Understanding Insulinoma Disease
Insulinoma is a rare tumor of the pancreas that can lead to hypoglycemia due to excess insulin production․ Understanding the symptoms‚ diagnosis‚ effects on blood sugar‚ and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively․
Introduction to Insulinoma
Insulinoma is a rare pancreatic tumor that arises from insulin-producing cells․ These tumors are typically benign and can lead to hyperinsulinemia‚ causing hypoglycemia․ The excess insulin production results in decreased blood glucose levels‚ leading to symptoms like confusion‚ dizziness‚ sweating‚ and fainting․
If you experience recurring episodes of hypoglycemia‚ it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation․ Early diagnosis and management of insulinoma are crucial to prevent complications related to low blood sugar levels․ Diagnostic tests such as blood glucose monitoring‚ fasting tests‚ and insulin levels can help confirm the presence of an insulinoma․
Once diagnosed‚ treatment options for insulinoma include surgery to remove the tumor and medical management to control symptoms․ Surgical removal of the tumor is the primary treatment method and can provide a potential cure for insulinoma․ However‚ in some cases‚ medical therapy with medications to help regulate blood sugar levels may be necessary․
Living with insulinoma requires regular monitoring of blood sugar levels‚ adherence to dietary changes‚ and lifestyle modifications to prevent hypoglycemic episodes․ It’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses your individual needs․
Insulinoma is a complex condition that requires ongoing management and follow-up care; By staying informed about the disease‚ following treatment recommendations‚ and making necessary lifestyle adjustments‚ individuals with insulinoma can effectively manage their condition and lead fulfilling lives․
Symptoms of Insulinoma
Recognizing the symptoms of insulinoma is crucial for early detection and management of this condition․ Common symptoms include confusion‚ dizziness‚ sweating‚ weakness‚ palpitations‚ and anxiety․ If you experience recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia‚ especially when fasting or during physical activity‚ it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly․
Other symptoms of insulinoma may include blurred vision‚ hunger‚ irritability‚ tremors‚ and difficulty concentrating․ These symptoms occur due to the low blood sugar levels resulting from the excess insulin produced by the tumor․ It’s important not to ignore these signs and to discuss them with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause․
In severe cases‚ insulinoma symptoms can lead to loss of consciousness or seizures․ If you or a loved one experiences these symptoms‚ it is critical to seek immediate medical help․ Hypoglycemia can be life-threatening if left untreated‚ so prompt intervention is necessary to stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent further complications․
By being aware of the signs and symptoms of insulinoma‚ you can advocate for your health and work with healthcare professionals to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment․ Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and reporting any changes or persistent symptoms to your medical team are essential steps in managing insulinoma effectively․
Diagnosis of Insulinoma
Diagnosing insulinoma involves a combination of clinical evaluation‚ blood tests‚ imaging studies‚ and glucose tolerance tests․ If you experience symptoms suggestive of insulinoma‚ such as recurrent hypoglycemia‚ your healthcare provider may conduct various diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis․
Blood tests play a crucial role in diagnosing insulinoma by measuring glucose‚ insulin‚ C-peptide‚ and other hormone levels in the blood․ Fasting tests‚ where blood samples are taken after a period of fasting‚ can help identify abnormal insulin and glucose levels that indicate the presence of an insulin-producing tumor․
Imaging studies‚ such as CT scans‚ MRI scans‚ and endoscopic ultrasound‚ can provide detailed images of the pancreas to locate the tumor․ These imaging tests help healthcare providers visualize the size‚ location‚ and characteristics of the insulinoma‚ guiding treatment decisions․
Glucose tolerance tests may be performed to assess the body’s response to glucose intake and evaluate insulin levels over time․ During these tests‚ blood sugar levels are monitored before and after consuming a glucose solution to determine how the body regulates insulin secretion․
Diagnosing insulinoma requires a comprehensive approach that may involve multiple tests and consultations with endocrinologists‚ radiologists‚ and surgeons․ By actively participating in the diagnostic process and sharing your symptoms and medical history with your healthcare team‚ you can help ensure an accurate diagnosis and timely initiation of treatment for insulinoma․
Effects of Insulinoma on Blood Sugar
Insulinoma can significantly impact blood sugar levels by causing excess insulin production in the body․ The tumor’s secretion of insulin leads to hypoglycemia‚ characterized by low blood glucose levels․ This hypoglycemia can present with symptoms like confusion‚ sweating‚ weakness‚ and dizziness․
Low blood sugar levels resulting from insulinoma can be dangerous if not promptly treated․ Severe hypoglycemia can potentially lead to seizures‚ loss of consciousness‚ and other critical complications․ It is essential to monitor blood sugar levels closely and seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of hypoglycemia․
The excessive release of insulin by the tumor can override the body’s natural mechanisms for regulating blood sugar‚ leading to frequent episodes of hypoglycemia․ These fluctuations in blood glucose levels can impact overall health and well-being‚ making it crucial to address the underlying cause of insulinoma through proper diagnosis and treatment․
Managing the effects of insulinoma on blood sugar involves a multidisciplinary approach‚ including close monitoring of glucose levels‚ adherence to prescribed treatment plans‚ and lifestyle modifications․ By working closely with healthcare providers and following their recommendations‚ individuals with insulinoma can achieve better control over their blood sugar levels and mitigate the risks associated with hypoglycemia․
Treatment Options for Insulinoma
When it comes to treating insulinoma‚ the primary approach is surgical removal of the tumor․ Surgery aims to excise the insulin-producing tumor from the pancreas and potentially cure the condition․ It is essential to consult with a skilled surgical team experienced in pancreatic procedures to ensure the best possible outcome;
In cases where surgical removal of the tumor is not feasible or if the tumor has metastasized‚ medical management becomes crucial․ Medications may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels and minimize the effects of excessive insulin secretion․ These medications work by regulating insulin release to prevent hypoglycemia․
Additionally‚ dietary changes play a significant role in managing insulinoma․ It is essential to work with a healthcare provider or dietitian to develop a meal plan that helps stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent hypoglycemic episodes․ Avoiding high-sugar foods and consuming complex carbohydrates can help regulate glucose levels․
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is vital for individuals with insulinoma to track their response to treatment and make necessary adjustments․ By staying proactive in managing the disease‚ individuals can better control their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life․ It is crucial to maintain open communication with healthcare providers and report any changes or concerns promptly․
Surgical Treatment for Insulinoma
Surgical treatment is the primary approach for managing insulinoma by removing the tumor from the pancreas․ The surgical procedure aims to excise the insulin-producing cells or the entire tumor‚ depending on its size and location․ It is essential to consult with a skilled surgical team specializing in pancreatic surgeries to ensure the best possible outcome․
Prior to surgery‚ comprehensive imaging studies such as CT scans‚ MRI scans‚ and endoscopic ultrasounds are performed to precisely locate the tumor and plan the surgical approach․ These imaging tests provide detailed information about the size‚ extent‚ and characteristics of the insulinoma‚ guiding the surgical team during the procedure․
The surgical removal of an insulinoma can often result in a complete cure‚ especially if the tumor is benign and localized․ However‚ in cases where the tumor is malignant or has spread to other organs‚ additional treatment may be necessary post-surgery․ Close follow-up care with healthcare providers is crucial to monitor for any recurrence or ongoing issues․
After surgery‚ patients may experience a recovery period during which they will need to follow post-operative instructions provided by their healthcare team․ These instructions may include dietary guidelines‚ activity restrictions‚ and medication management to support healing and optimize outcomes․ It is essential to adhere to the post-operative care plan and attend follow-up appointments for monitoring and evaluation․
Medical Management of Insulinoma
Medical management plays a crucial role in treating insulinoma‚ particularly in cases where surgical intervention is not possible or as an adjunct to treatment․ Medications may be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels and control the effects of excess insulin production․
One common medication used in the medical management of insulinoma is diazoxide․ Diazoxide works by inhibiting insulin release from the pancreas‚ thereby preventing hypoglycemia․ It is important to take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider and adhere to the recommended dosage and schedule․
In cases where diazoxide is not effective or well-tolerated‚ other medications such as octreotide may be considered․ Octreotide works by suppressing the release of various hormones‚ including insulin‚ and can help manage symptoms of insulinoma․ Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and communication with your healthcare team are essential when taking these medications․
In addition to medications‚ dietary modifications are also crucial in the medical management of insulinoma․ Working with a dietitian to create a meal plan that supports stable blood sugar levels is essential․ Avoiding high-sugar foods‚ consuming balanced meals‚ and monitoring carbohydrate intake can help regulate glucose levels and prevent hypoglycemic episodes․
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to assess the effectiveness of medical management‚ monitor for any side effects of medications‚ and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan․ By actively engaging in your care and collaborating with your medical team‚ you can optimize the medical management of insulinoma and improve your overall well-being․
Lifestyle Changes for Insulinoma Patients
Managing insulinoma involves making lifestyle changes that support stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being․ It is essential for insulinoma patients to adopt healthy habits that can help prevent hypoglycemic episodes and improve their quality of life․
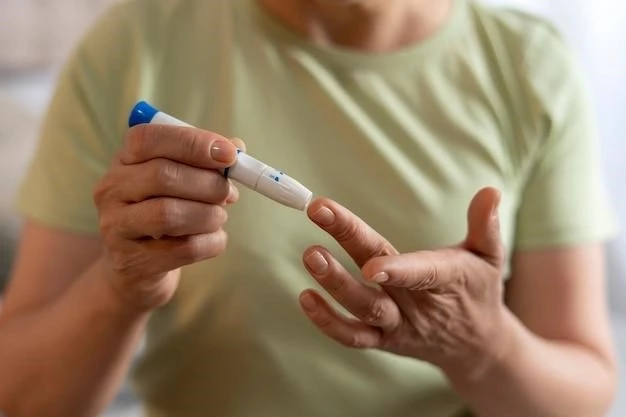
Diet plays a key role in managing insulinoma․ Working with a healthcare provider or dietitian to create a balanced meal plan is crucial․ Focus on consuming regular‚ balanced meals with a mix of complex carbohydrates‚ lean proteins‚ and healthy fats to help regulate blood sugar levels throughout the day․
Avoiding high-sugar foods and beverages is important for insulinoma patients as they can quickly raise blood glucose levels and trigger hypoglycemic episodes․ Monitoring carbohydrate intake and spacing out meals and snacks evenly can help prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels․
Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can also benefit insulinoma patients․ Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity‚ regulate blood sugar levels‚ and promote overall health․ Consult with your healthcare provider to develop a safe and effective exercise plan tailored to your individual needs and capabilities․
Managing stress is another crucial aspect of lifestyle changes for insulinoma patients․ Stress can impact blood sugar levels and exacerbate symptoms of hypoglycemia․ Incorporating stress-reducing techniques such as meditation‚ yoga‚ deep breathing exercises‚ or engaging in hobbies can help promote relaxation and well-being․
By making positive lifestyle changes‚ insulinoma patients can take an active role in managing their condition and improving their overall health․ It is important to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses dietary needs‚ physical activity‚ stress management‚ and other factors that impact insulinoma management․
Monitoring and Follow-up for Insulinoma Patients
Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential for insulinoma patients to ensure effective management of the condition and to prevent complications․ Healthcare providers will schedule follow-up appointments to assess treatment response‚ monitor blood sugar levels‚ and address any concerns or changes in symptoms․
Monitoring blood sugar levels at home is an important aspect of managing insulinoma․ Regularly checking your blood glucose levels with a glucometer can help track fluctuations and trends‚ allowing you to make informed decisions about your diet‚ medication‚ and overall care plan․ Keep a record of your readings to share with your healthcare team during follow-up visits․
Follow-up appointments with endocrinologists‚ surgeons‚ and other healthcare professionals are necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment‚ monitor for any recurrence of insulinoma‚ and address any new symptoms or side effects․ These appointments allow for ongoing assessment and adjustment of the treatment plan as needed․
Imaging studies‚ such as CT scans or MRI scans‚ may be scheduled periodically to monitor the status of the pancreas and check for any signs of tumor recurrence․ These imaging tests provide detailed information about the size‚ location‚ and characteristics of the insulinoma‚ helping healthcare providers make informed decisions about further treatment or management․
Open communication with your healthcare team is key during follow-up visits․ Be sure to discuss any changes in symptoms‚ concerns about medication side effects‚ or challenges in managing your insulinoma․ By actively participating in your care‚ adhering to recommended monitoring guidelines‚ and attending follow-up appointments‚ you can optimize the management of insulinoma and promote your overall well-being․
Conclusion
In conclusion‚ understanding insulinoma‚ a rare pancreatic tumor that causes excess insulin production‚ is crucial for early detection and effective management․ Recognizing the symptoms of hypoglycemia‚ undergoing diagnostic tests‚ and exploring treatment options are essential steps in addressing this condition․
Whether through surgical intervention to remove the tumor or medical management to regulate blood sugar levels‚ there are various approaches to managing insulinoma․ Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet‚ engaging in regular physical activity‚ managing stress‚ and monitoring blood sugar levels play a significant role in supporting well-being․
Follow-up care and consistent monitoring are key components of insulinoma management to track treatment response‚ assess any changes‚ and address concerns promptly․ By working closely with healthcare providers‚ adhering to treatment recommendations‚ and making necessary lifestyle adjustments‚ individuals with insulinoma can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition․
Overall‚ proactive engagement in care‚ regular communication with healthcare professionals‚ and a commitment to self-care can help individuals navigate the challenges of living with insulinoma․ By prioritizing health and well-being‚ insulinoma patients can empower themselves to take control of their condition‚ optimize treatment outcomes‚ and improve their quality of life․
