Introduction to Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
In primary sclerosing cholangitis, inflammation causes scars within the bile ducts. These scars lead to serious liver damage.
Definition and Overview
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, leading to liver damage. It is a progressive condition that often coexists with inflammatory bowel disease. Symptoms include fatigue, itching, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preserving liver function.
Causes and Risk Factors
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) has an unknown exact cause but is believed to involve an immune system response triggering inflammation and scarring in the bile ducts. Genetic predisposition and associations with inflammatory bowel disease may play a role in the development of PSC.
Underlying Factors
The exact cause of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is unknown, but it is believed to involve an immune system response triggering inflammation and scarring in the bile ducts. Genetic predisposition and associations with inflammatory bowel disease may play a role in the development of PSC.
Genetic Predisposition
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is believed to have a genetic component, with certain genetic factors potentially increasing susceptibility to developing the condition. Research suggests a complex interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers in the pathogenesis of PSC.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) presents symptoms such as fatigue, itching, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Diagnosis involves liver function tests and imaging studies of the bile ducts.
Clinical Presentation
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) commonly presents symptoms such as abdominal pain, fatigue, itching, jaundice, and fever. The disease progression can vary, and patients may be asymptomatic or exhibit signs of liver dysfunction.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) involves liver function tests to assess liver enzymes and imaging studies such as MRIs to visualize the bile ducts. Additionally, endoscopic procedures like ERCP may be performed for further evaluation.
Complications Associated with PSC
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can lead to liver damage and biliary strictures, which may progress to serious complications affecting liver function and bile flow.
Liver Damage
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can lead to progressive liver damage characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, and scarring within the bile ducts. Over time, this can impact liver function and may lead to complications such as cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease.
Biliary Strictures
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can lead to the development of biliary strictures, which are abnormal narrowing of the bile ducts due to inflammation and scarring. These strictures can impede bile flow, causing further complications and potentially requiring interventions to alleviate the blockages.
Treatment Options for Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Treatment for primary sclerosing cholangitis focuses on managing symptoms, monitoring liver function, and addressing any blockages in the bile ducts;
Medical Management
Medical management of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) involves monitoring liver function, addressing symptoms such as fatigue and itching, and managing complications like biliary strictures. Medications may be prescribed to help alleviate symptoms and slow down disease progression.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions for primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) may be necessary to address complications such as biliary strictures or to alleviate blockages in the bile ducts. Procedures like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or liver transplant may be recommended in severe cases.
Relationship Between PSC and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The relationship between primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) involves a significant co-occurrence of these conditions. Individuals with PSC often have underlying IBD, which can impact the progression and management of both diseases.
Co-Occurrence of Conditions
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) often coexists with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. This co-occurrence can impact disease progression and treatment strategies for individuals affected by both conditions.
Impact on Disease Progression
The co-occurrence of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can influence the progression of both conditions, potentially leading to more severe liver damage and complications. The presence of IBD may impact the course of PSC and the effectiveness of treatment strategies.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
The prognosis for individuals with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) varies based on disease progression and treatment response. Long-term outlooks include monitoring liver function, managing symptoms, and potentially addressing complications through surgical interventions or liver transplantation.
Disease Progression
The progression of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can vary, impacting liver function and potentially leading to complications such as cirrhosis or liver failure. Monitoring disease progression is crucial to determine treatment effectiveness and outcomes.
Survival Rates
Survival rates for individuals with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) vary based on disease progression, treatment response, and potential complications such as liver failure. Long-term outcomes depend on disease management and the individual’s response to therapy.
Lifestyle Modifications for PSC Patients
Lifestyle modifications for individuals with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) may include dietary adjustments, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight to support liver health and overall well-being.
Dietary Recommendations
Dietary recommendations for individuals with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) may focus on reducing fat intake, ensuring adequate hydration, and incorporating foods that support liver health. A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage symptoms and support overall health.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise and physical activity can play a crucial role in managing primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) by promoting overall health, improving energy levels, and supporting liver function. Consultation with healthcare providers may help tailor exercise regimens to individual needs.
Current Research and Treatment Innovations
Ongoing research on primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) focuses on emerging therapies and clinical trials aimed at improving treatment outcomes and developing innovative approaches to manage this chronic liver disorder.
Emerging Therapies
Research in primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is focusing on emerging therapies to address the root causes of the disease, enhance treatment efficacy, and improve patient outcomes. Innovative approaches are being explored to target inflammation, fibrosis, and biliary strictures associated with PSC.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are critical in advancing the understanding and treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). These trials evaluate new therapies, interventions, and diagnostic approaches to improve patient outcomes and enhance the management of this chronic liver disease.
Support Resources for Individuals with PSC
For individuals with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), seeking support from patient organizations and online communities can provide valuable resources, information, and a sense of community while navigating the challenges of managing this chronic liver condition.
Patient Organizations
Engaging with patient organizations dedicated to primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can offer valuable support, educational resources, and advocacy for individuals affected by this chronic liver condition. These organizations can provide a sense of community and access to relevant information.
Online Communities
Online communities provide a platform for individuals living with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) to connect, share experiences, access support, and gather valuable information regarding the management of this chronic liver condition. Engaging with online communities can offer emotional support and insights into coping strategies.
Impact of PSC on Quality of Life
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life due to symptoms like fatigue, itching, jaundice, and abdominal pain. Managing the chronic liver disorder can influence various aspects of daily life and overall well-being.
Psychological Effects
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can have psychological effects, impacting an individual’s emotional well-being, mental health, and quality of life. Coping with a chronic liver condition can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression, highlighting the importance of holistic patient care.
Social Implications
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can have social implications, affecting relationships, work life, and daily activities. Coping with a chronic liver condition may lead to changes in social interactions, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
Preventive Measures and Risk Reduction Strategies
Implementing preventive measures and risk reduction strategies can help individuals with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) manage potential complications, maintain liver health, and improve overall quality of life. Monitoring liver function and following recommended dietary and lifestyle practices are key components in minimizing risks associated with PSC.
Disease Prevention
Preventive measures for primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) focus on lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring of liver function, and early detection of complications to help reduce the progression of the disease and improve long-term outcomes. Implementing strategies to maintain liver health and overall well-being is essential in disease prevention.
Monitoring and Surveillance
Regular monitoring and surveillance are essential in managing primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) to track disease progression, assess liver function, and detect potential complications early. Routine check-ups, imaging studies, and liver function tests help healthcare providers tailor treatment strategies and optimize patient care.
Global Trends in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Research
The global research landscape on primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) includes studies on inflammation, scarring of bile ducts, and liver damage. Ongoing investigations aim to elucidate disease mechanisms, develop new therapies, and enhance patient outcomes.
Market Analysis
The global market for primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is expected to exhibit growth, driven by ongoing research, emerging therapies, and increasing awareness of this chronic liver disorder. Market trends indicate a rise in treatment options and improved patient care strategies.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) involves continuous advancements in research, diagnostic tools, and treatment modalities. Efforts are focused on enhancing early detection methods, elucidating disease mechanisms, and optimizing personalized therapies to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
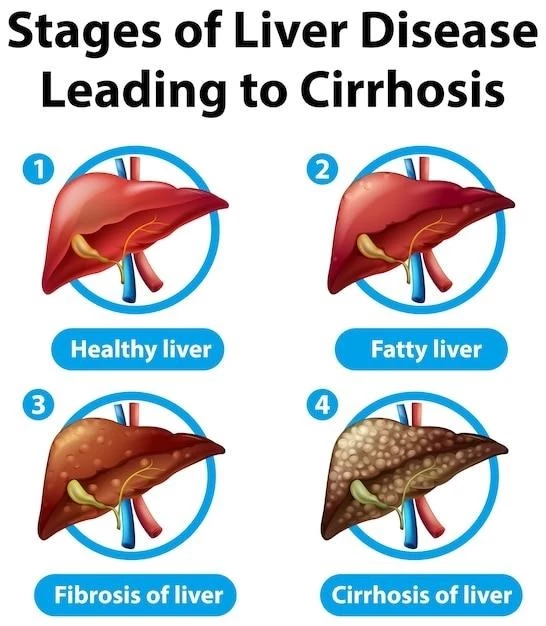
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts. Key takeaways include the importance of early detection, monitoring liver function, and exploring emerging therapies to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.