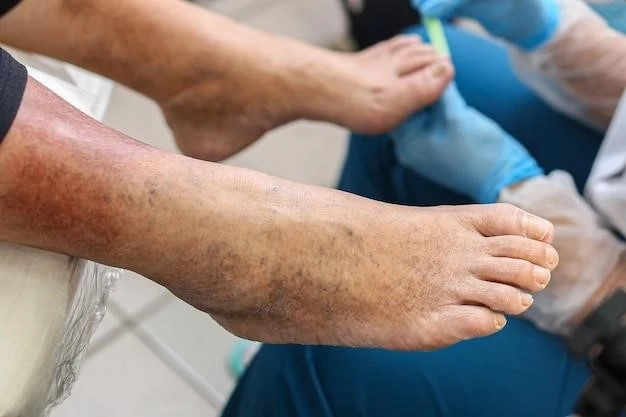
Disease ౼ Hyperkeratosis Palmoplantar with Palmar Crease Hyperkeratosis
Overview of Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is a dermatological condition characterized by the abnormal thickening of the outer layer of the skin‚ known as the epidermis. This condition can manifest in various forms‚ including palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and palmar crease hyperkeratosis. In hyperkeratosis‚ there is an excessive production of keratin‚ a protein that provides structure to the skin‚ leading to the formation of thickened areas.
Hyperkeratosis can affect different parts of the body‚ but palmoplantar and palmar crease hyperkeratosis specifically target the palms of the hands and soles of the feet‚ as well as the creases on the palms. These areas may develop hardened‚ hyperkeratotic lesions that can be accompanied by other symptoms such as pain‚ cracking‚ and redness.
The condition can arise due to various factors‚ including genetic predisposition‚ environmental influences‚ and underlying health conditions. Hyperkeratosis can impact the quality of life of individuals‚ affecting their mobility and causing discomfort.
Understanding hyperkeratosis is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. Treatment options for hyperkeratosis aim to alleviate symptoms‚ reduce thickening of the skin‚ and improve the overall health of the affected areas. Research into this condition continues to explore new avenues for more effective treatments and better management strategies for patients.
Understanding Palmoplantar Hyperkeratosis
Palmoplantar hyperkeratosis is a type of hyperkeratosis that primarily affects the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. This condition is characterized by the abnormal thickening of the skin in these regions‚ leading to the development of hyperkeratotic lesions.
The thickened skin in palmoplantar hyperkeratosis can present as hardened areas that may be yellowish or brownish in color. These areas can become rough‚ dry‚ and prone to cracking‚ which can cause discomfort and pain‚ especially when walking or using the hands for tasks.
Individuals with palmoplantar hyperkeratosis may experience a progressive worsening of symptoms over time‚ impacting their daily activities and quality of life. The condition can be challenging to manage‚ requiring a multidisciplinary approach involving dermatologists‚ podiatrists‚ and other healthcare professionals.
Diagnostics for palmoplantar hyperkeratosis may involve clinical evaluation‚ skin biopsies‚ and genetic testing to determine underlying causes. Treatment strategies often focus on softening the thickened skin‚ reducing pain and inflammation‚ and preventing complications such as infections.
Managing palmoplantar hyperkeratosis may include regular moisturization‚ keratolytic agents to promote skin shedding‚ and custom orthotic devices to reduce pressure on affected areas. In severe cases‚ procedures such as cryotherapy or laser therapy may be considered to improve symptoms.
Palmar Crease Hyperkeratosis
Palmar crease hyperkeratosis is a specific form of hyperkeratosis that targets the creases on the palms of the hands. This condition is characterized by the excessive thickening of the skin in these areas‚ leading to the formation of hyperkeratotic lesions within the creases.
Individuals with palmar crease hyperkeratosis may experience symptoms such as itchiness‚ redness‚ and a feeling of tightness in the affected skin folds. The thickened skin in the palmar creases can be unsightly and uncomfortable‚ impacting hand function and dexterity.
Diagnosing palmar crease hyperkeratosis typically involves a physical examination by a dermatologist‚ who may assess the appearance and texture of the skin in the creases. In some cases‚ a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential conditions.
Treatment options for palmar crease hyperkeratosis aim to reduce the thickening of the skin‚ alleviate symptoms‚ and improve the overall appearance of the palms. This may involve the use of topical medications‚ moisturizers‚ and keratolytic agents to soften the skin and promote shedding of excess keratin.
Managing palmar crease hyperkeratosis may also include lifestyle modifications such as avoiding repetitive friction on the palms and keeping the hands well-moisturized. In severe cases‚ dermatological procedures like chemical peels or corticosteroid injections may be considered to address stubborn lesions and improve skin texture.
Pathophysiology of the Disorder
The pathophysiology of hyperkeratosis‚ including palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and palmar crease hyperkeratosis‚ involves alterations in the normal processes of skin cell turnover and keratinization. In individuals with these conditions‚ there is a disruption in the balance between keratin production and shedding‚ leading to the accumulation of excess keratin in the epidermal layer of the skin.
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of hyperkeratosis‚ with mutations in genes responsible for skin structure and function contributing to the abnormal thickening of the skin. These genetic alterations can affect the regulation of keratinocytes‚ the predominant cell type in the epidermis‚ leading to the proliferation of these cells and the formation of hyperkeratotic lesions.
In palmoplantar hyperkeratosis‚ the excessive keratin production mainly affects the palms and soles due to the unique characteristics of the skin in these areas‚ which have a thicker epidermal layer compared to other parts of the body. The constant pressure and friction experienced by the palms and soles during daily activities can exacerbate the thickening of the skin.
Palmar crease hyperkeratosis‚ on the other hand‚ specifically targets the skin within the creases of the palms. The folds and creases in this area provide an ideal environment for the accumulation of excess keratin‚ leading to the development of hyperkeratotic plaques within the creases.

Understanding the underlying pathophysiology of palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and palmar crease hyperkeratosis is essential for developing targeted treatment approaches that address the root cause of the disorder and help restore the normal function and appearance of the affected skin.
Treatment Options for Hyperkeratosis
Treating hyperkeratosis‚ including palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and palmar crease hyperkeratosis‚ involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications aimed at managing symptoms‚ reducing skin thickening‚ and improving overall skin health.
Topical treatments are commonly used to soften the hyperkeratotic lesions and promote the shedding of excess keratin. These may include keratolytic agents such as salicylic acid and urea-based creams‚ which help break down the thickened skin and encourage exfoliation.
Moisturizers are essential in maintaining skin hydration and preventing further dryness and cracking. Emollients and humectants can be applied regularly to the affected areas to keep the skin soft and supple‚ reducing discomfort and improving the appearance of the skin.
In some cases‚ occlusive dressings or custom-made orthotic devices may be recommended to protect the skin and reduce friction‚ especially in palmoplantar hyperkeratosis where pressure on the palms and soles can worsen symptoms.
For more severe or persistent cases of hyperkeratosis‚ dermatological procedures such as cryotherapy‚ laser therapy‚ or chemical peels may be considered to target stubborn lesions and improve skin texture. These treatments are typically performed under the guidance of a dermatologist or specialized healthcare provider.
It is essential for individuals with hyperkeratosis to follow a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to their specific needs. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals can help track progress‚ adjust treatment protocols as needed‚ and address any new symptoms or concerns that may arise.
By combining targeted treatments‚ proper skincare practices‚ and ongoing management‚ individuals with hyperkeratosis can effectively control their symptoms‚ enhance the health of their skin‚ and ultimately improve their quality of life.
Impact on Quality of Life
Hyperkeratosis‚ including palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and palmar crease hyperkeratosis‚ can have a significant impact on the quality of life of affected individuals. The physical symptoms and cosmetic changes associated with these conditions can lead to emotional distress‚ discomfort‚ and limitations in daily activities.
Individuals with hyperkeratosis may experience pain‚ itching‚ and tenderness in the thickened areas of the skin. The presence of hyperkeratotic lesions on the palms and soles can make it challenging to walk‚ grasp objects‚ or perform tasks that involve manual dexterity.
The visible signs of hyperkeratosis‚ such as hardened skin‚ rough patches‚ and discoloration‚ can also affect self-esteem and body image. These changes may lead to feelings of self-consciousness‚ embarrassment‚ or social withdrawal‚ impacting interpersonal relationships and overall emotional well-being.
Furthermore‚ the chronic nature of hyperkeratosis and the need for ongoing treatment and management can be emotionally taxing for individuals‚ adding to the burden of living with a dermatological condition. The financial costs associated with medical appointments‚ medications‚ and skincare products may also pose challenges for some patients.
Addressing the impact of hyperkeratosis on quality of life requires a holistic approach that considers both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition. Healthcare providers‚ including dermatologists‚ psychologists‚ and support groups‚ can offer guidance‚ support‚ and resources to help individuals cope with the challenges posed by hyperkeratosis.
By raising awareness about the impact of hyperkeratosis‚ promoting self-care practices‚ and fostering a supportive environment‚ it is possible to empower individuals living with these conditions to manage their symptoms‚ seek appropriate treatment‚ and enhance their overall well-being and quality of life;
Research and Future Perspectives
Ongoing research into hyperkeratosis‚ including palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and palmar crease hyperkeratosis‚ is focused on advancing our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of these conditions and exploring novel treatment approaches to improve patient outcomes.
One area of research involves investigating the genetic factors that contribute to the development of hyperkeratosis. By identifying specific gene mutations associated with these conditions‚ researchers aim to develop targeted therapies that address the root cause of the disorder and provide more effective treatment options.
Furthermore‚ studies are exploring the role of environmental triggers‚ immune system dysregulation‚ and inflammatory processes in the pathogenesis of hyperkeratosis. By unraveling the complex interplay of these factors‚ researchers hope to uncover new targets for therapeutic intervention and disease management.
Advancements in dermatological research are also driving the development of innovative treatment modalities for hyperkeratosis. Novel drug formulations‚ biologic therapies‚ and gene-based therapies are being investigated to provide more tailored and personalized approaches to treating hyperkeratotic skin conditions.
In addition to pharmacological interventions‚ research is exploring the use of advanced technologies such as laser therapy‚ photodynamic therapy‚ and microsurgical techniques for addressing hyperkeratosis. These approaches offer precise and targeted treatment options that may lead to improved outcomes and reduced side effects for patients.
Future perspectives in the field of hyperkeratosis research aim to translate scientific discoveries into clinical practice‚ with a focus on enhancing the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions. Collaborative efforts between researchers‚ healthcare providers‚ and patient advocacy groups will be instrumental in advancing knowledge‚ promoting innovation‚ and ultimately transforming the landscape of hyperkeratosis management.