Understanding Contact Dermatitis and Photocontact Dermatitis
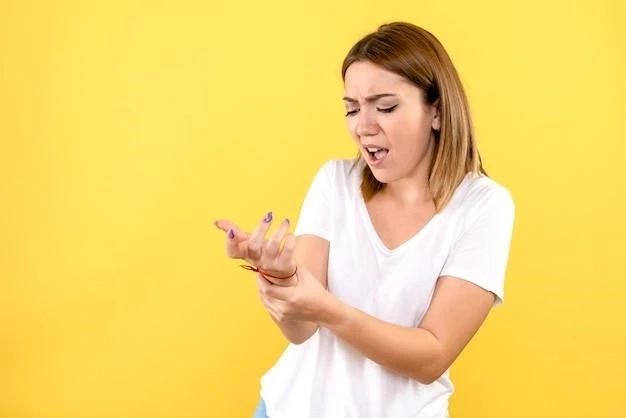

Causes of Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis can be caused by various factors, including irritants like chemicals, detergents, soaps, and cosmetics. Allergens such as metals, latex, fragrances, and plants are common triggers as well. Genetics, environmental factors, and a compromised skin barrier also play a role in the development of contact dermatitis.
Symptoms of Photocontact Dermatitis
Photocontact dermatitis presents with symptoms similar to contact dermatitis, but with the added component of being triggered by exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet light. Common symptoms include redness, blistering, itching, and burning sensation on sun-exposed areas like the face, neck, and arms. In severe cases, it may lead to swelling, oozing, and crusting of the skin.
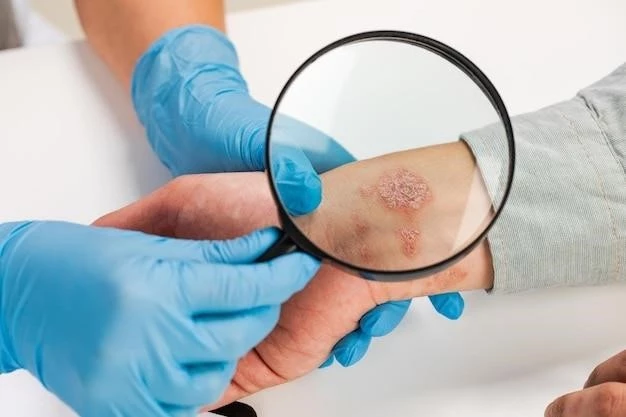
Diagnosis of Contact Dermatitis
Diagnosis of contact dermatitis involves a comprehensive evaluation by a dermatologist. The process includes a thorough medical history review, physical examination of the affected skin, and sometimes patch testing to identify specific allergens. In some cases, additional tests like skin biopsies or allergy tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Contact Dermatitis
Treatment of contact dermatitis typically involves identifying and avoiding the triggers, along with topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching. Emollients can help restore the skin barrier. For severe cases, oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed. In cases of allergic contact dermatitis, allergen immunotherapy may be considered. It is essential to follow the treatment plan prescribed by a dermatologist for effective management of contact dermatitis.
Prevention of Photocontact Dermatitis
Preventing photocontact dermatitis involves minimizing exposure to sunlight and UV light. This can be done by wearing protective clothing, using broad-spectrum sunscreen, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and avoiding photosensitizing substances like certain medications or fragrances. It is crucial to be aware of potential triggers and take necessary precautions to prevent the development of photocontact dermatitis.
Difference Between Allergic and Irritant Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is an immune response triggered by exposure to an allergen, leading to a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. Irritant contact dermatitis, on the other hand, occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an irritant substance, causing immediate damage. While both conditions share similar symptoms like redness, itching, and rash, allergic contact dermatitis is specific to the allergen, whereas irritant contact dermatitis can be caused by various irritants.
Managing Contact Dermatitis Flare-ups
Managing contact dermatitis flare-ups involves promptly identifying and avoiding triggers. It is essential to follow a proper skincare routine using gentle, fragrance-free products and moisturizers to maintain skin hydration. Topical corticosteroids can help alleviate inflammation during flare-ups; In severe cases, a dermatologist may recommend oral medications or phototherapy. Additionally, practicing stress-reducing techniques and avoiding known irritants can aid in managing and preventing recurrent flare-ups.
Common Triggers for Photocontact Dermatitis
Common triggers for photocontact dermatitis include certain plants like limes, celery, and fennel, as well as medications such as certain antibiotics, diuretics, and antihistamines. Fragrances found in perfumes, lotions, and cosmetics can also induce photocontact dermatitis. Additionally, some chemicals used in sunscreens, metals like nickel, and exposure to certain essential oils can lead to a phototoxic reaction. It is important to be vigilant about these triggers and take necessary precautions to prevent photocontact dermatitis.