Exostoses ー Understanding Bone Growth Abnormalities
Exostoses are abnormal bone growths that can be hereditary or genetic. These growths, known as osteochondromas, arise from cartilage and protrude from the bony surface near joints, impacting the skeleton. Distinguishing between benign and malignant exostoses is crucial.
Introduction to Exostoses
Exostoses are bone growth abnormalities characterized by benign tumors known as osteochondromas. These growths can be hereditary or genetic, manifesting as bony protrusions near joints. Understanding the difference between benign and malignant exostoses is crucial in diagnosis and treatment. Exostoses impact the skeleton and joints, affecting overall mobility and functionality. Early detection and proper management are essential in addressing these growths effectively.
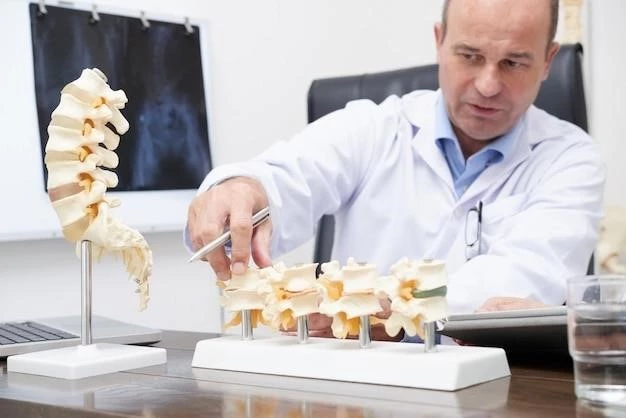
Types of Exostoses
Exostoses present in different forms, with the most common being osteochondromas. These benign growths arise from the cartilage and can develop on any bony surface near joints. While most exostoses are harmless, some cases may progress to malignant, cancerous growths. Understanding the various types of exostoses is vital in determining the appropriate treatment approach and ensuring optimal outcomes for affected individuals.
Hereditary and Genetic Factors
Exostoses can have hereditary and genetic components, making certain individuals more predisposed to developing these abnormal bone growths. Specific genetic mutations may play a role in the formation of exostoses, particularly osteochondromas. Understanding the hereditary and genetic factors associated with exostoses is crucial in both diagnosis and treatment, as it can help healthcare providers develop personalized care plans for affected individuals.
Understanding Osteochondromas
Osteochondromas are the most common type of benign bone growths seen in exostoses. These growths originate from the cartilage, developing as bony projections near joints. While typically non-cancerous, osteochondromas can impact skeletal structures and joint functionality. Understanding the characteristics and behavior of osteochondromas is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of exostoses.
Differences Between Benign and Malignant Exostoses
The primary distinction between benign and malignant exostoses lies in their behavior and potential risks. Benign exostoses, such as osteochondromas, are non-cancerous growths that typically do not spread to other tissues. In contrast, malignant exostoses are cancerous and can invade surrounding structures, posing significant health risks. Recognizing the variances between benign and malignant exostoses is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and long-term outcomes for individuals affected by these bone growth abnormalities.
Impact on Joints and Skeleton
Exostoses can have a significant impact on the joints and skeleton of affected individuals. These abnormal bone growths, such as osteochondromas, can disrupt normal joint function and mobility, leading to discomfort and reduced range of motion. When located near joints, exostoses may cause pain, swelling, and stiffness. Furthermore, exostoses can affect the overall structural integrity of the skeleton, potentially altering bone alignment and causing skeletal abnormalities. Understanding the implications of exostoses on the joints and skeleton is essential for developing comprehensive treatment strategies and improving the quality of life for those with these bone growth abnormalities.
Diagnosis of Exostoses
Diagnosing exostoses typically involves a combination of imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, to visualize the abnormal bone growths. Clinical evaluation by healthcare professionals is crucial in identifying the location, size, and characteristics of exostoses. Biopsy may be performed to differentiate between benign and malignant exostoses. Understanding the diagnostic process for exostoses is vital in providing accurate and timely intervention to manage these bone growth abnormalities effectively.
Treatment Options for Exostoses
Treatment options for exostoses vary based on the type, location, and severity of the bone growths. In many cases, observation and monitoring are sufficient for benign exostoses that do not cause symptoms. Surgical removal may be required for symptomatic or malignant exostoses to alleviate pain and prevent complications. Physical therapy and rehabilitation can help restore joint function and mobility post-surgery. Each treatment approach is tailored to the individual’s specific condition and aims to improve quality of life.
Preventive Measures for Exostoses
As exostoses can have genetic or hereditary components, there are limited preventive measures to avoid their development. Regular monitoring by healthcare providers for individuals with a family history of exostoses can help detect any abnormal bone growths early. Maintaining overall bone health through a balanced diet rich in calcium and regular exercise may support skeletal integrity. Understanding the risk factors and staying informed about the condition can also aid in early intervention and management of exostoses.
Living with Exostoses
Living with exostoses, especially osteochondromas, can present challenges related to joint discomfort, mobility issues, and potential skeletal deformities. Individuals with exostoses may benefit from regular medical follow-ups to monitor the growths and address any symptoms that arise. Engaging in physical activities that are joint-friendly and seeking support from healthcare professionals can help manage the impact of exostoses on daily life. Maintaining a positive outlook and staying proactive in care can enhance overall well-being while living with these bone growth abnormalities.
Research and Advancements in Exostoses Treatment
Ongoing research in exostoses treatment aims to improve diagnosis, surgical techniques, and non-invasive management options for individuals with these bone growth abnormalities. Advancements in imaging technology allow for more precise identification and monitoring of exostoses. Clinical trials and studies explore novel treatment modalities to enhance outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patients plays a crucial role in driving progress and innovation in the field of exostoses treatment.
Case Studies and Real-Life Experiences
Exploring case studies and real-life experiences of individuals living with exostoses can provide valuable insights into the challenges and triumphs associated with these bone growth abnormalities. Personal accounts offer a glimpse into the journey of diagnosis, treatment decisions, and daily life with exostoses. Sharing experiences can foster a sense of community and support among those affected by these conditions, highlighting the importance of awareness, advocacy, and resilience in navigating the complexities of living with exostoses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exostoses, particularly osteochondromas, are bone growth abnormalities that can impact the skeleton and joints. Understanding the differences between benign and malignant exostoses is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Advances in research and treatment modalities offer hope for improved outcomes for individuals with these conditions. By exploring real-life experiences and staying informed, individuals can better cope with the challenges of living with exostoses. Continued efforts in research and patient-centered care are essential in ensuring better management and quality of life for those affected by exostoses.
