Introduction
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) involves the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys due to a genetic disorder.
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the formation of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. There are two main types of PKD⁚ autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD).
Overview of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) involves the growth of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys due to a genetic disorder.
Genetic Basis of the Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is primarily caused by gene mutations that lead to the development of multiple fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. In most cases, the gene mutation responsible is inherited from one or both parents.

Development of Cysts in the Kidneys
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is characterized by the formation of multiple fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys due to genetic mutations. These cysts can lead to kidney enlargement and impact kidney function over time.
Types of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) has two main types ⸺ autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD);
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is an inherited condition characterized by the development of small fluid-filled sacs called cysts in the kidneys. It is a genetic disorder passed down from parents.
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder that mainly affects the kidneys and liver, characterized by the development of cysts in these organs. ARPKD is typically diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and can lead to serious complications.
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) can manifest with high blood pressure, back or side pain, blood in urine, kidney infection, and kidney stones. Diagnosis often involves imaging tests and genetic testing to confirm the presence of cysts and genetic mutations.
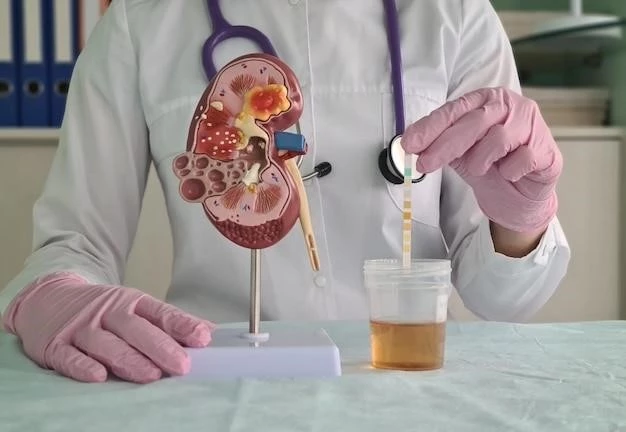
Diagnostic Procedures for Identifying Polycystic Kidney Disease
Patients with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) may undergo imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize kidney cysts. Genetic testing can confirm the presence of gene mutations associated with PKD.
Common Symptoms Experienced by Patients
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) commonly presents with symptoms such as high blood pressure, back or side pain, blood in the urine, kidney infections, and kidney stones. These symptoms may vary in severity among individuals affected by the condition.
Medication⁚ Tolvaptan
Treatment for polycystic kidney disease (PKD) includes the use of medications like Tolvaptan, recommended to slow cyst growth and preserve kidney function in affected individuals.
Management of Kidney Growth and Function Preservation
Treatment options for polycystic kidney disease (PKD) include medications like Tolvaptan to slow cyst growth and management strategies to preserve kidney function as the disease progresses. Lifestyle changes and regular monitoring play a crucial role in managing PKD effectively.
Survival Rates and Progression to Kidney Failure
Individuals with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) exhibit varying survival rates and may progress to kidney failure at different ages. Factors such as gender and genetic mutations influence the progression of the disease and overall prognosis.
Survival rates and progression to kidney failure in polycystic kidney disease (PKD) vary based on factors like gender, age, and genetic mutations, impacting the overall prognosis and life expectancy of affected individuals.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy in Polycystic Kidney Disease
Survival rates and the progression to kidney failure in polycystic kidney disease (PKD) are influenced by factors such as gender, age, genetic mutations, and individual variations in disease progression.
Vertex Pharmaceuticals plans to initiate a phase I study on VX-407 targeting autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). This study aims to assess a small molecule corrector’s efficacy in restoring PC1 protein function related to certain PKD1 genetic variants.
Pharmaceutical Interventions⁚ VX-407 Study
A study on VX-407 for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease aims to evaluate a small molecule corrector’s efficacy in restoring specific genetic variants’ protein function.
Advancements in Genetic Correction Therapies
Researchers are exploring genetic correction therapies to target specific gene mutations in polycystic kidney disease, aiming to restore normal protein function and potentially slow down disease progression.
Recent research in polycystic kidney disease (PKD) focuses on genetic correction therapies, pharmaceutical interventions like VX-407, and advancements aimed at slowing cyst growth and preserving kidney function. These studies offer hope for improved treatment strategies for individuals with PKD.
Managing polycystic kidney disease (PKD) poses challenges for individuals, including coping with symptoms, potential progression to kidney failure, and making lifestyle adjustments to preserve kidney function.
Challenges Faced by Individuals with Polycystic Kidney Disease
Living with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) involves managing symptoms like high blood pressure, kidney infections, and the emotional impact of a chronic condition. Coping with the unpredictable nature of the disease and its potential progression towards kidney failure can present significant challenges for affected individuals.
Support Systems and Coping Mechanisms
Individuals with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) benefit from support systems that may include healthcare professionals, family, and patient communities. Implementing coping mechanisms like healthy lifestyle choices, mental health support, and disease education can improve the quality of life for individuals managing PKD.
Understanding the Genetic Inheritance Pattern
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner, depending on the specific genetic mutation present. Understanding the inheritance pattern is crucial in assessing the risk for future generations and implementing preventive measures.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Individuals with a family history of polycystic kidney disease (PKD) can consider genetic testing for early detection. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes maintaining blood pressure, managing stress, staying hydrated, and avoiding excessive salt intake can help slow the progression of the disease.
Impact on Family and Future Generations
Genetic counseling plays a vital role in family planning for individuals with polycystic kidney disease (PKD), aiding in understanding the risk of passing on the genetic mutation to future generations. Educational initiatives and awareness campaigns are essential in empowering families to make informed decisions regarding the hereditary nature of PKD.
Stage 3 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and Beyond
Stage 3 CKD indicates moderate kidney damage, with an eGFR between 30 and 59. Options for advanced PKD include renal replacement therapy (RRT) like dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Options for Kidney Replacement Therapy (KRT)
Individuals with advanced stage polycystic kidney disease, including stage 3 chronic kidney disease and beyond, may require kidney replacement therapy (KRT) such as dialysis or kidney transplantation to manage kidney failure effectively and maintain quality of life.
Stage 3 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and Beyond
In advanced stages of polycystic kidney disease like Stage 3 CKD and beyond, individuals may explore options such as kidney replacement therapy (KRT) like dialysis or kidney transplantation to manage declining kidney function effectively and improve quality of life.
Genetic Counseling and Family Planning
Genetic counseling plays a crucial role in helping individuals with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) understand the hereditary implications of the condition and make informed choices about family planning. By providing information about the genetic inheritance pattern and potential risks to future generations, genetic counselors support families in making decisions that consider the impact of PKD on family members.
Educational programs and awareness campaigns play a crucial role in disseminating information about the hereditary nature of polycystic kidney disease (PKD) and empowering individuals to make informed decisions about family planning. By increasing awareness about the genetic inheritance pattern and potential risks of PKD transmission, these initiatives aim to support families in understanding the implications of the condition across generations.
Educational Initiatives and Awareness Campaigns
Educational programs and awareness campaigns are vital in informing individuals about the hereditary nature of polycystic kidney disease (PKD). By promoting understanding of the genetic inheritance pattern and potential risks for future generations, these initiatives empower families to make informed decisions regarding the implications of PKD across generations.
Latest Studies and Findings in Polycystic Kidney Disease Research
Current trends in polycystic kidney disease research focus on genetic correction therapies, pharmaceutical interventions such as VX-407٫ and advancements to slow cyst growth and maintain kidney function٫ offering hope for enhanced treatment strategies.
Public Health Policies and Advocacy Efforts
Public health policies and advocacy efforts are essential in raising awareness about polycystic kidney disease (PKD) and promoting research funding. By advocating for improved resources, funding, and support for individuals and families affected by PKD, these initiatives aim to enhance the quality of care and drive progress in PKD management and treatment.
Hearing from individuals affected by polycystic kidney disease provides valuable insights into the challenges, resilience, and daily life impact of managing this condition. Understanding their experiences can offer support and inspiration to others navigating similar health journeys.
Real-life Experiences of Individuals Living with Polycystic Kidney Disease
Hearing personal stories offers valuable insights into the challenges and resilience of individuals managing polycystic kidney disease (PKD).
Personal Stories and Testimonials
Real-life experiences offer insights into the challenges and resilience of individuals living with polycystic kidney disease (PKD).
Insights from Caregivers and Healthcare Professionals
Caregivers and healthcare professionals offer valuable perspectives on supporting individuals with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) and navigating the challenges associated with the condition. Their insights can provide guidance, emotional support, and specialized care for PKD patients.
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder that leads to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys, impacting kidney function and requiring various treatment options, including genetic therapies and kidney replacement therapy for advanced stages.
Summary of Key Takeaways on Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder leading to the development of multiple fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys, impacting kidney function. Treatment options include genetic therapies and kidney replacement therapy for advanced stages.
