Disease ⏤ Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation
I. Introduction
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the complex interplay between Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation. This article delves into the definitions, causes, symptoms, and implications of these conditions. Understanding the relationship between these two distinct yet interconnected health challenges is crucial in providing comprehensive care to individuals affected by these conditions. Join us on this enlightening journey through the intricacies of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation.
II. Understanding Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis
In this section, we delve into the intricacies of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis, exploring its definition and diverse causes. We also shed light on the range of symptoms associated with this condition and the diagnostic approaches employed in identifying it. Understanding these aspects is crucial in the comprehensive management and treatment of individuals affected by Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis.
A. Definition and Causes
Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis is a condition characterized by the inability of the vocal cords to open fully during inhalation, impacting respiratory function and causing speech difficulties. It can result from various factors, including neurological disorders, trauma, or underlying medical conditions such as neurodegenerative diseases. Understanding the specific causes of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis is essential in guiding treatment strategies and rehabilitation efforts to support individuals affected by this condition.
B. Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis may include stridor (noisy breathing), breathy voice, and respiratory distress. Diagnosis often involves a thorough clinical evaluation, laryngeal endoscopy, and imaging studies to assess vocal cord movement. Physicians may also conduct specialized tests such as electromyography to evaluate nerve function. Early and accurate diagnosis of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis is vital in initiating appropriate treatment interventions and enabling individuals to manage their respiratory and communication challenges effectively.
III. Exploring Mental Retardation
This section provides an in-depth exploration of Mental Retardation, encompassing an overview of the condition and the various types it encompasses. Mental Retardation is characterized by significant limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behaviors. Understanding the nuances of Mental Retardation is essential in developing individualized care plans and support systems for individuals impacted by this condition. Join us as we delve into the complexities of Mental Retardation and its implications for affected individuals.
A. Overview of Mental Retardation
Mental Retardation, also known as intellectual disability, is a condition characterized by limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behaviors. These limitations can manifest in areas such as communication, self-care, and social skills. The severity of Mental Retardation can vary widely, affecting individuals in different ways and requiring personalized support and interventions. Understanding the broad overview of Mental Retardation is crucial in providing holistic care and promoting the well-being of individuals living with this condition.
B. Types of Mental Retardation
Mental Retardation encompasses various types, including mild, moderate, severe, and profound intellectual disabilities. Each type is characterized by differing degrees of impairment in cognitive functioning, communication skills, and daily living activities. Individuals with mild mental retardation may require minimal support, while those with profound-level disability may need extensive assistance in all aspects of life. Recognizing the different types of Mental Retardation is essential in tailoring interventions and services to meet the specific needs of individuals and optimize their quality of life.
IV. The Relation Between Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation
Understanding the correlation between Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation is crucial in addressing the complex healthcare needs of individuals affected by both conditions. While Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis primarily affects respiratory and vocal function, Mental Retardation poses challenges in cognitive, social, and adaptive functioning. The combined impact of these conditions highlights the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to care, ensuring comprehensive support for individuals dealing with the overlapping effects of both Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation.
V. Impact on Communication
The combination of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation can lead to significant communication difficulties for affected individuals. The speech impairments associated with Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis, combined with the cognitive challenges of Mental Retardation, can result in limited verbal expression and understanding. Addressing these communication barriers requires a comprehensive approach that integrates speech therapy, adaptive communication strategies, and supportive interventions to enhance the quality of communication and promote effective interaction for individuals facing these complex conditions.
A. Communication Difficulties
Individuals with the co-occurrence of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation often face profound challenges in communication. The combination of impaired vocal function from Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and cognitive deficits from Mental Retardation can result in difficulties expressing needs, emotions, and thoughts effectively. Communication difficulties may necessitate the use of augmentative and alternative communication methods to support meaningful interaction and ensure that individuals can effectively convey their messages and engage in social interactions.
B. Speech Therapy for Patients
Speech therapy plays a crucial role in addressing the communication challenges faced by individuals with Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation. Through tailored intervention programs, speech therapists work to improve vocal function, enhance language skills, and facilitate effective communication strategies. Speech therapy sessions may focus on strengthening vocal muscles, developing alternative communication methods, and improving articulation. The personalized approach of speech therapy aims to optimize communication abilities, empower individuals to express themselves confidently, and enhance their overall quality of life despite the complex challenges presented by these conditions.
VI. Effects on Respiratory Function
The combined presence of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation can significantly impact respiratory function in affected individuals. Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis hinders the vocal cords’ ability to open fully during inhalation, leading to breathing difficulties and potential respiratory distress. Coupled with the cognitive and physical challenges of Mental Retardation, managing respiratory function becomes crucial in ensuring adequate oxygenation and addressing potential complications. Healthcare providers must closely monitor and address respiratory issues in individuals facing the complex interplay of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation to optimize their respiratory health and overall well-being.
VII. Developmental Delays and Cognitive Disabilities
The coexistence of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation can lead to developmental delays and cognitive disabilities. Individuals facing these conditions may experience challenges in achieving developmental milestones, motor skills acquisition, and cognitive processing. The combination of these factors can impact educational attainment, social interaction, and overall independence. Understanding the unique developmental and cognitive needs of individuals with Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation is crucial in implementing interventions that support their growth, learning, and comprehensive development.
A. Motor Skill Impairments
Individuals diagnosed with the combination of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation may experience motor skill impairments due to the impact of both conditions on neurological functions. Motor skill impairments can affect activities such as coordination, fine motor movements, and balance, influencing an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks independently. Addressing these motor skill challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach that may involve occupational therapy, physical therapy, and adaptive strategies to enhance motor function and promote greater autonomy in daily living activities despite the complexities presented by Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation.
B. Language Development Challenges
Individuals affected by both Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation may encounter significant challenges in language development. The combination of impaired vocal function and cognitive deficits can impact expressive and receptive language skills, hindering the ability to communicate effectively. Language development challenges may encompass difficulties in vocabulary acquisition, grammar comprehension, and overall language fluency. Implementing tailored interventions, including speech therapy, language enrichment activities, and assistive communication devices, is crucial in supporting individuals to overcome language barriers and enhance their communication abilities despite the complexities posed by these concurrent conditions.
VIII. Vocal Cord Dysfunction in Patients
Vocal cord dysfunction in individuals with the co-occurrence of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation can significantly impact vocal function and communication abilities. The impaired movement of the vocal cords due to Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis, coupled with cognitive challenges from Mental Retardation, can lead to vocal cord inefficiency and difficulties in producing clear speech sounds. Managing vocal cord dysfunction requires a comprehensive approach that may include speech therapy, vocal exercises, and assistive technologies to optimize vocal quality and promote effective communication for individuals facing the complex interaction of these conditions.
IX. Genetic Mutations and Neurological Impairments
Genetic mutations and neurological impairments can play a significant role in the manifestation of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation. Certain genetic mutations may predispose individuals to neurological conditions that affect vocal cord function and cognitive abilities simultaneously. The interplay between genetic factors and neurological impairments underscores the complexity of these conditions and highlights the importance of genetic testing and neurologic assessments in diagnosing and managing individuals with Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation. Understanding the genetic and neurologic components is vital in providing targeted interventions and personalized care for affected individuals.
X. Rehabilitation and Medical Interventions
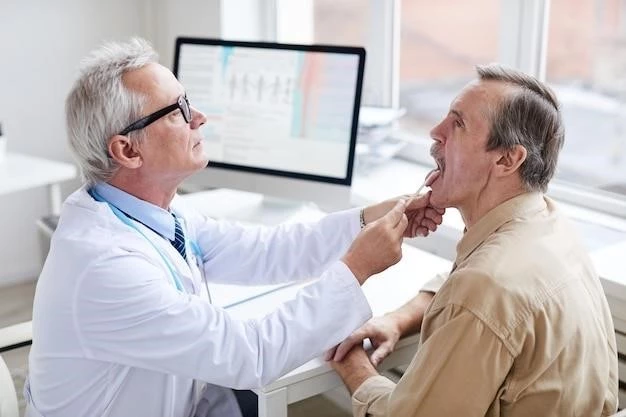
Rehabilitation and medical interventions for individuals with Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation encompass a multifaceted approach designed to address the complex healthcare needs arising from these conditions. Rehabilitation may include speech therapy to improve communication skills, physical therapy to enhance motor function, and occupational therapy to promote independent living abilities. Medical interventions may involve the management of respiratory issues, genetic counseling, and neurologic assessments to guide treatment decisions. The collaborative efforts of healthcare professionals in rehabilitation and medical fields are essential in providing holistic care and supporting the well-being of individuals facing the challenges associated with Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation.
A. Treatment Plans
Individuals with Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation benefit from comprehensive treatment plans tailored to address their unique needs. Treatment may include a combination of speech therapy to improve communication, respiratory support to manage breathing difficulties, and educational interventions to promote cognitive development. Physical and occupational therapy may be incorporated to enhance motor skills and foster independence. These individualized treatment plans aim to optimize functional abilities, enhance quality of life, and support individuals in overcoming the challenges posed by the coexistence of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation.
B. Supportive Therapies
Supportive therapies play a crucial role in enhancing the overall well-being of individuals managing Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation. These therapies may encompass psychological support to address emotional needs, social skills training to promote interaction, and nutritional counseling to maintain optimal health. Additionally, music therapy, art therapy, and recreational activities can contribute to holistic care by fostering creativity and emotional expression. The integration of supportive therapies into the treatment plan aims to provide comprehensive support, improve quality of life, and promote overall wellness for individuals navigating the complexities of these co-occurring conditions.
XI. Role of Speech Therapy in Managing the Conditions
Speech therapy plays a pivotal role in managing the interconnected challenges of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation. Speech therapists employ specialized techniques to improve vocal function, enhance language skills, and address communication difficulties. By tailoring interventions to the unique needs of each individual, speech therapy can empower patients to express themselves effectively, foster social connections, and navigate the complexities of these conditions. The collaborative efforts between patients, caregivers, and speech therapists are instrumental in maximizing communication abilities, promoting independence, and supporting individuals in their journey towards improved quality of life.
XII. Long-term Prognosis and Quality of Life
The long-term prognosis and quality of life for individuals with Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation depend on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, access to interventions, and ongoing support systems. With early diagnosis and comprehensive management strategies, individuals can experience improvements in communication, motor skills, and overall well-being. Long-term prognosis may vary, but with multidisciplinary care, personalized treatment plans, and consistent support, individuals can enhance their quality of life, achieve greater independence, and navigate the challenges posed by these conditions with resilience and strength.
XIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to care. Addressing communication difficulties, respiratory challenges, developmental delays, and cognitive disabilities requires tailored interventions such as speech therapy, supportive therapies, and medical treatments. By recognizing the impact of genetic mutations and neurological impairments, healthcare professionals can provide personalized care to enhance the overall quality of life for individuals facing these complex conditions. Through collaborative efforts and holistic support, individuals can navigate the challenges of Laryngeal Abductor Paralysis and Mental Retardation with compassion, dignity, and optimal care.
