Conductive hearing loss can result from earwax buildup, fluid in the ear, or abnormal bone growth in the middle ear.
Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss
There are several causes of conductive hearing loss, such as ear infections, abnormal bone growth in the middle ear, perforated eardrum, fluid in the middle ear, earwax buildup, and malformation of the outer ear. These conditions can disrupt the normal transmission of sound to the inner ear, leading to hearing loss. Identifying the specific cause is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach for each individual.
Common symptoms include muffled or faint sounds, difficulty hearing in noisy environments, ear pain or pressure, and recurrent ear infections.
Symptoms of Conductive Hearing Loss
Individuals with conductive hearing loss may experience symptoms such as a sensation of fullness in the ear, difficulty understanding speech, the need for increased volume when listening to conversations or TV, and issues with localization of sounds. They may also have a tendency to speak loudly, especially in noisy environments, and may exhibit frustration due to communication difficulties.
Diagnosis of Conductive Hearing Loss
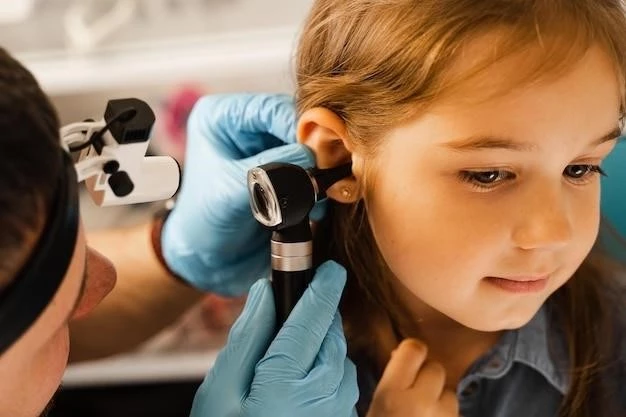
Diagnosis of conductive hearing loss involves a thorough examination by an audiologist or otolaryngologist. This may include a physical examination of the ear, hearing tests such as audiometry, tympanometry to assess middle ear function, and imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs to identify structural abnormalities. The healthcare provider will consider the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and test results to determine the underlying cause of the hearing loss and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Conductive Hearing Loss
The treatment for conductive hearing loss depends on the underlying cause. It may include interventions such as earwax removal, medications for ear infections, surgical procedures to repair the eardrum or middle ear bones, or hearing aids to amplify sound. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary to address the hearing loss effectively. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment option based on the individual’s specific condition and needs.
Individualized management strategies may include regular check-ups, hearing aid fittings, surgical interventions, or middle ear implants.
Management Strategies for Conductive Hearing Loss
Management of conductive hearing loss involves a multidisciplinary approach. Strategies may include regular monitoring by an audiologist, surgical interventions like tympanoplasty or stapedectomy, hearing aid fittings, bone conduction implants, or middle ear implants. The choice of management depends on the individual’s specific condition, underlying cause of the hearing loss, and their lifestyle needs. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare team to tailor an effective management plan that addresses the unique requirements of the patient.
Prevention of Conductive Hearing Loss
Preventing conductive hearing loss involves avoiding exposure to loud noises, practicing good ear hygiene, treating ear infections promptly, and protecting the ears from trauma. It is essential to use ear protection in noisy environments, refrain from inserting foreign objects into the ear canal, and seek medical attention for any ear-related concerns. By taking proactive measures to safeguard hearing health, individuals can reduce the risk of developing conductive hearing loss and promote overall ear wellness.
Technological solutions include hearing aids, bone conduction devices, and middle ear implants for managing conductive hearing loss effectively.
Technologies for Managing Conductive Hearing Loss
Technological advancements offer various solutions for managing conductive hearing loss. Hearing aids are commonly used to amplify sound for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss. Bone conduction devices transmit sound vibrations through the bones of the skull to stimulate the inner ear, bypassing the outer or middle ear. Middle ear implants surgically placed behind the eardrum can enhance sound transmission for those with specific types of hearing loss. These technological solutions play a critical role in improving hearing abilities and overall quality of life for individuals affected by conductive hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss can affect communication, social interactions, work performance, and overall quality of life. Early intervention is crucial.
Impact of Conductive Hearing Loss on Daily Life
Conductive hearing loss can significantly impact an individual’s daily life by hindering effective communication, leading to feelings of isolation and frustration. It may affect personal relationships, limit social interactions, impede academic or work performance, and reduce overall quality of life. The inability to hear clearly in various settings can result in misunderstandings, difficulty following conversations, and challenges in participating in social gatherings or professional meetings. Addressing conductive hearing loss through appropriate interventions and management strategies is essential in minimizing the negative impact on daily activities and improving overall well-being.
