Introduction
Kidney Cancer, also known as renal cancer, occurs when abnormal cells in the kidneys grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. The kidneys are vital organs responsible for filtering waste products.
Overview of Renal Cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a disease that originates in the kidneys and is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. The most common type is renal cell carcinoma, which accounts for a majority of cases in adults. Other forms include transitional cell carcinomas and renal sarcoma, affecting different parts of the kidney. Symptoms may include blood in the urine, abdominal lump, back pain, fever, weight loss, and fatigue. Treatments range from surgery to drug therapies targeted at cancer cells.
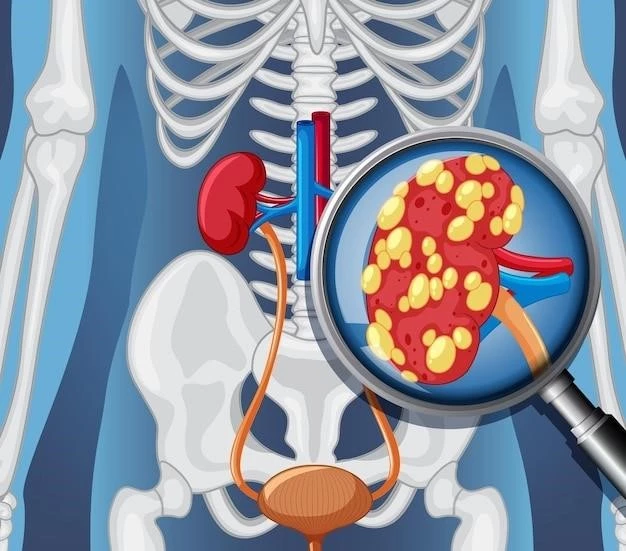
Symptoms and Causes
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, may present symptoms like blood in urine, abdominal lump, back pain, fever, weight loss, and fatigue. The causes of renal cancer are linked to genetic and environmental factors.
Common signs of renal cancer include blood in the urine, abdominal lump, back pain, fever, weight loss, and fatigue. Early detection through symptoms is crucial for timely treatment and better outcomes for patients.
Common Signs of Renal Cancer
Common signs of renal cancer include blood in the urine, abdominal lump, back pain, fever, weight loss, and fatigue. Early detection through symptoms is crucial for timely treatment and better outcomes for patients.
Methods for Detecting Renal Cancer
Various methods are used to detect renal cancer, including imaging tests like CT scans and MRIs, urine tests, blood tests, and kidney biopsies. Early detection is crucial for improved treatment outcomes in patients with renal cancer.
Types of Renal Cancer
Kidney cancer presents in various forms, with renal cell carcinoma being the most common type. Other types include transitional cell carcinomas and rare renal sarcomas, each affecting the kidneys differently.
Different Forms of Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer can manifest in various forms, with renal cell carcinoma being the most prevalent. Other types include transitional cell carcinomas and rare renal sarcomas. Each type impacts different parts of the kidney and may require tailored treatment approaches.
Survival Rates and Prognosis
Survival rates for kidney cancer vary based on factors like the stage of the cancer. Improved treatments have positively impacted patient prognosis over the years, increasing survival rates significantly.
Outcomes for Patients with Renal Cancer
The prognosis for patients with renal cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer and the treatment received. With advancements in treatment options and early detection, the survival rates for renal cancer have significantly improved in recent years, offering hope for better outcomes.
Prevention and Awareness
Prevention strategies for renal cancer include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals, regular exercise, and staying hydrated. Increasing awareness about the symptoms and risk factors can promote early detection and better outcomes for individuals at risk of renal cancer.
Strategies for Reducing the Risk of Renal Cancer
To reduce the risk of renal cancer, individuals can adopt preventative strategies like maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals, and staying informed about the symptoms and risk factors associated with renal cancer. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can also play a role in reducing the risk of developing renal cancer.
