by this autoimmune disorder.
Recognizing the risks of untreated dermatitis herpetiformis underscores the importance of timely diagnosis, intervention, and adherence to treatment recommendations. Lifestyle adjustments, skincare routines, stress management techniques, and a supportive network play integral roles in enhancing the overall well-being of individuals living with dermatitis herpetiformis.
Through education, collaboration, and proactive self-care practices, individuals can optimize their management of dermatitis herpetiformis, mitigate risks, and improve their quality of life. Embracing a holistic approach to care and staying connected to resources and support can make a significant difference in the journey towards effectively managing this autoimmune skin condition.