Tracheobronchomalacia is a condition where the airway walls are weak and collapse during breathing or coughing.
Definition and Characteristics
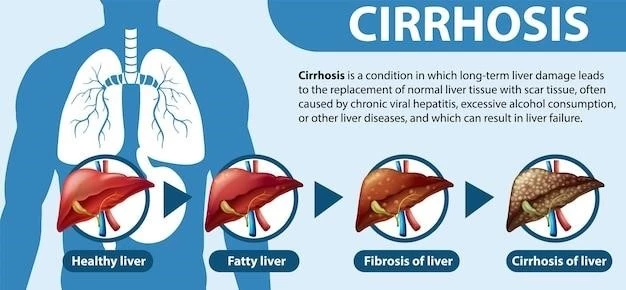
Tracheobronchomalacia is a rare condition characterized by weak airway walls that collapse during breathing or coughing. It can be congenital or develop later in life, leading to breathing difficulties and other respiratory symptoms.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Tracheobronchomalacia can cause coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, and phlegm, leading to a challenging diagnosis process.
Common Symptoms
Tracheobronchomalacia often presents with symptoms like coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, and phlegm, causing challenges in daily life.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing tracheobronchomalacia often involves specialized tests such as dynamic airway computed tomography (CT) and bronchoscopy to evaluate airway collapse and confirm the condition. Additional pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess lung function.
Causes and Risk Factors
Tracheobronchomalacia can develop due to weakened cartilage in the airway walls, leading to collapse.
Possible Causes
The weakening of cartilage in the airway walls can lead to the development of tracheobronchomalacia.
Associated Risk Factors
Risk factors associated with tracheobronchomalacia include underlying medical conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pulmonary fibrosis, which can contribute to the weakening of airway walls.
Treatment Options
Doctors will focus on treating any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the development of tracheobronchomalacia.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions for tracheobronchomalacia may include bronchodilators, inhaled steroids, and other medications to manage symptoms and improve breathing.
Surgical Procedures
In severe cases of tracheobronchomalacia, surgical interventions such as tracheal stents or tracheoplasty may be considered to provide structural support to the weakened airway walls and improve breathing function.
Management of Tracheobronchomalacia
Patients with tracheobronchomalacia are best assessed and managed by a multidisciplinary team in centers specializing in complex airway disorders.
Multidisciplinary Approach
A multidisciplinary approach involving specialists in pulmonology, thoracic surgery, and respiratory therapy is crucial in managing tracheobronchomalacia effectively.
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Care
Patients with tracheobronchomalacia may require long-term care, including pulmonary rehabilitation programs to improve respiratory function and quality of life. Close monitoring and support are essential for managing this complex condition.

Research and Future Directions
Ongoing studies focus on understanding the underlying processes of tracheobronchomalacia to improve diagnosis and treatment outcomes. Advancements in treatment aim to provide more effective and targeted interventions for patients with this condition.
Ongoing Studies
Ongoing research aims to enhance understanding of tracheobronchomalacia causes, symptoms, and treatment strategies, advancing towards more effective and tailored interventions for patients with this challenging condition.
Advancements in Treatment
Researchers are investigating new treatment options for tracheobronchomalacia to enhance patient outcomes and provide more effective and personalized care. Stay updated on the latest advancements in the management of this condition.