Retinoschisis is an eye disease characterized by the abnormal splitting of the retinas neurosensory layers. It causes compromised vision in the affected area. Juvenile retinoschisis typically affects males and worsens vision early in life.
Retinoschisis is an eye disease where the retinas neurosensory layers split, leading to compromised vision. This condition commonly affects males and can deteriorate vision early in life. There are two main causes of juvenile retinoschisis⁚ X-Linked Retinoschisis and abusive head trauma.
Definition and Description
Retinoschisis is a condition where the layers of the retina split, leading to compromised vision. This disease typically affects males and often presents early in life. There are two main causes of juvenile retinoschisis, including X-linked Retinoschisis and abusive head trauma.
X-Linked Juvenile Retinoschisis
X-linked Juvenile Retinoschisis is a rare congenital disease caused by mutations in the RS1 gene, affecting males with impaired vision starting in childhood.
Abusive Head Trauma (AHT)
Abusive Head Trauma (AHT) is another cause of juvenile retinoschisis and can lead to vision impairment in affected individuals. It is essential to consider this trauma as a potential factor in cases of retinal damage and compromised vision.
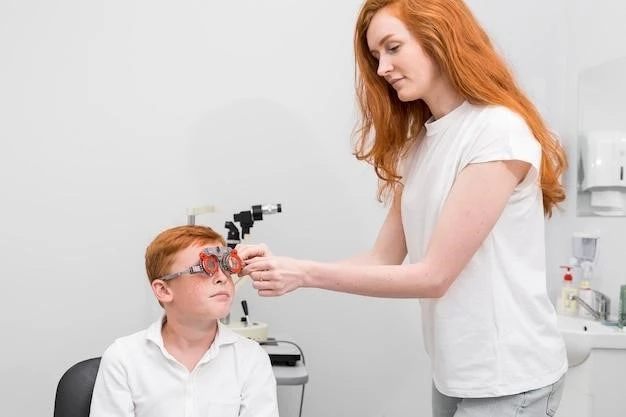
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Retinoschisis often presents with decreased vision that cannot be corrected with glasses. Diagnosis involves retinal examination by an ophthalmologist and genetic testing of the RS1 gene.
Visual Impairment
Retinoschisis often manifests with decreased vision that cannot be fully corrected with glasses. This visual impairment is a key symptom that warrants a thorough examination by an eye specialist.
Genetic Testing and Retinal Examination
To diagnose juvenile retinoschisis, a comprehensive approach involving genetic testing of the RS1 gene and meticulous retinal examination by a qualified eye specialist is crucial for accurate identification and management of this condition.

Treatment Options
Current treatments for juvenile retinoschisis focus on managing symptoms and may include surgical interventions. In the future, small gauge vitreoretinal surgery and gene therapy hold promise for improved outcomes.
Current Treatments
Current treatments for juvenile retinoschisis primarily focus on managing symptoms and may include surgical interventions to address the condition. Exciting future perspectives involve small gauge vitreoretinal surgery and potential gene therapy advancements.
Future Perspectives⁚ Small Gauge Vitreoretinal Surgery and Gene Therapy
Future perspectives for juvenile retinoschisis treatment include advancements in small gauge vitreoretinal surgery for improved surgical outcomes and the potential of gene therapy to target the underlying genetic mutations responsible for the condition, offering hope for enhanced therapeutic approaches in the future.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
Retinoschisis affects both peripheral and central retina and typically manifests with compromised vision, primarily impacting males. The incidence of juvenile retinoschisis is estimated to be 1 in 5,000 to 1 in 25,000 individuals;
Incidence Rates
The estimated incidence of juvenile retinoschisis is approximately 1 in 5,000 to 1 in 25,000 individuals, with a higher prevalence in males. This condition predominantly affects the peripheral and central retina, leading to compromised vision, particularly in males.
Demographics⁚ Gender and Age of Onset
Retinoschisis predominantly affects males, usually presenting in childhood with symptoms like decreased vision that cannot be corrected with glasses. This condition, particularly juvenile retinoschisis, impacts vision early in life, often leading to visual acuity ranging between 20/60 and 20/120.
Impact on Vision and Quality of Life
Retinoschisis has a significant impact on vision, particularly affecting males early in life. The compromised vision can vary from 20/60 to 20/120, impacting daily activities and quality of life.
Visual Acuity and Progression
Juvenile retinoschisis typically presents in childhood with impaired vision that cannot be corrected by glasses. Visual acuity is commonly between 20/60 and 20/120, highlighting the significant impact on vision early in life.
Challenges Faced by Individuals with Juvenile Retinoschisis
Individuals with juvenile retinoschisis encounter challenges related to impaired vision that begins early in life, affecting daily activities and quality of life. The progressive nature of the condition can pose ongoing visual difficulties requiring specialized care and support.
Research and Genetic Understanding
X-linked Retinoschisis research focuses on gene mutations and ongoing studies. Understanding RS1 mutations and clinical trials are integral in advancing treatment options and outcomes for individuals.
RS1 Gene Mutations
X-linked Retinoschisis research focuses on mutations in the RS1 gene٫ which encodes retinoschisin٫ a protein involved in the retina’s cellular organization. Understanding these gene mutations is crucial in advancing treatment options for juvenile retinoschisis.
Ongoing Studies and Clinical Trials
Ongoing studies and clinical trials are fundamental in advancing the understanding of juvenile retinoschisis and identifying potential therapeutic interventions. Research on the RS1 gene mutations and emerging treatments aim to enhance the management of this condition.