Overview of Primary Progressive Aphasia
Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) is a neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects language functions. It is characterized by a gradual decline in language abilities, impacting communication skills. PPA presents with distinct linguistic deficits and can be classified into different variants based on underlying pathologies.
Definition and Background
Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) is a distinctive form of dementia that primarily impairs language abilities due to neurodegenerative processes affecting language networks in the brain. The disorder gradually worsens over time, leading to significant challenges in communication. PPA encompasses different variants, each associated with specific underlying pathologies.
Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) encompasses distinct linguistic deficits and can be classified into different variants based on specific underlying pathologies. The major variants include semantic variant PPA (svPPA), agrammatic variant PPA (agPPA), and logopenic variant PPA (lvPPA), each associated with characteristic proteinopathies or degenerations in different language networks of the brain.
Variants and Pathologies
Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) encompasses distinct linguistic deficits and can be classified into different variants based on specific underlying pathologies. Major variants include semantic variant PPA (svPPA), agrammatic variant PPA (agPPA), and logopenic variant PPA (lvPPA), each associated with characteristic proteinopathies or degenerations in different language networks of the brain.
Language Impairment and Communication Challenges
Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) results in a gradual deterioration of language abilities, leading to challenges in communication. Individuals with PPA experience impairments in understanding, speaking, reading, and writing, impacting daily interactions and social interactions. The language decline varies based on the specific subtype of PPA and the areas of the brain affected by neurodegeneration.
Diagnostic Procedures and Criteria
Diagnosing Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) involves comprehensive assessment and criteria based on the distinctive linguistic deficits observed. Diagnostic procedures often include language evaluations, neuroimaging scans, and neuropsychological tests to characterize the specific variant of PPA and differentiate it from other neurological conditions affecting language. The diagnostic criteria aim to identify the progressive language impairment seen in PPA patients.
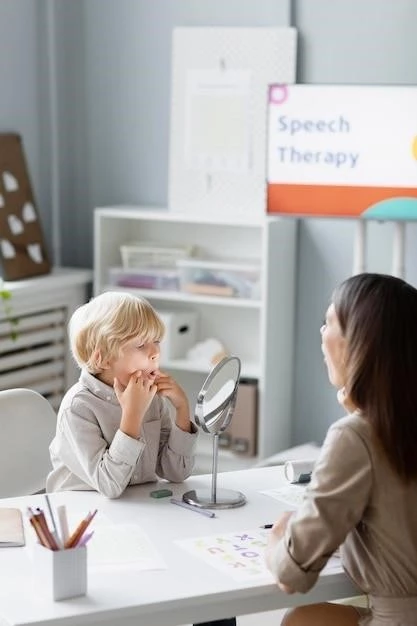

Causes and Progression of PPA
Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) is a neurological syndrome where brain tissue gradually degenerates, affecting speech and language capabilities. The progression and manifestations of PPA can vary depending on the specific subtype and the areas of the brain impacted by neurodegeneration.
Neurodegenerative Processes in the Brain
Primary progressive aphasia (PPA) involves the gradual deterioration of brain tissue, specifically affecting language networks. This neurodegenerative process results in the impairment of speech and language functions over time. The different variants of PPA are linked to distinct pathological changes in the brain, contributing to the progression of the disorder.
The progression of Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) can be influenced by various factors such as the specific subtype of PPA, the individual’s overall health, genetic predispositions, and environmental factors. Understanding these factors is crucial in determining the rate and pattern of language decline in PPA patients and guiding treatment strategies.
Treatment and Management of PPA
Effective management of Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) involves specialized speech therapy tailored to address language impairments and communication difficulties. Additionally, pharmacological interventions and supportive care play crucial roles in alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life for individuals with PPA.
Factors Influencing Disease Progression
Factors influencing the progression of Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) include the specific subtype of the disorder, individual health conditions, genetic predispositions, and environmental influences. These factors play a crucial role in determining the rate of language decline and overall disease advancement in individuals with PPA.
Pharmacological Interventions and Supportive Care
Pharmacological interventions play a vital role in managing Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) symptoms. Medications may target underlying neurodegenerative processes and help alleviate specific language impairments. Alongside pharmacotherapy, supportive care strategies, including counseling and education, can enhance the quality of life for individuals living with PPA.
Impact and Challenges Faced by Individuals with PPA
The impact of Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) on individuals includes significant challenges in communication and social interactions due to progressive language impairment. Coping mechanisms and support systems are essential for addressing the emotional and social effects experienced by individuals living with PPA.
Emotional and Social Effects
Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) can have profound emotional and social effects on individuals, leading to frustration, isolation, and challenges in maintaining relationships due to communication difficulties. Engaging in coping mechanisms and establishing robust support systems are essential for navigating these emotional and social impacts.
Coping Mechanisms and Support Systems
Individuals with Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) rely on various coping mechanisms to manage the challenges posed by language impairment. Establishing robust support systems involving family, friends, caregivers, and speech-language therapists can significantly alleviate the impact of PPA on daily life and enhance overall well-being.
Research Advances and Future Directions in PPA
The field of Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) research continues to advance with a focus on biomarkers, genetics, and novel therapeutic approaches. Collaborative efforts and awareness campaigns are driving progress towards understanding PPA pathophysiology and developing targeted interventions for improved patient outcomes.
Biomarkers, Genetics, and Novel Therapeutic Approaches
Advancements in Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) research focus on identifying biomarkers, exploring genetic factors, and developing innovative therapeutic strategies. Collaborative initiatives aim to uncover underlying disease mechanisms, genetic influences, and novel treatment options to enhance the understanding and management of PPA.
Collaborative Efforts and Awareness Campaigns
In the field of Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA), collaborative research efforts and awareness campaigns aim to improve understanding, diagnosis, and treatment approaches for individuals affected by the disorder. By fostering partnerships between researchers, clinicians, patients, and advocacy groups, these initiatives strive to elevate awareness, drive advancements, and enhance support systems for individuals living with PPA.
