Introduction
Odontophobia, also known as dental fear, is a common emotional reaction to dental stimuli․ Dental anxiety and phobia can vary in severity, impacting individuals’ oral health and quality of life․
Definition of Odontophobia and its Significance
Odontophobia, also known as dental fear, is an emotional reaction to dental stimuli․ Dental anxiety and phobia vary in severity, impacting oral health and quality of life․ Click here to read more․

Understanding Odontophobia
Dental fear, or dentophobia, is a normal emotional reaction to specific threatening stimuli in the dental situation․ Dental anxiety and phobia can vary in severity, impacting oral health and quality of life․
Odontophobia, or dental fear, can stem from a mix of factors such as traumatic dental experiences, fear of pain, embarrassment, loss of control, and even fear of needles or dental drills․ These causes contribute to the emotional reactions exhibited in odontophobic individuals․
Causes of Odontophobia
Odontophobia, or dental fear, can stem from a mix of factors such as traumatic dental experiences, fear of pain, embarrassment, loss of control, fear of needles or dental equipment, and anxiety related to past negative feedback․ These causes contribute to the emotional reactions in odontophobic individuals․
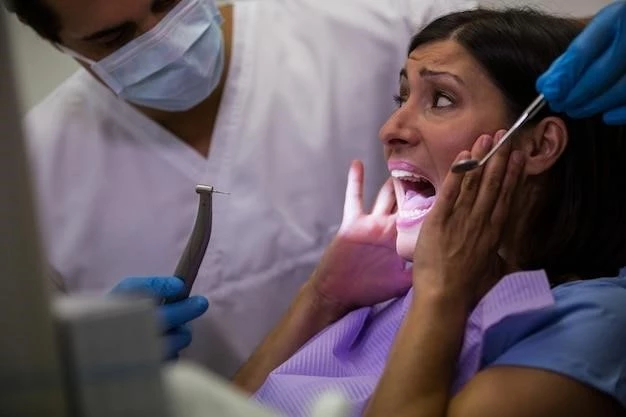
Types of Odontophobia
Three classes of dental phobia can be recognized⁚ Mild odontophobia, also called dental anxiety, is the most frequent among the population; Moderate odontophobia, called dental fear; Severe dental phobia, the real dental phobia, decidedly rarer and more difficult to manage by the dentist․
Mild Odontophobia (Dental Anxiety)
Dental fear, or dentophobia, is a normal emotional reaction to one or more specific threatening stimuli in the dental situation․ However, dental anxiety is indicative of a state of apprehension that something dreadful is going to happen in relation to dental treatment, usually coupled with a sense of losing control․
Moderate Odontophobia (Dental Fear)
When discussing dental fears, it’s essential to distinguish between dental anxiety and dental phobia․ Dental anxiety refers to a general unease or apprehension about visiting the dentist, while dental phobia is an intense fear that can lead to avoiding dental care altogether․ This fear can be triggered by various factors, including past traumatic experiences, fear of pain, embarrassment, and a general loss of control during dental procedures․ Managing dental fear often requires a personalized approach to help individuals overcome their specific triggers and anxieties․
Severe Odontophobia (Real Dental Phobia)
Severe odontophobia, known as dental phobia, is an intense and irrational fear of dental treatment․ This extreme fear can result in avoidance of necessary dental care, leading to severe consequences for oral health․ Individuals with severe odontophobia may experience emotional distress, panic attacks, and physical symptoms when faced with dental procedures, making it challenging for dentists to provide adequate treatment․
Impact of Odontophobia
Odontophobia٫ a common emotional reaction٫ can have profound effects on individuals’ oral health and overall well-being․ The fear of dental treatment can lead to avoidance behaviors٫ compromised dental care٫ and negative psychological implications․
Effects on Dental Health
Odontophobia, or dental fear, can result in individuals avoiding dental visits, neglecting oral hygiene, and postponing necessary treatments, leading to poor dental health outcomes such as tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral issues․ The fear of dental procedures can have a significant impact on overall dental well-being if not addressed effectively․
Psychological Implications
Odontophobia, or dental fear, can have significant psychological implications, leading to heightened anxiety, stress, and avoidance behaviors surrounding dental care․ Individuals may experience panic attacks, nightmares, and intrusive thoughts related to dental treatment, affecting their overall mental well-being and quality of life․
Diagnosis and Treatment
Assessing odontophobia involves evaluating a patient’s response to dental stimuli and identifying the underlying causes of their fear․ Treatment strategies for odontophobia may include cognitive-behavioral therapy, desensitization techniques, relaxation methods, and, in severe cases, pharmacological interventions to manage anxiety and support patients during dental procedures․
Evaluation of Odontophobia
Assessing odontophobia involves understanding a patient’s response to dental stimuli, identifying triggers of fear, and assessing the impact on daily life․ Evaluation may require assessing past dental experiences, anxiety levels, psychological factors, and the individual’s overall coping mechanisms to develop an effective treatment plan․
Managing Odontophobia
Effective strategies for managing odontophobia include cognitive-behavioral therapy, desensitization techniques, relaxation methods, and, in severe cases, pharmacological interventions․ By addressing triggers and developing coping mechanisms, individuals can gradually overcome their fear of dental treatment and improve their oral health outcomes․
Prevention Strategies
Early intervention for odontophobia involves identifying fear triggers, providing education, and fostering a trusting relationship with dental professionals․ Regular dental visits play a vital role in desensitizing individuals to dental procedures and reducing anxiety associated with oral care․
Early Intervention for Odontophobia
Early intervention for odontophobia involves identifying fear triggers, providing education, and fostering a trusting relationship with dental professionals․ Encouraging regular dental visits from a young age and incorporating positive dental experiences can help prevent the development of severe dental fears․
Importance of Regular Dental Visits
Regular dental visits play a crucial role in desensitizing individuals to dental procedures and reducing anxiety associated with oral care․ Early interventions and positive dental experiences can help prevent the development of severe dental fears, ensuring optimal oral health outcomes․
Coping Mechanisms
Therapeutic approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy and relaxation techniques help individuals manage odontophobia effectively․ Medication can also play a role in alleviating anxiety during dental treatments․
Therapeutic Approaches for Odontophobia
Therapeutic approaches for odontophobia include cognitive-behavioral therapy, desensitization techniques, relaxation methods, and medication․ These strategies aim to help individuals manage their fear of dental treatment and improve their overall well-being․
Role of Medication in Odontophobia Treatment
Medication can play a supportive role in alleviating anxiety during dental procedures for individuals with odontophobia․ Drugs like benzodiazepines (e․g․, Valium, Xanax) or other sedatives can help patients relax and manage their fear during dental treatments, enhancing their overall dental experience․
Research and Studies on Odontophobia
Scientific literature on dental anxiety and phobias explores the psychological and behavioral mechanisms associated with odontophobia․ Recent advancements focus on therapeutic interventions, patient care management, and innovative approaches to alleviate anxiety during dental treatments․
Scientific Literature on Dental Anxiety
The scientific literature on dental anxiety delves into the psychological and behavioral mechanisms associated with odontophobia, exploring the factors contributing to dental fear and examining interventions to alleviate anxiety and enhance patient care management․
Recent Advancements in Odontophobia Research
Recent advancements in odontophobia research focus on innovative therapeutic interventions, patient care management strategies, and technology-driven approaches to address dental anxiety effectively․ Studies explore the impact of hypnosis, virtual reality exposure therapy, audiovisual aids, and sedation techniques on alleviating fear during dental procedures, enhancing the overall dental experience for individuals with odontophobia․