Introduction to Disease⁚ Myxoma-Spotty Pigmentation-Endocrine Overactivity
The introduction to the disease encompasses the complex of myxomas‚ spotty pigmentation‚ and endocrine overactivity‚ also known as Carney complex. It was first described in 1985‚ with common manifestations being cardiac‚ cutaneous‚ and mammary myxomas‚ spotty skin pigmentation‚ and various endocrine tumors or overactivity.
Definition and Background
The Carney complex (CNC) is an autosomal dominant inherited syndrome characterized by various manifestations such as myxomas‚ spotty skin pigmentation‚ and endocrine tumors. Initially described in the mid-1980s‚ this syndrome has gained recognition for its distinct combination of cardiac‚ cutaneous‚ and endocrine abnormalities.
Carney Complex⁚ The Syndrome
The Carney complex‚ also known as CNC‚ is an autosomal dominant inherited syndrome featuring myxomas‚ spotty pigmentation‚ and endocrine abnormalities.
Characteristics and Components
The Carney complex is characterized by a unique combination of cardiac myxomas‚ spotty skin pigmentation‚ and various endocrine abnormalities‚ presenting a challenging clinical scenario for affected individuals.
Inheritance and Prevalence
The Carney complex‚ an autosomal dominant syndrome‚ has been reported in more than 500 patients worldwide since its description in 1985. The prevalence is significant‚ with approximately 70% of patients having a positive family history of the condition.
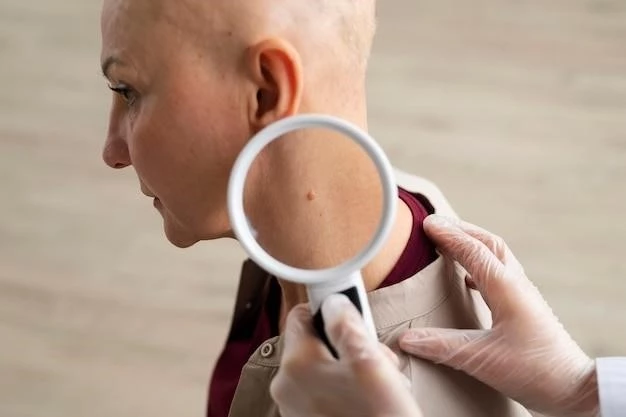
Clinical Manifestations of the Disease
The clinical manifestations of the Carney complex include cardiac myxomas‚ spotty skin pigmentation‚ and endocrine abnormalities.
Cardiac Myxomas
Cardiac myxomas are a hallmark of the Carney complex‚ presenting as tumors in the heart chambers. These myxomas can cause various cardiac complications and require surgical intervention for management.
Spotty Skin Pigmentation
Spotty skin pigmentation is a characteristic feature of Carney complex‚ presenting as pigmented spots on the skin that can be associated with various mucocutaneous manifestations. These pigmented lesions are often one of the early signs of the syndrome‚ aiding in the diagnosis and management of affected individuals.
Endocrine Overactivity
Endocrine overactivity in Carney complex includes conditions such as Cushing syndrome‚ sexual precocity‚ and acromegaly‚ adding to the complexity and management challenges of the syndrome.

Diagnosis and Screening Methods
Diagnosis of the Carney complex involves imaging for cardiac myxomas‚ dermatological examination for spotty pigmentation‚ and hormonal tests for endocrine overactivity.
Imaging Findings
Imaging is essential for diagnosing the Carney complex‚ especially to detect cardiac myxomas through techniques like echocardiography and MRI. Additionally‚ imaging aids in assessing the extent of spotty skin pigmentation and associated endocrine abnormalities.
Clinical and Pathological Correlation
In patients with the Carney complex‚ clinical findings such as cardiac myxomas‚ spotty skin pigmentation‚ and endocrine overactivity often correlate with pathological features observed in imaging studies and biopsies‚ aiding in the definitive diagnosis and treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Myxoma-Spotty Pigmentation-Endocrine Overactivity
Treatment for the Carney complex involves surgical interventions to address cardiac myxomas‚ medications for endocrine abnormalities‚ and management of spotty pigmentation.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions play a crucial role in managing the Carney complex‚ especially for the removal of cardiac myxomas to prevent associated complications and improve patient outcomes.
Medication and Hormonal Therapy
Medication and hormonal therapy are essential components of the treatment plan for Carney complex patients with endocrine overactivity‚ such as Cushing syndrome‚ sexual precocity‚ and acromegaly‚ aiming to manage hormone levels and associated symptoms effectively.
Prognosis and Complications Associated with the Condition
Understanding the prognosis of Carney complex is vital‚ as it involves cardiac risks from myxomas and long-term effects on the endocrine system from overactivity.
Cardiac Risks
Patients with the Carney complex face significant cardiac risks due to the presence of myxomas in the heart chambers‚ which can lead to complications such as obstructing blood flow and require timely management to prevent adverse outcomes.
Long-Term Effects on Endocrine System
The long-term effects on the endocrine system in Carney complex involve the management of conditions such as Cushing syndrome‚ sexual precocity‚ and acromegaly to minimize complications and maintain hormonal balance.
Research and Advancements in Understanding the Disease
Research on the Carney complex includes genetic studies to better understand the syndrome’s hereditary aspects and ongoing clinical trials to improve treatment strategies for affected individuals.
Genetic Studies and Discoveries
Genetic studies in the Carney complex aim to unravel the hereditary aspects of the syndrome‚ focusing on identifying genetic mutations associated with myxomas‚ spotty pigmentation‚ and endocrine overactivity‚ providing valuable insight into the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
Current Clinical Trials and Future Directions
Ongoing clinical trials aim to advance the understanding and management of Carney complex‚ with future directions focusing on personalized therapies and genetic-based treatments to address the complex’s diverse manifestations.
Conclusion⁚ Management and Care for Individuals with Myxoma-Spotty Pigmentation-Endocrine Overactivity
In conclusion‚ effective management of the Carney complex involves a multidisciplinary approach focusing on surgical interventions for myxomas‚ hormonal therapy for endocrine abnormalities‚ and careful monitoring of spotty skin pigmentation. With ongoing research and clinical advancements‚ personalized care plans tailored to each individual’s needs are crucial for improving outcomes and quality of life.
