Introduction
Variegate porphyria is a subtype of porphyria characterized by skin photosensitivity and systemic symptoms. It is a rare inherited disorder prevalent in South Africa.
Definition and Background
Variegate porphyria is a subtype of porphyria, an inherited disorder characterized by skin photosensitivity and systemic symptoms. It is rare globally but more prevalent in South Africa, particularly among individuals of Dutch ancestry.
Clinical Characteristics
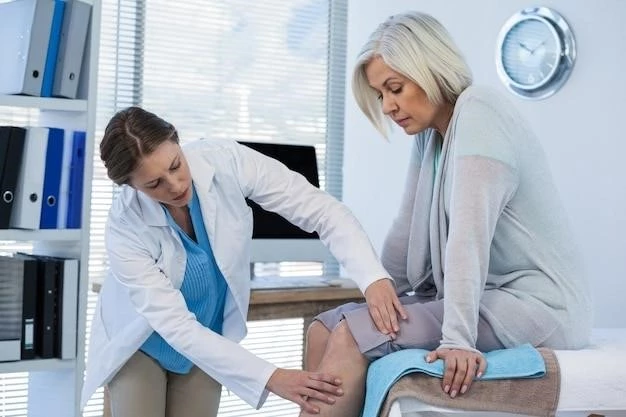
Variegate porphyria presents with skin photosensitivity, chronic blistering skin lesions, and acute neurovisceral symptoms. The skin manifestations often include subepidermal vesicles, bullae, erosions, and facial involvement.
Symptoms of Variegate Porphyria
Variegate porphyria manifests in various symptoms including skin photosensitivity, blistering, skin fragility, muscle weakness, and neurological changes. These symptoms typically appear in adulthood and may include abdominal pain, dark urine, and neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Diagnosis and Genetic Causes
Variegate porphyria is diagnosed through symptoms, clinical examination, and genetic testing for mutations in the PPOX gene. Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern is observed.
Genetic Mutations and Inheritance Pattern
Variegate porphyria is primarily caused by mutations in the PPOX gene, leading to a deficiency of protoporphyrinogen oxidase. It follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, with a higher prevalence observed in individuals of Dutch ancestry in South Africa due to a founder effect.
Treatment and Management
Management of variegate porphyria involves strategies to reduce symptoms triggered by sunlight, including avoiding sun exposure, protective clothing, and specific medications. Patients may benefit from regular monitoring and medical management to minimize the impact of acute attacks and long-term complications.
Approaches to Managing Variegate Porphyria
Management of variegate porphyria focuses on avoiding triggers like sunlight, using protective clothing, and medications to control symptoms. Regular medical follow-ups are essential for monitoring and ensuring appropriate care.
Prevalence and Geographic Distribution
Variegate porphyria is rare globally but more prevalent in South Africa, especially among individuals of Dutch ancestry due to a founder effect.
Occurrence in South Africa
In South Africa, variegate porphyria is more prevalent, with estimates suggesting 1 in 300 of the white population is affected. The condition is particularly common among individuals of Dutch ancestry due to historical factors.

Differential Diagnosis
Variegate porphyria must be differentiated from other porphyrias, especially acute intermittent porphyria (AIP), due to overlapping symptoms and shared genetic causes.
Distinct Features from Other Porphyrias
Variegate porphyria presents unique features that differentiate it from other porphyrias, especially in terms of clinical manifestations, genetic mutations, and specific triggers that exacerbate symptoms. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Variegate porphyria can lead to complications such as chronic skin issues, neurological problems, and potential acute attacks with severe health implications. Long-term effects may include scarring and neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Potential Risks and Health Implications
Variegate porphyria carries various risks including chronic skin issues, neurological complications, and possible acute attacks with severe implications on the individual’s health. Understanding these risks is crucial for effective management and long-term care.
Research and Advancements
Research on variegate porphyria focuses on understanding its genetic causes, improving diagnostic methods, and exploring new treatment modalities. Recent advancements aim to enhance patient care and outcomes.
Current Studies and Future Prospects
Recent research on variegate porphyria focuses on exploring new treatment options, improving diagnostic accuracy, and investigating potential gene therapies. Advancements in understanding the disease’s pathophysiology offer promising prospects for enhanced patient outcomes in the future.
Support and Resources
For individuals affected by variegate porphyria, seeking support from patient advocacy groups and accessing reliable resources can provide valuable information and assistance for both patients and caregivers.
Information and Assistance for Patients and Caregivers
For individuals and caregivers dealing with variegate porphyria, reliable information sources and support networks play a crucial role in understanding the condition, managing symptoms, and accessing necessary resources for comprehensive care and guidance.
