Understanding and Managing Inguinal Hernia
Learn about the causes‚ symptoms‚ and treatment options for inguinal hernia‚ a condition where abdominal contents bulge through the groin. Discover the risks and complications associated with hernia repair surgery. Get insights into preventing hernia recurrence and identifying risk factors.
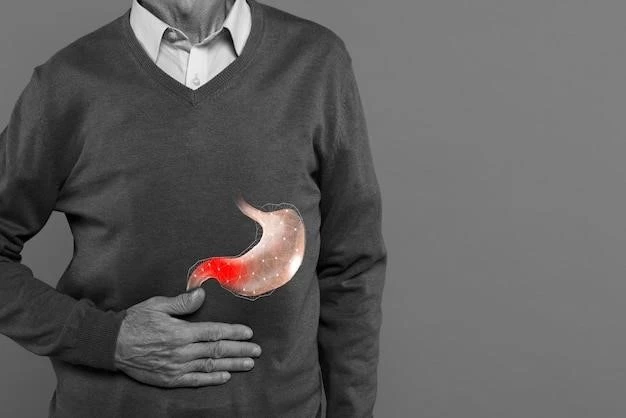
What is an Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia occurs when a portion of the small intestine or other abdominal contents protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall‚ typically in the groin area. This leads to a noticeable bulge or swelling that may cause discomfort or pain‚ especially when lifting heavy objects or straining. Surgery is often the recommended treatment to repair the hernia and prevent complications. Understanding the nature of inguinal hernias can help individuals recognize symptoms early and seek timely medical intervention.
Recognizing Symptoms of Inguinal Hernia
Recognizing the symptoms of an inguinal hernia is crucial for early diagnosis and prompt treatment. Common signs include a visible bulge in the groin area‚ especially when standing or straining‚ along with discomfort‚ aching‚ or burning sensations. Some individuals may experience a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the groin. If you notice any of these symptoms‚ particularly if they worsen over time‚ consult a healthcare professional. Delaying treatment can lead to complications and increased discomfort.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing an inguinal hernia typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider‚ sometimes supplemented by imaging tests like ultrasound. Once diagnosed‚ the recommended treatment is hernia repair surgery‚ which aims to push the protruding tissue back into place and strengthen the weakened abdominal wall. Surgical procedures for hernia repair include open surgery and laparoscopic techniques. Consulting with a qualified surgeon is essential to determine the most suitable approach based on individual factors and preferences. It is important to address an inguinal hernia promptly to alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Types of Hernia Repair Surgery
There are two main types of hernia repair surgeries commonly used for treating inguinal hernias⁚ open surgery and laparoscopic surgery. Open surgery involves making an incision directly over the hernia‚ allowing the surgeon to repair the weakened abdominal wall and push the protruding tissue back into place. On the other hand‚ laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive approach that involves small incisions and the use of a camera and specialized tools for the repair. Each type of surgery has its own benefits and considerations‚ so discussing with a healthcare provider or surgeon can help determine the most appropriate option based on individual circumstances.
Risks and Complications of Hernia Repair Surgery
While hernia repair surgery is generally safe and effective‚ it is important to be aware of potential risks and complications. Common risks include infection‚ bleeding‚ pain‚ and recurrence of the hernia. In rare cases‚ complications such as nerve damage‚ bowel obstruction‚ or chronic pain may occur. It is essential to follow postoperative care instructions carefully‚ attend follow-up appointments‚ and promptly report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider. Understanding the risks associated with hernia repair surgery can help you make informed decisions and take necessary precautions for a successful recovery.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
After undergoing hernia repair surgery‚ proper postoperative care is essential for a smooth recovery. Follow all instructions provided by your healthcare team‚ including wound care‚ physical activity restrictions‚ and medications. It is important to gradually resume daily activities‚ avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous exercises during the initial recovery period. Be mindful of any signs of infection‚ such as increasing pain‚ redness‚ or swelling at the incision site‚ and seek medical attention if needed. Attend all follow-up appointments to monitor progress and address any concerns promptly. Taking care of yourself and following postoperative guidelines can promote healing and minimize complications.
Preventing Inguinal Hernia Recurrence
After undergoing hernia repair surgery‚ taking steps to prevent recurrence is vital. Follow a gradual return to physical activities as advised by your healthcare provider to allow adequate healing. Maintain a healthy weight‚ as excess weight can strain the abdominal wall and increase the risk of hernia recurrence. Practice proper lifting techniques‚ avoiding heavy objects or using proper lifting equipment to reduce strain on the abdomen. Stay active and engage in exercises that strengthen the core muscles to support the repaired area. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare team can help monitor your progress and address any concerns to prevent inguinal hernia recurrence.
Identifying Risk Factors for Inguinal Hernia
Understanding the risk factors for inguinal hernia can help individuals take preventive measures and seek early treatment if needed. Factors such as a family history of hernias‚ male gender‚ advanced age‚ chronic coughing‚ heavy lifting‚ obesity‚ and certain medical conditions like cystic fibrosis can increase the likelihood of developing an inguinal hernia. Being mindful of these risk factors and adopting healthy lifestyle practices‚ such as maintaining a healthy weight‚ incorporating core-strengthening exercises‚ and practicing proper lifting techniques‚ can help reduce the risk of inguinal hernia development. Regular health check-ups and proactive management of risk factors can play a crucial role in maintaining abdominal health and reducing the chances of hernia occurrence.