Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is...
Definition and Overview
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), commonly referred to as Lupus, is a complex autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissues in different areas of the body. The condition presents with a wide range of symptoms and severity levels, impacting various organs and tissues. Genetic, immunological, and environmental factors contribute to the development of this chronic autoimmune disorder.
Symptoms and Manifestations of SLE
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) presents a wide array of symptoms, including joint pain, fever, chest pain, hair loss, and fatigue. The disease can also manifest as swollen lymph nodes, mouth ulcers, and a distinct red rash.
Varied Symptoms
The symptoms of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) can range from joint pain, fever, chest pain, and fatigue to skin manifestations like rashes. Additionally, individuals with SLE may experience systemic issues affecting multiple organs and systems.
Severity Levels
The severity of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) can vary significantly, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms while others may face more severe manifestations affecting various organs. Monitoring and understanding the severity of SLE is crucial for personalized treatment and management strategies.
Causes and Risk Factors
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is influenced by genetic, immunological, and environmental factors, contributing to the development of this chronic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs. Understanding these risk factors is essential for managing the condition effectively.
Genetic Factors
Genetic, immunological, and environmental factors play significant roles in the development of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). These factors contribute to the autoimmune response that leads to tissue damage and the multisystem manifestations characteristic of SLE.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors, in conjunction with genetic predisposition, play a crucial role in the development of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). These triggers may include exposure to ultraviolet light, certain medications, infections, and hormonal fluctuations, contributing to the onset and exacerbation of the autoimmune response in individuals susceptible to SLE.
Diagnosis and Testing for SLE
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) diagnosis involves laboratory tests and imaging studies to assess the extent of organ involvement and confirm the presence of characteristic autoantibodies. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment strategies and monitoring disease progression effectively.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests play a crucial role in diagnosing Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) by identifying specific autoantibodies and assessing organ function. These tests help healthcare providers evaluate disease activity and monitor treatment responses, aiding in the comprehensive management of SLE.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies play a critical role in the diagnosis and monitoring of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), providing insights into organ involvement and disease progression. Techniques like MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds help healthcare providers visualize affected tissues and organs, aiding in the comprehensive management of SLE.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is managed through medications and lifestyle changes to control symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent organ damage. Treatment plans may involve a combination of immunosuppressants, anti-inflammatory drugs, and corticosteroids along with measures to maintain overall health and well-being.
Treatment Approaches for SLE
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is managed through medications and lifestyle changes to control symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent organ damage. Treatment plans may involve a combination of immunosuppressants, anti-inflammatory drugs, and corticosteroids along with measures to maintain overall health and well-being.
Lifestyle Changes
Alongside medications, incorporating lifestyle changes is essential in managing Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). These changes may include maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and avoiding known triggers to promote overall well-being and enhance the effectiveness of treatment.
Managing SLE Flares
When dealing with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) flares, identifying triggers and implementing effective coping strategies are essential for symptom control and overall well-being. By recognizing individual flare triggers and adopting personalized coping mechanisms, individuals can better manage the unpredictable nature of SLE exacerbations.
Flare Triggers
Identifying triggers for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) flares is crucial for effective symptom management. Common triggers include stress, infections, ultraviolet light exposure, hormonal changes, and certain medications. Understanding and avoiding these triggers can help minimize the frequency and severity of SLE flares.
Coping Strategies
Implementing effective coping strategies is essential for individuals with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) to manage the physical and emotional impact of the condition. Coping mechanisms may include stress management techniques, seeking support from healthcare professionals and support groups, maintaining a balanced lifestyle, setting realistic goals, and adapting activities based on energy levels and symptoms.
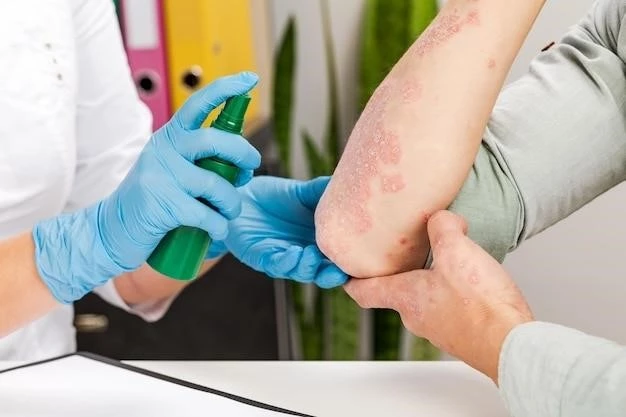
Complications Associated with SLE
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) can lead to various complications, including organ involvement and long-term effects that need careful management. Understanding these complications is crucial for healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care and support to individuals with SLE.
Organ Involvement
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) can affect various organs, including the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, lungs, and blood-forming system. Understanding the potential organ involvement is crucial for early detection, appropriate treatment, and preventing long-term complications in individuals with SLE.
Long-Term Effects
Long-term implications of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) may include chronic pain, reduced quality of life, increased risk of infections, organ damage, cardiovascular complications, osteoporosis, and potential impact on fertility. Managing these long-term effects requires a comprehensive approach to care and regular monitoring.
Living with SLE⁚ Patient Perspectives
Patient perspectives on living with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) reflect the challenges posed by the disease’s impact on various organs. Managing symptoms, maintaining quality of life, and accessing support networks are vital for individuals navigating life with SLE.
Quality of Life
Quality of life for individuals living with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) can be significantly impacted by the chronic nature of the disease, its symptoms, and the potential limitations it imposes. Maintaining a good quality of life involves effective symptom management, support networks, access to appropriate care, and strategies for improving overall well-being.
Support Networks
Support networks play a crucial role for individuals managing Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), providing emotional support, practical assistance, and shared experiences. Connecting with support groups, healthcare professionals, family, and friends can help individuals cope with the challenges of SLE and improve their overall well-being.
Ongoing Research and Advancements in SLE
Stay informed about the latest breakthroughs in research and advancements in the treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Explore novel therapies and ongoing clinical trials that aim to improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with SLE.
Novel Therapies
Stay updated on the latest advancements in novel therapies for treating Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Explore innovative treatment approaches that aim to target specific pathways and improve outcomes for individuals living with SLE.
Clinical Trials
Advancements in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) treatment are being explored through ongoing clinical trials. These trials aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new therapeutic approaches, providing hope for improved outcomes and management strategies in individuals with SLE.
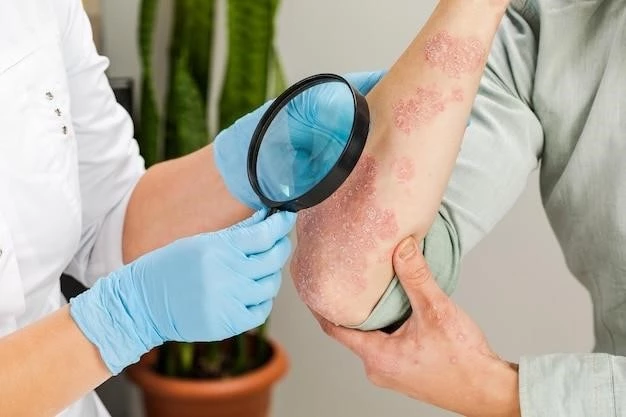
Public Awareness and Education on SLE
Learn about Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) to raise awareness and educate the public about this chronic autoimmune disease. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and management of SLE can help promote early detection and improve the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Advocacy Efforts
Engaging in advocacy efforts is crucial in raising awareness and supporting individuals affected by Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Advocacy initiatives help promote research, access to care, and public understanding of SLE, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.
