Article Plan⁚ Disease ‒ Urticaria Pigmentosa
Introduction to Urticaria Pigmentosa
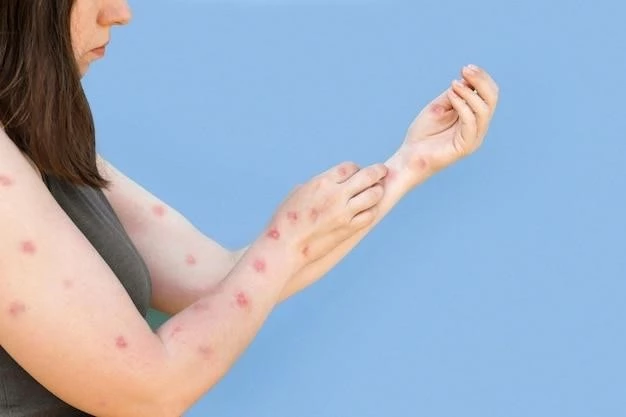
Urticaria pigmentosa is a skin disease characterized by hives, itching, and redness on the skin. It is triggered by histamine release from mast cells. Typically affecting children more than adults, the condition can lead to complications such as diarrhea and systemic mastocytosis. Treatment includes antihistamines, corticosteroids, and light therapy. Learn about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this condition.
Causes of Urticaria Pigmentosa
Urticaria pigmentosa, also known as maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis, is a skin disease that causes redness, itching, and hives on the skin. Triggered by the release of histamine from mast cells, this condition can lead to complications like diarrhea and systemic mastocytosis. While more common in children, adults can also be affected. Treatment involves antihistamines, corticosteroids, and light therapy. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Symptoms of Urticaria Pigmentosa
Urticaria pigmentosa, also known as maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis, is a skin condition characterized by brown patches and freckles that can be itchy and unsightly. It is the most common type of mastocytosis and can affect both children and adults. The condition is caused by abnormal collections of mast cells, part of the immune system, leading to the release of histamine and triggering symptoms like hives, itching, and redness on the skin. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for managing this skin condition effectively.
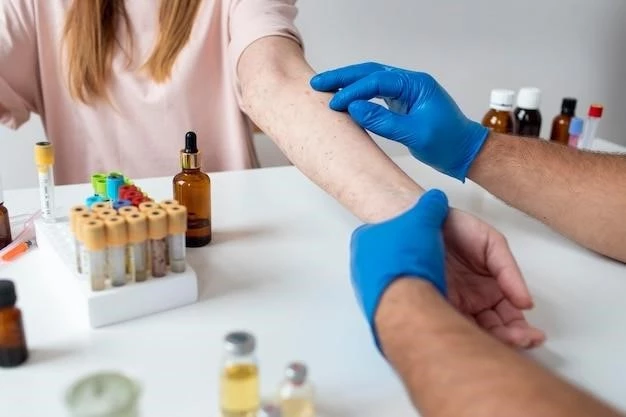
Diagnosis of Urticaria Pigmentosa
Diagnosing urticaria pigmentosa involves a thorough examination of the skin lesions and their characteristic features, such as brown spots that swell and itch transiently when rubbed. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be recommended to confirm the presence of mast cells. Additional tests like blood tests and bone marrow examinations may be conducted to rule out systemic involvement. Seeking medical advice for proper evaluation and diagnosis is essential for effective management of this skin condition.
Treatment Options for Urticaria Pigmentosa
Urticaria pigmentosa can be managed effectively with various treatment options. Antihistamines are commonly used to alleviate itching and reduce histamine release. Corticosteroids may be prescribed to control inflammation, especially during flare-ups. Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, can help in some cases by reducing lesions and symptoms. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on individual needs and the severity of the condition.
Risk Factors Associated with Urticaria Pigmentosa
Understanding the risk factors associated with urticaria pigmentosa is crucial for effective management. While the condition can affect individuals of all ages, children are more commonly affected. Genetic mutations play a role in the development of the disease, and certain triggers like rubbing the skin can exacerbate symptoms. Seeking medical advice to identify potential risk factors and develop a personalized treatment plan is essential for individuals with this skin condition.
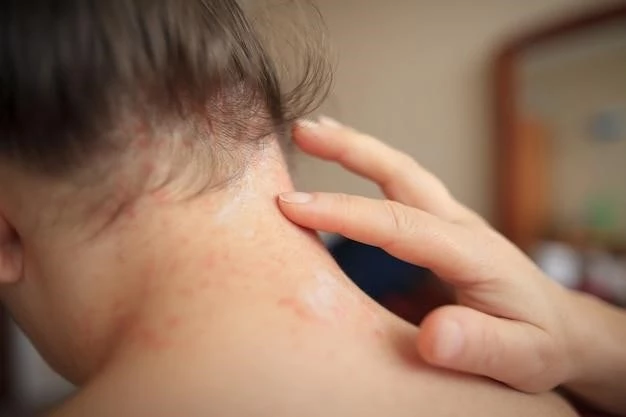
Complications of Urticaria Pigmentosa
Urticaria pigmentosa, if left untreated, can lead to various complications. These may include systemic mastocytosis, a condition where mast cells accumulate in tissues throughout the body. Individuals with urticaria pigmentosa may also experience symptoms such as diarrhea, fainting, and other allergic reactions if histamine release is not controlled. Seeking early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent complications and manage the condition effectively.
Differences Between Urticaria Pigmentosa and Other Skin Conditions
When comparing urticaria pigmentosa with other skin conditions, the distinctive feature lies in the presence of brown spots that can swell and itch transiently. Unlike conditions like urticaria and other forms of mastocytosis, urticaria pigmentosa specifically presents with brownish spots that contain mast cells. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Prognosis and Outlook for Individuals with Urticaria Pigmentosa
The prognosis for individuals with urticaria pigmentosa is generally good, especially if the condition is managed effectively. With proper treatment and monitoring, most cases can be controlled, and symptoms minimized. While urticaria pigmentosa can lead to complications if untreated, early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the outlook. Working closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive care plan can help individuals with this skin condition maintain a good quality of life.
Prevention Strategies for Urticaria Pigmentosa
While there are no specific ways to prevent urticaria pigmentosa as it is a skin condition influenced by genetic factors, individuals can manage the symptoms and reduce flare-ups by avoiding triggers like rubbing the skin vigorously. It is essential to follow the prescribed treatment plan provided by healthcare providers to keep the condition under control. Maintaining good skin hygiene and minimizing exposure to known irritants can also help in managing the symptoms effectively.