Plan⁚ Understanding Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
Causes of Cholelithiasis
Symptoms of Gallstones
Treatment Options for Cholelithiasis
Complications of Gallstones
Prevention of Cholelithiasis
Risk Factors for Gallstones
Diagnosis of Cholelithiasis
Lifestyle Changes for Gallstone Prevention
Causes of Cholelithiasis
Cholelithiasis, or gallstones, may develop due to various factors such as imbalanced bile components, rapid weight loss, obesity, genetics, certain medical conditions like cirrhosis, or conditions that affect the gallbladder contraction. Other causes include high cholesterol, lack of physical activity, and prolonged fasting.
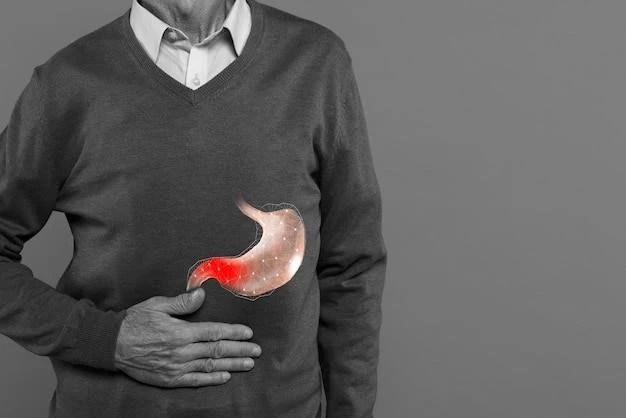
Symptoms of Gallstones
The symptoms of gallstones can include pain in the upper abdomen, back, or right shoulder, nausea, vomiting, bloating, indigestion, and jaundice. Some individuals may experience sudden intense pain, known as a gallbladder ″attack″, which can occur after consuming a high-fat meal.
Treatment Options for Cholelithiasis
The treatment for cholelithiasis may involve watchful waiting, medication to dissolve stones, surgical procedures like cholecystectomy to remove the gallbladder, or minimally invasive procedures such as ERCP or lithotripsy. The choice of treatment depends on the size, composition, and location of the gallstones, as well as the individual’s overall health condition.
Complications of Gallstones
Complications of gallstones may include inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), blockage of the bile ducts causing jaundice, pancreatitis due to blockage of the pancreatic duct, cholangitis from bile duct infection, and potentially life-threatening conditions like sepsis or gallstone pancreatitis. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent or address these complications.
Prevention of Cholelithiasis
Preventing cholelithiasis involves maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and regular exercise, consuming a balanced diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, staying hydrated, avoiding rapid weight loss methods, and incorporating fiber-rich foods into meals. Additionally, moderating alcohol intake and avoiding smoking can also contribute to reducing the risk of gallstone formation.
Risk Factors for Gallstones
Risk factors for gallstones include obesity, rapid weight loss, a high-fat or high-cholesterol diet, family history of gallstones, certain medical conditions like diabetes or liver disease, age over 40, being female, pregnancy, use of hormone replacement therapy, and sedentary lifestyle. Understanding and managing these risk factors can help prevent the development of gallstones.
Diagnosis of Cholelithiasis
Diagnosis of cholelithiasis typically involves a physical exam, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scan to visualize gallstones, blood tests to check for signs of infection or blockage, and sometimes an oral cholecystogram or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) for further evaluation. Accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
Lifestyle Changes for Gallstone Prevention
Adopting lifestyle changes for gallstone prevention involves maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, limiting saturated fats and cholesterol, staying physically active, staying hydrated, avoiding rapid weight loss, and managing underlying conditions such as diabetes. These modifications can help reduce the risk of developing gallstones.
