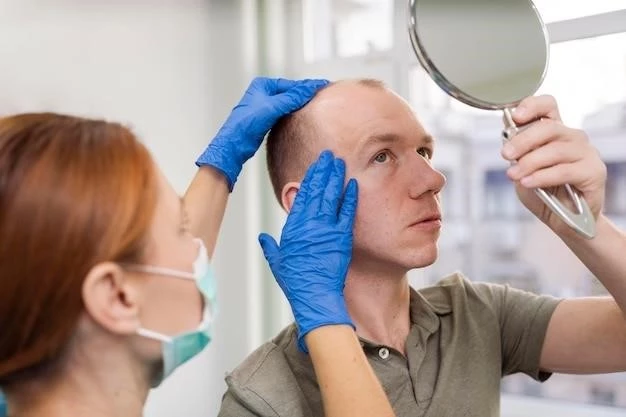
Understanding Alopecia⁚ Causes and Treatments
Causes of Alopecia
Alopecia can be caused by various factors‚ including genetics‚ hormonal imbalances‚ medical conditions such as autoimmune diseases‚ and stress. Other possible causes include certain medications‚ nutrient deficiencies‚ and underlying health issues affecting the hair follicles. Understanding the specific cause of alopecia is crucial in determining the most effective treatment options for each individual.
Types of Alopecia
There are several types of alopecia‚ including Androgenetic Alopecia (male/female pattern baldness)‚ Alopecia Areata (autoimmune-related hair loss)‚ Telogen Effluvium (temporary hair shedding)‚ and Traction Alopecia (hair loss due to pulling or tension). Each type presents with distinct characteristics and may require different treatment approaches based on the underlying cause. Understanding the specific type of alopecia is essential for developing a targeted treatment plan;
Treatment Options
Treatment for alopecia may include medications such as minoxidil or finasteride‚ corticosteroid injections‚ platelet-rich plasma therapy‚ and low-level laser therapy. In severe cases‚ surgical interventions like hair transplant surgery may be considered. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider specializing in hair loss to determine the most suitable treatment option based on the type and severity of alopecia.
Hypogonadism in Men and Women⁚ Symptoms and Management
Symptoms of Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism in both men and women can present with symptoms such as decreased libido‚ infertility‚ fatigue‚ muscle weakness‚ and mood changes. Men may also experience decreased beard and body hair growth‚ while women may have irregular or absent menstrual periods. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate management of hypogonadism.
Hypogonadism in Men vs. Women
Hypogonadism manifests differently in men and women. In men‚ symptoms may include erectile dysfunction‚ decreased muscle mass‚ and decreased facial hair growth. In women‚ symptoms can include hot flashes‚ vaginal dryness‚ and decreased breast size. The treatment approach may vary based on gender-specific symptoms and hormone levels. Management strategies focus on restoring hormonal balance to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Management Strategies
The management of hypogonadism involves hormone replacement therapy to restore testosterone or estrogen levels. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise‚ a balanced diet‚ and stress management techniques can also help. For severe cases‚ surgical interventions like testicular or ovarian implants may be considered. Close monitoring by healthcare providers is essential to assess treatment effectiveness and adjust therapy as needed to optimize outcomes for individuals with hypogonadism.
Exploring Extrapyramidal Disorders⁚ Types and Symptoms
Types of Extrapyramidal Disorders
Extrapyramidal disorders encompass conditions such as Parkinson’s disease‚ dystonia‚ and tardive dyskinesia. Parkinson’s disease is characterized by tremors‚ bradykinesia‚ and muscle rigidity. Dystonia involves involuntary muscle contractions leading to repetitive movements or abnormal postures. Tardive dyskinesia presents with involuntary facial movements and jerky motions. Each disorder has unique characteristics and may require specific treatment approaches for symptom management and quality of life improvement.
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of extrapyramidal disorders include tremors‚ muscle stiffness‚ slow movement‚ impaired posture‚ and involuntary movements. Patients may also experience difficulties with coordination‚ speech‚ and balance. These symptoms can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life. Early recognition and diagnosis of these common symptoms are essential for timely intervention and appropriate management of extrapyramidal disorders to help patients maintain optimal health and well-being.
Diagnosis and Prognosis
Diagnosing extrapyramidal disorders involves a comprehensive evaluation‚ including physical examination‚ neurological tests‚ and imaging studies. Prognosis varies depending on the specific disorder‚ its severity‚ and the individual’s response to treatment. Early diagnosis and personalized management play a crucial role in improving outcomes and quality of life. Close monitoring‚ regular follow-ups‚ and collaboration with healthcare providers are essential in managing extrapyramidal disorders effectively and optimizing long-term prognosis.

Hair Loss Solutions for Alopecia Patients
Non-Surgical Solutions
Non-surgical solutions for alopecia may include topical minoxidil to promote hair growth‚ corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation‚ and light therapy to stimulate hair follicles. Additionally‚ dietary supplements like biotin and iron may support hair health. These approaches aim to slow down hair loss‚ promote regrowth‚ and improve the overall condition of the scalp. Consultation with a dermatologist or trichologist can help determine the most suitable non-surgical solution based on individual needs.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions for alopecia include hair transplant procedures such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE). These surgeries involve moving hair follicles from donor sites to balding areas to restore natural hair growth. Scalp reduction surgery and scalp flaps are also options for specific cases. Surgical interventions aim to provide long-lasting results and improve the aesthetic appearance of individuals experiencing hair loss. Consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon is essential to discuss the most appropriate surgical intervention based on individual needs and expectations.
Hormonal Imbalance⁚ Effects of Hypogonadism on the Body
Impact on Reproductive Health
Hypogonadism can significantly impact reproductive health by causing infertility‚ reduced sex drive‚ and menstrual irregularities. In men‚ low testosterone levels can lead to erectile dysfunction and decreased sperm production. In women‚ hormone imbalances may result in disrupted ovulation and fertility issues. Managing hypogonadism through hormone replacement therapy can help restore reproductive function and improve fertility outcomes. Consulting with a healthcare provider specializing in reproductive endocrinology is crucial for addressing these concerns and optimizing reproductive health.
Metabolic Consequences
Hypogonadism can lead to metabolic consequences such as increased body fat‚ reduced muscle mass‚ and insulin resistance. Low testosterone levels in men and estrogen fluctuations in women can impact metabolism‚ potentially increasing the risk of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Managing hypogonadism through hormone replacement therapy and lifestyle modifications like regular exercise and a balanced diet can help mitigate these metabolic consequences. Collaborating with healthcare providers specializing in endocrinology is crucial for addressing metabolic concerns and promoting overall health.
Psychological Impacts
Hypogonadism can have profound psychological impacts‚ including mood changes‚ decreased self-esteem‚ and anxiety or depression. The hormonal imbalances associated with hypogonadism can affect emotional well-being and overall quality of life. Addressing these psychological impacts may involve counseling‚ support groups‚ and therapy in addition to medical management. Psychological support is essential in helping individuals cope with the emotional challenges that arise from hypogonadism‚ promoting mental health‚ and enhancing overall resilience.