Introduction
Rubeola, also known as measles, is a type of infectious disease. It is caused by a virus that is transmitted via person-to-person contact as well as airborne spread.
Overview of Rubeola
Rubeola, commonly known as measles, is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects children. It is transmitted through airborne droplets and direct contact with infected individuals. Measles typically starts with flu-like symptoms and progresses to a distinctive rash. Vaccination is crucial in preventing the spread of this disease.
Information from Dr. Tracy Evans-Gilbert about the clinical aspects of measles and rubella, highlighting their differences from other diseases.
Information from Dr. Tracy Evans-Gilbert
Dr. Tracy Evans-Gilbert, an expert in Clinical Pediatrics, shares insights on the clinical aspects of measles and rubella, underscoring the importance of understanding the distinct characteristics of these diseases.
Clinical Aspects
Guidance on clinical aspects provided by Dr. Tracy Evans-Gilbert, emphasizing key differences between measles and rubella for better understanding.
Guidance on Measles Prevention
Health authorities emphasize the importance of measles prevention through timely vaccination and public health initiatives targeting high-risk populations to curb the spread of this highly contagious disease.
Congenital Rubella Syndrome
Effects on fetal development due to congenital rubella syndrome, which can lead to serious complications and health issues post-birth.
Effects on Fetal Development
Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS) can have detrimental effects on fetal development, including potential birth defects and long-term health implications for infants exposed to rubella during pregnancy.
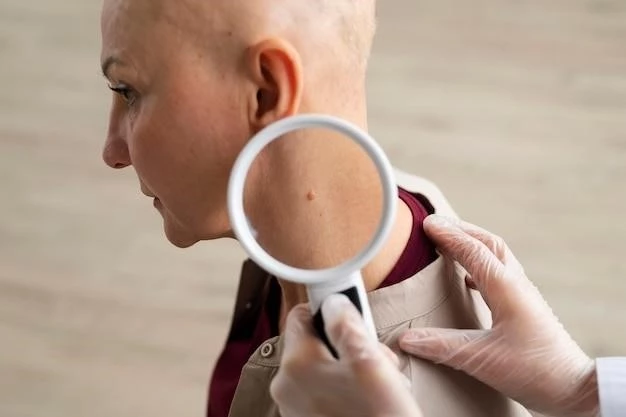
Symptoms
Characteristics of measles and rubella rash, which are distinctive features of these infectious diseases, aiding in their identification and diagnosis.
Characteristics of Measles and Rubella Rash
Measles and rubella present distinct rash patterns as primary symptoms, aiding in the identification and differentiation of these illnesses during clinical evaluation.
Diagnosis
Methods for diagnosing rubella and measles, including lab tests and clinical assessments used by healthcare professionals to identify these viral infections.
Methods for Diagnosing Rubella and Measles
Healthcare professionals utilize laboratory tests, physical examinations, and patient history assessments to diagnose measles and rubella accurately, ensuring appropriate treatment and containment protocols are implemented.
Treatment
Self-care measures for rubella include rest and fever management, while more severe cases may require medical attention for complications and supportive care.
Self-Care Measures for Rubella
When dealing with rubella, self-care measures like rest, fever management, and symptom monitoring at home can aid in the recovery process, ensuring comfort and facilitating the body’s healing mechanisms.
Vaccination
Importance of rubella immunization to prevent the spread and potential complications of this highly contagious viral infection, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Importance of Rubella Immunization
Health authorities stress the significance of rubella immunization as a crucial preventive measure against this highly contagious viral infection, particularly highlighting its importance for vulnerable groups within the population.
Global Impact
Statistics on measles-related deaths indicating the significant impact of the disease on global health, particularly among vulnerable populations and unvaccinated individuals.
Statistics on Measles Related Deaths
Global statistics on deaths caused by measles highlight the severe impact of the disease on public health, underscoring the importance of vaccination programs and public health interventions to mitigate fatalities and prevent outbreaks.
Shortages in measles vaccine supply, impacting vaccination efforts and potentially leading to gaps in immunization coverage, particularly in high-risk regions.
Current Challenges
Shortages in measles vaccine supply have been reported by manufacturers, potentially impacting vaccination programs and public health efforts globally to combat the spread of the disease effectively.
