Introduction
Photosensitive epilepsy is a type of epilepsy that causes seizures triggered by flashing lights or high contrasting patterns.
Overview of Photosensitive Epilepsy
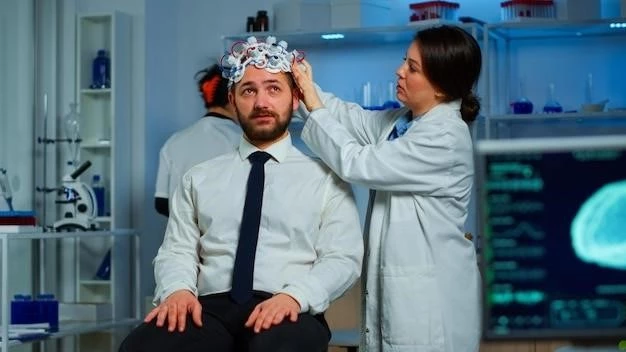
Photosensitive epilepsy is a type of epilepsy where seizures are triggered by flashing or flickering lights, and high contrasting patterns. It is relatively rare, affecting about 3% of people with epilepsy. Most individuals affected are between 7 and 19 years old, with a higher incidence in females. Genetics also play a role in predisposing individuals to this condition. To diagnose photosensitive epilepsy, an electroencephalogram (EEG) test may be conducted to detect changes in brainwave patterns when exposed to specific visual stimuli. Treatment often involves medication and lifestyle adjustments to manage and reduce seizure occurrences.
Causes and Triggers
Photosensitive epilepsy is often more common in children and adolescents, particularly those with certain epilepsy syndromes. Genetics can also play a role; individuals with a parent sensitive to flashing lights may be more prone to developing photosensitive seizures.
Genetic Factors in Photosensitive Epilepsy
Photosensitive epilepsy may have a genetic component, especially in cases where parents or family members also exhibit sensitivity to flashing lights. Research suggests that specific epilepsy syndromes, such as Dravet syndrome, may be associated with genetic alterations predisposing individuals to photosensitive seizures.
Photosensitive seizures can be triggered by exposure to flashing lights, high-intensity strobes, specific visual patterns, or contrasting visual stimuli. These triggers vary from person to person, and some individuals may also be sensitive to certain colors or movements that can induce seizures.

Symptoms and Diagnosis
Photosensitive epilepsy manifests with seizures triggered by flashing lights, flickering lights, or contrasting patterns.
Common Seizure Triggers
Seizures in photosensitive epilepsy can be triggered by exposure to flashing or flickering lights, high-intensity strobes, specific patterns, or contrasting visual stimuli. These triggers can vary from person to person, with some individuals also being sensitive to particular colors or movements that may induce seizures.
Diagnostic Tests for Photosensitive Epilepsy
The diagnosis of photosensitive epilepsy often involves an electroencephalogram (EEG) test to observe brainwave patterns when exposed to specific visual stimuli, such as flashing lights or contrasting patterns. This test helps in confirming the presence of photosensitivity that can trigger seizures.
Treatment Options
Most individuals with photosensitive epilepsy are treated with medication to reduce seizure risk and by avoiding seizure triggers.
Medication for Photosensitive Epilepsy
Most individuals with photosensitive epilepsy are treated with epilepsy medications, such as anti-seizure drugs, to help reduce the frequency and severity of seizures triggered by lights or specific patterns. These medications work to stabilize brain activity and lower the risk of seizure occurrence.
Lifestyle Changes and Seizure Prevention
Managing photosensitive epilepsy involves making lifestyle changes to avoid seizure triggers like flashing lights, patterns, or colors. Practical adjustments can be made to mitigate the risk of seizures, such as minimizing exposure to known triggers and ensuring proper sleep and alcohol intake.

Management Strategies
Individuals with photosensitive epilepsy can manage their condition by avoiding seizure triggers and implementing preventive measures.
Avoiding Photosensitive Seizure Triggers
Individuals with photosensitive epilepsy can minimize the risk of seizures by avoiding triggers such as flashing lights, high-contrast patterns, and certain colors. Making practical changes in daily routines to reduce exposure to potential triggers is essential for effective seizure prevention.
Special Glasses and Other Preventive Measures
Some individuals with photosensitive epilepsy may benefit from wearing special glasses with dark or filtered lenses. These glasses can help reduce the risk of seizure triggers by minimizing exposure to specific colors and light intensities that can induce seizures. Additionally, practical measures like adjusting screen settings on devices to reduce sensitivity to triggers can be helpful in managing photosensitive epilepsy.
Legal and Social Considerations
Reporting nuisance lights to local authorities and online seizure-triggering content helps safeguard individuals with photosensitive epilepsy. Awareness campaigns and support services are crucial for effective management.
Reporting Nuisance Lights and Online Content
Individuals with photosensitive epilepsy may need to report nuisance lights to local authorities to prevent potential seizure triggers. Similarly, reporting seizure-triggering online content to the relevant platforms can help create a safer digital environment for those with this condition.
Support Services and Awareness Campaigns
Support services for individuals with photosensitive epilepsy can include helplines, online resources, and trained advisors offering assistance and guidance. Additionally, awareness campaigns aim to educate the public on seizure triggers and available support, promoting better understanding and safety for those affected by this condition;