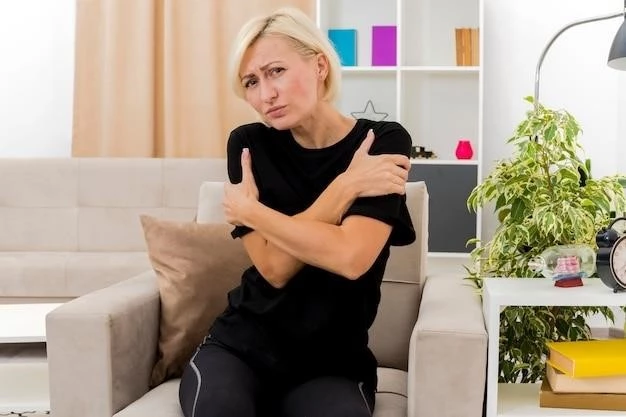
Introduction to Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a condition that causes pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the muscles, predominantly around the shoulders, neck, and hips. It is more prevalent in individuals over 50 years of age. The hallmark symptom is morning muscle stiffness lasting over 45 minutes. PMR is often associated with elevated inflammatory markers in the blood.
Definition and Description
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is an inflammatory rheumatic disorder that primarily affects individuals over the age of 50, causing pain and stiffness in the muscles around the shoulders, neck, and hips. The condition is characterized by morning muscle stiffness lasting longer than 45 minutes, often accompanied by elevated inflammatory markers in the blood.
Symptoms of Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) presents symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and inflammation in muscles around the shoulders, neck, and hips. Morning stiffness lasting over 45 minutes is a common hallmark symptom.
Common Symptoms
The common symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) include pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the muscles around the shoulders, neck, and hips. Morning stiffness lasting over 45 minutes is a characteristic indicator of this condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is believed to be caused by an abnormal immune response, although the exact cause is unknown. Factors such as genetic predisposition and environmental triggers may contribute to the development of this inflammatory condition.
Factors Contributing to Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Factors contributing to polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) may include abnormalities in the immune system, genetic susceptibility, and potential environmental triggers. These factors can lead to the onset of the inflammatory condition affecting the muscles, especially in older individuals.
Diagnosis of Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Diagnosing polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) typically involves a medical history review, physical examination, and blood tests to assess inflammatory markers. Imaging studies may be conducted to rule out other conditions.
Methods for Diagnosing the Condition
Diagnosing polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and blood tests to evaluate inflammatory markers such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP). Imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI may be utilized to support the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Treatment for polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) typically involves medication such as corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments may also be recommended to manage the condition.
Medications and Therapies
Treatment for polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) often involves the use of corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve mobility and strength. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and a balanced diet can complement medical interventions in managing the condition.
Complications Associated with Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Complications related to polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) may include potential risks and issues such as side effects from long-term corticosteroid use, adrenal insufficiency, increased susceptibility to infections, and osteoporosis due to the effects of prolonged corticosteroid therapy.
Potential Risks and Issues
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) poses potential risks and issues such as complications from long-term corticosteroid use, adrenal insufficiency, increased susceptibility to infections, and the development of osteoporosis due to prolonged corticosteroid therapy. It is crucial for healthcare providers to monitor and manage these risks in patients with PMR.
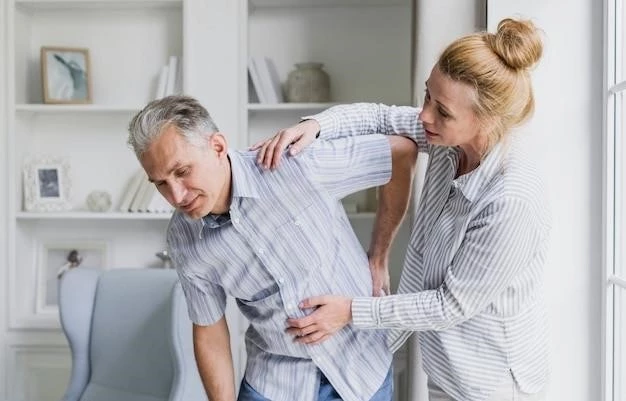

Relationship Between Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is closely associated with giant cell arteritis (GCA), also known as Horton disease. Both conditions may occur together and share similarities, yet they represent distinct manifestations affecting individuals, particularly older adults.
Understanding the Connection
The relationship between polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) and giant cell arteritis (GCA) involves an overlap in symptoms and potential co-occurrence, particularly in older individuals. While both conditions share similarities, they represent distinct inflammatory disorders affecting specific regions of the body.
Management and Prevention of Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Managing and preventing polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) typically involves a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Corticosteroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms, while regular exercise and a healthy diet can help improve overall well-being and mobility in individuals with PMR.
Strategies for Coping with the Condition
Individuals with polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) can employ various strategies to cope with the condition, including maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, following prescribed medication regimens, attending follow-up appointments with healthcare providers, and seeking support from family and community resources. Additionally, techniques such as mindfulness meditation or relaxation exercises may help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
Research and Development in Polymyalgia Rheumatica Treatment
Recent advancements in the research and development of polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) treatment have focused on identifying novel therapeutic approaches to manage inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Ongoing studies aim to enhance treatment efficacy and reduce the potential side effects associated with current medications, ultimately improving outcomes for individuals with PMR.
Advancements in Medical Approaches
Ongoing research in the field of polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) treatment has led to advancements in medical approaches aimed at enhancing the management of inflammation and symptoms. These developments focus on improving the effectiveness of existing therapies, exploring novel treatment modalities, and addressing potential side effects associated with prolonged medication use. The goal is to optimize patient outcomes and quality of life through innovative medical strategies.
Impact of Polymyalgia Rheumatica on Elderly Individuals
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) can have a significant impact on elderly individuals, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the neck, shoulders, and hips. Managing this condition is essential to improve the quality of life for older adults affected by PMR.
Considerations for Older Adults
Elderly individuals affected by polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) may experience significant pain and stiffness in areas such as the neck, shoulders, and hips, affecting mobility and daily activities. It is crucial to tailor treatment plans to meet the unique needs of older adults, considering factors such as existing comorbidities and potential medication interactions to ensure effective management of PMR.
Global Market Trends and Projections for Polymyalgia Rheumatica Treatment
The global market for polymyalgia rheumatica treatment is expected to show significant growth, with projections estimating a substantial increase in market size. Market analysts anticipate a rise in demand for innovative treatment options and advancements in medical approaches aimed at enhancing outcomes for individuals with polymyalgia rheumatica.
