Understanding Hypersensitivity Type IV
Understanding Hypersensitivity Type IV is crucial for managing conditions like Dermatitis and Allergy. This type of immune response involves T cells, leading to Contact Dermatitis. It triggers an Inflammatory response and can be diagnosed through a Patch Test. Recognizing the Autoimmune aspects and Delayed Hypersensitivity is key in handling Type IV reactions.
Overview of Hypersensitivity Type IV
Hypersensitivity Type IV, also known as delayed-type hypersensitivity or cell-mediated hypersensitivity, is a vital component of the immune system’s response. Unlike immediate hypersensitivity reactions seen in Type I, Type IV reactions typically occur over 48-72 hours after exposure to the allergen.
This type of hypersensitivity is primarily mediated by T cells, specifically CD4 T helper cells and CD8 cytotoxic T cells. These T cells recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells, leading to the activation of an inflammatory response. Type IV reactions play a crucial role in defense against intracellular pathogens and in the development of autoimmune diseases.
One of the most common manifestations of Hypersensitivity Type IV is Contact Dermatitis, which includes allergic reactions to metals like nickel, skin irritants, and certain plant substances. These reactions can result in redness, itching, and even blisters on the skin.
Individuals with a predisposition to allergic conditions or autoimmune diseases may be more susceptible to Type IV hypersensitivity reactions. Understanding the mechanisms behind this type of hypersensitivity is essential for proper diagnosis and management of related conditions.
It is important to differentiate Type IV reactions from other types of hypersensitivity, as the treatment and management approaches vary. Prompt identification and targeted interventions can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications associated with delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
Overall, having a comprehensive understanding of Hypersensitivity Type IV is crucial for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating allergic and autoimmune conditions. By recognizing the immune mechanisms involved in Type IV reactions, proper steps can be taken to address the underlying causes and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these hypersensitivity responses.
Dermatitis and Allergy
Dermatitis and Allergy are common conditions associated with Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions. Contact Dermatitis, a form of Dermatitis primarily caused by exposure to allergens, irritants, or certain substances, is a classic manifestation of Type IV hypersensitivity.
When an individual comes into contact with a substance they are allergic to, the immune system, particularly T cells, mounts an inflammatory response. This response leads to symptoms such as redness, itching, swelling, or blistering of the skin. It is essential to identify the specific allergen or irritant triggering the allergic reaction to effectively manage Dermatitis and associated symptoms.
Allergic reactions in Dermatitis can be acute or chronic, depending on the intensity and duration of exposure to the allergen. Avoiding contact with the triggering substance is crucial in preventing flare-ups and minimizing discomfort for individuals with allergic Dermatitis.
Understanding the difference between allergic Dermatitis and other types of skin conditions is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare professionals may perform patch tests to determine the specific allergen causing the hypersensitivity reaction and develop a personalized management plan.
Individuals prone to allergies or autoimmune diseases should be particularly cautious when coming into contact with potential allergens or irritants to avoid triggering hypersensitivity reactions. Maintaining proper skincare routines and using hypoallergenic products can also help reduce the risk of developing allergic Dermatitis.
If you suspect that you may have allergic Dermatitis or are experiencing skin irritation that does not improve with over-the-counter treatments, it is advisable to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can conduct a thorough evaluation, including a patch test if necessary, to identify the underlying cause of your skin condition and recommend appropriate treatment options.
By being aware of the relationship between Dermatitis, Allergy, and Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions, you can take proactive steps to manage your skin health and minimize the impact of allergic symptoms. Working closely with a healthcare professional can help you better understand your condition and develop an effective care plan tailored to your specific needs.
Sensitivity and Immune Response
Sensitivity and Immune Response are key components of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions. Sensitivity refers to the body’s heightened reaction to specific allergens or irritants, triggering an immune response that leads to inflammation and tissue damage.
In Type IV hypersensitivity, the immune response is mediated by T cells, particularly CD4 T helper cells and CD8 cytotoxic T cells. These T cells recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells, activating an immune cascade that results in the recruitment of inflammatory cells to the site of exposure.
Individuals with an increased sensitivity to certain substances are more likely to develop Type IV hypersensitivity reactions upon contact. It is important to be aware of potential allergens or irritants in your environment and take precautions to avoid exposure if you have a history of hypersensitivity reactions.
Understanding the immune response involved in Type IV hypersensitivity can help individuals recognize early signs of allergic reactions and seek appropriate medical attention. Symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions may include redness, itching, swelling, or blistering of the skin, depending on the severity of the response.
If you suspect that you have heightened sensitivity to specific allergens or irritants, consider keeping a symptom diary to track your reactions and identify potential triggers. This information can be valuable when discussing your concerns with a healthcare provider and determining the best course of action to manage your hypersensitivity.
It is important to remember that each individual may have unique sensitivities and immune responses, making personalized care essential in managing hypersensitivity reactions. By working collaboratively with healthcare professionals, you can develop a comprehensive plan to address your sensitivities and minimize the impact of allergic symptoms on your daily life.
Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you experience persistent or severe symptoms of hypersensitivity. A healthcare provider can conduct tests, such as a patch test, to pinpoint the specific allergen causing your reaction and recommend tailored treatment options to help alleviate your symptoms;
By being proactive about understanding your sensitivity and immune response in relation to Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions, you can take control of your health and well-being. Empower yourself with knowledge about potential triggers and develop strategies to optimize your quality of life while effectively managing your hypersensitivity condition.
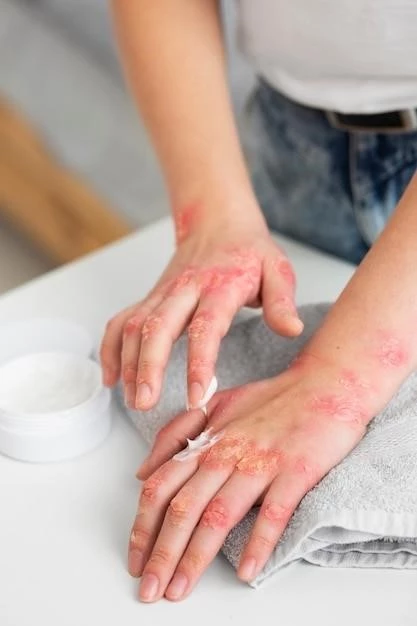
Types of Hypersensitivity Type IV
Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions encompass various types of immune responses that differ in their triggers and manifestations. The classic Type IV hypersensitivity reaction involves the activation of T cells and the release of cytokines, leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
One common type of Type IV hypersensitivity is Contact Dermatitis, which can be further classified into allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the immune system reacts to a specific allergen upon skin contact, while irritant contact dermatitis results from direct damage to the skin by irritants.
Another form of Type IV hypersensitivity is Granulomatous Hypersensitivity, characterized by the formation of granulomas in response to persistent antigen exposure. Granulomas are nodular inflammatory lesions that contain immune cells, typically observed in conditions like sarcoidosis and tuberculosis.
Drug-induced hypersensitivity reactions can also fall under Type IV hypersensitivity, where T cells recognize drugs or their metabolites as antigens, triggering an immune response. This type of reaction can manifest in various ways, including skin rashes, blistering, and systemic symptoms.
Occupational contact dermatitis is a specific subtype of hypersensitivity that occurs due to exposure to allergens or irritants in the workplace. Individuals in occupations like healthcare, cleaning, or food handling may be at higher risk of developing this form of hypersensitivity and should take precautions to minimize exposure.
Understanding the different types of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions is essential for accurate diagnosis and management. Healthcare professionals may utilize patch tests, blood tests, and other diagnostic tools to identify the specific type of hypersensitivity and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
If you suspect that you are experiencing symptoms of Type IV hypersensitivity, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for evaluation and guidance. Early detection and intervention can help alleviate discomfort, prevent complications, and improve your overall quality of life.
By familiarizing yourself with the various types of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions and their distinguishing features, you can better navigate your healthcare journey and collaborate effectively with your healthcare team to address your specific hypersensitivity condition.
Remember to communicate openly with your healthcare provider about your symptoms, triggers, and any concerns you may have regarding hypersensitivity reactions. Working together, you can develop a tailored approach to managing your condition and promoting long-term well-being.
Contact Dermatitis and T Cells
Contact Dermatitis, a common manifestation of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions, involves the intricate interplay between allergens, irritants, and the immune system’s T cells. When the skin comes into contact with a triggering substance, such as nickel, fragrances, or plants like poison ivy, it can lead to an allergic response mediated by T cells.
T cells play a central role in the pathogenesis of Contact Dermatitis by recognizing the allergen as a foreign invader and initiating an immune response. CD4 T helper cells release cytokines that promote inflammation٫ while CD8 cytotoxic T cells directly attack and destroy infected or damaged skin cells.
Individuals with a predisposition to allergic conditions or autoimmune diseases may have an increased risk of developing Contact Dermatitis due to heightened immune reactivity. It is crucial to identify the specific allergen or irritant responsible for the reaction through comprehensive testing, such as patch tests, to effectively manage Contact Dermatitis.
Managing Contact Dermatitis involves avoiding known triggers, practicing proper skincare routines, and using hypoallergenic products to reduce the risk of flare-ups. If you suspect that you have Contact Dermatitis or are experiencing persistent skin irritation, seek guidance from a healthcare professional for evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.
Education plays a vital role in preventing Contact Dermatitis and minimizing its impact on daily life. By understanding the connection between T cell-mediated immune responses and skin reactions, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their skin and avoid potential allergens or irritants.
If you have a history of Contact Dermatitis or other skin conditions, consider keeping a record of your symptoms and suspected triggers to share with your healthcare provider. This information can aid in accurately diagnosing the condition and tailoring a management plan that suits your unique needs.
Collaborating with a dermatologist or allergist can help you navigate the complexities of Contact Dermatitis and develop strategies to mitigate its effects. By working together, you can address underlying immune mechanisms, explore treatment options, and foster skin health and overall well-being.
Remember that early intervention and proper management of Contact Dermatitis are essential in preventing complications and improving skin comfort. By prioritizing skin care and staying informed about T cell-mediated immune responses, you can take control of your skin health and lead a more comfortable and confident life.
Inflammatory Response in Hypersensitivity Type IV
The inflammatory response in Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions is a crucial component of the immune system’s defense mechanism against perceived threats. When an individual is exposed to an allergen or irritant that triggers a Type IV hypersensitivity reaction, a cascade of inflammatory events is set in motion.
T cells, particularly CD4 T helper cells٫ play a pivotal role in orchestrating the inflammatory response in Type IV hypersensitivity. Upon recognition of the allergen٫ these T cells release pro-inflammatory cytokines٫ such as interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha٫ which stimulate the recruitment and activation of immune cells at the site of exposure.
The influx of immune cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, and eosinophils, contributes to the development of inflammation, leading to characteristic symptoms such as redness, swelling, and heat in the affected area. The inflammatory response is a vital part of the body’s attempt to eliminate the perceived threat and restore tissue homeostasis.
In some cases, however, an exaggerated or prolonged inflammatory response in Type IV hypersensitivity can lead to tissue damage and the exacerbation of symptoms. Chronic inflammation resulting from repeated exposure to allergens or irritants can contribute to the development of conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or inflammatory bowel disease.
Managing the inflammatory response in Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at reducing inflammation, alleviating symptoms, and preventing further tissue damage. Topical corticosteroids, emollients, and antihistamines may be prescribed to control inflammation and relieve discomfort associated with allergic reactions.
It is essential for individuals experiencing symptoms of Type IV hypersensitivity to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and treatment. Healthcare providers can assess the severity of the inflammatory response, identify triggers, and recommend personalized interventions to address the underlying immune mechanisms.
By understanding the inflammatory pathways involved in Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions, individuals can play an active role in managing their condition and minimizing the impact of inflammation on their health and well-being. Taking proactive steps to reduce exposure to known allergens and irritants can help prevent flare-ups and promote skin and immune health.
Working closely with healthcare professionals, including dermatologists and allergists, can provide valuable insights into navigating the inflammatory response in Type IV hypersensitivity. By following their guidance, staying informed about potential triggers, and advocating for your health, you can take control of your inflammatory response and optimize your quality of life.
Diagnosis through Patch Test
The patch test is a valuable diagnostic tool used to identify specific allergens or irritants responsible for triggering Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions, such as Contact Dermatitis. This non-invasive test involves applying small amounts of suspected allergens onto patches placed on the skin to observe the reaction over a period of time.
Before conducting a patch test, it is essential to provide your healthcare provider with a detailed medical history, including information about your symptoms, potential triggers, and previous exposures to allergens or irritants. This information will help guide the selection of allergens to be tested during the patch test.
During the patch test, allergens commonly associated with Contact Dermatitis, such as metals, fragrances, preservatives, and plant extracts, are applied to the skin and covered with adhesive patches. The patches are typically left in place for 48 hours to allow for a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to occur.
After the designated period, the patches are removed, and the healthcare provider assesses the skin for any signs of allergic reactions, such as redness, swelling, itching, or blistering. The location and severity of the skin response help determine which substances may be triggering the hypersensitivity reaction.
Interpreting the results of a patch test requires expertise and careful consideration of various factors, including the timing and appearance of skin reactions, the intensity of symptoms, and the correlation with known allergens. Healthcare providers use their clinical judgment to determine the significance of test results.
If the patch test reveals positive reactions to specific allergens, your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a comprehensive management plan aimed at reducing exposure to those triggers. This may involve lifestyle modifications, avoidance strategies, and the use of hypoallergenic products to minimize the risk of future allergic reactions.
In some cases, a patch test may produce inconclusive or false-negative results, necessitating further evaluation or additional testing to pinpoint the allergen causing the hypersensitivity reaction. It is essential to communicate openly with your healthcare provider throughout the diagnostic process to ensure accurate and effective management of your condition.
By undergoing a patch test and collaborating with your healthcare team, you can gain valuable insights into the specific allergens or irritants triggering your Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your skincare routine, lifestyle choices, and treatment options to optimize your overall well-being.
Remember that early detection and accurate diagnosis through a patch test are key steps in effectively managing Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions; By taking a proactive approach to identify and address allergens, you can minimize the impact of allergic symptoms, enhance skin health, and improve your quality of life.
Autoimmune Aspects of Hypersensitivity Type IV
Autoimmune aspects of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions involve the immune system mistakenly attacking the body’s own tissues in response to specific antigens. In some cases, what begins as a protective immune response against external threats can evolve into an autoimmune condition characterized by tissue damage and chronic inflammation.
The involvement of T cells in Type IV hypersensitivity plays a significant role in the development of autoimmune aspects. T cells can become activated in response to self-antigens, leading to an immune cascade that targets healthy tissues and initiates an autoimmune response.
Autoimmune manifestations of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions may present as diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease, among others. These conditions involve a dysregulated immune response that mistakenly recognizes self-proteins as foreign, resulting in tissue destruction.
Recognizing the autoimmune aspects of Type IV hypersensitivity is crucial in diagnosing and managing autoimmune diseases effectively. Healthcare providers may conduct specialized tests to evaluate immune function, identify autoantibodies, and assess the extent of tissue damage caused by the autoimmune response.
Treatment of autoimmune aspects of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions often focuses on suppressing the inappropriate immune response, reducing inflammation, and protecting target tissues from further damage. Immunosuppressive medications, corticosteroids, and biologic therapies may be prescribed to modulate the immune system and manage autoimmune symptoms.
Individuals with autoimmune aspects of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions should work closely with healthcare providers, including rheumatologists, immunologists, and gastroenterologists, to monitor their condition, adjust treatment strategies, and optimize their quality of life. Regular follow-up appointments and communication with the healthcare team are essential in managing autoimmune diseases effectively.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management, and adequate rest, can also support immune health and improve overall well-being for individuals with autoimmune aspects of Type IV hypersensitivity. It is essential to prioritize self-care and adhere to prescribed treatment regimens to minimize disease activity and promote long-term health.
By understanding the autoimmune aspects of Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions and taking proactive steps to manage autoimmune conditions, individuals can better navigate the complexities of their immune health. Empower yourself with knowledge, seek support from healthcare professionals, and advocate for comprehensive care to address autoimmune aspects effectively.
Remember that autoimmune diseases associated with Hypersensitivity Type IV reactions require a multidisciplinary approach to treatment and ongoing support. By engaging in open communication with your healthcare team and staying informed about autoimmune aspects, you can take control of your condition and work towards achieving optimal health outcomes.
Delayed Hypersensitivity in Type IV Reactions
Delayed hypersensitivity is a hallmark feature of Type IV reactions, distinguishing them from immediate hypersensitivity responses seen in other hypersensitivity types. In Type IV reactions, the immune response unfolds gradually over 48-72 hours after exposure to the triggering antigen.
The delayed nature of hypersensitivity in Type IV reactions is attributed to the involvement of T cells, particularly CD4 T helper cells and CD8 cytotoxic T cells. These T cells recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells and initiate a cascade of immune events that lead to the delayed onset of symptoms.
Common conditions associated with delayed hypersensitivity in Type IV reactions include Contact Dermatitis, Granulomatous Hypersensitivity, and certain drug-induced hypersensitivity reactions. These conditions provoke an inflammatory response that manifests over time, contributing to redness, swelling, blistering, and other skin or systemic symptoms.
Diagnosing delayed hypersensitivity in Type IV reactions often requires a comprehensive evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and possibly specialized tests like patch tests or T cell assays. Identifying the specific antigen triggering the immune response is essential for effective management.
Managing delayed hypersensitivity in Type IV reactions involves strategies aimed at minimizing exposure to allergens or irritants, reducing inflammation, and alleviating symptoms associated with the immune response. Healthcare providers may recommend topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, or avoidance measures to control hypersensitivity reactions.
Individuals experiencing delayed hypersensitivity in Type IV reactions should be proactive in monitoring their symptoms, tracking potential triggers, and seeking timely medical advice when necessary. Open communication with healthcare providers is crucial in identifying the underlying cause of hypersensitivity and implementing tailored treatment plans.
Preventing delayed hypersensitivity reactions in Type IV responses requires a proactive approach to recognizing and avoiding known allergens or irritants. Practicing good skin hygiene, using protective measures in occupational settings, and selecting hypoallergenic products can help reduce the risk of hypersensitivity flare-ups.
Educating yourself about the delayed nature of hypersensitivity in Type IV reactions and staying informed about potential triggers empowers you to take control of your immune health. By adhering to treatment recommendations, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and maintaining regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, you can manage delayed hypersensitivity effectively.
Remember that delayed hypersensitivity in Type IV reactions may vary in severity and presentation among individuals. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and personalized management are key in addressing delayed hypersensitivity effectively and promoting overall well-being. Stay vigilant, prioritize self-care, and collaborate with your healthcare team to achieve optimal outcomes for your hypersensitivity condition.
