Introduction to Polycystic Kidney Disease, Type 3 (PKD3)
Polycystic kidney disease, type 3 (PKD3), is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by renal and liver cysts that may lead to organ dysfunction.
Polycystic kidney disease type 3 (PKD3) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by the development of renal and liver cysts. The presence of these cysts can lead to organ dysfunction, particularly affecting the kidneys and liver. PKD3 is often associated with progressive cyst formation in these organs, with individuals typically presenting symptoms in mid to late adulthood.
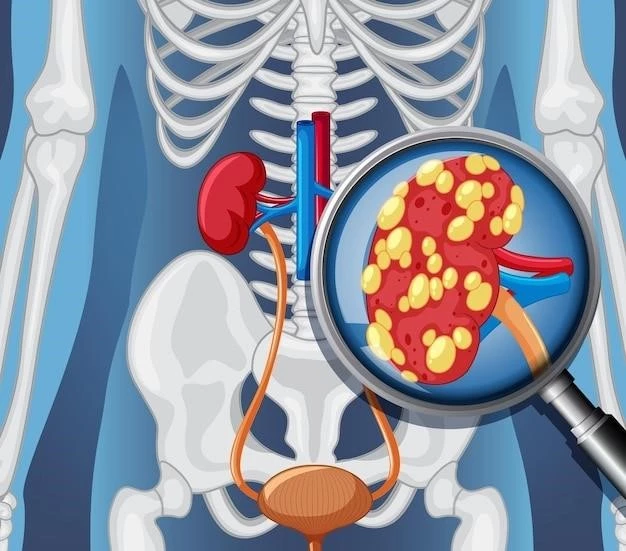
Understanding Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by kidney and liver cysts that can lead to organ dysfunction.
Overview of ADPKD
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is a hereditary disorder characterized by the development of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys and liver. This condition leads to progressive organ damage and is commonly diagnosed in mid to late adulthood. Individuals with ADPKD may experience a range of symptoms related to kidney and liver dysfunction.
Definition and Characteristics of PKD3
Polycystic kidney disease type 3 (PKD3) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by the development of renal and liver cysts. The presence of these cysts can lead to organ dysfunction, particularly affecting the kidneys and liver. PKD3 is often associated with progressive cyst formation in these organs, with individuals typically presenting symptoms in mid to late adulthood.

Relationship Between Kidney and Liver Cysts in PKD3
Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3) is characterized by the development of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys and liver, potentially leading to organ dysfunction and progressive cyst formation.
Association of Renal and Liver Cysts
Polycystic kidney disease type 3 (PKD3) is characterized by the presence of renal cysts that are often accompanied by liver cysts. These cysts can contribute to organ dysfunction and may progress over time٫ impacting the overall health of individuals with PKD3.
Progression of PKD3 and Organ Dysfunction
Polycystic kidney disease type 3 (PKD3) can progress with renal and liver cysts leading to organ dysfunction over time. Understand the implications and management strategies for PKD3 progression.
Impact on Kidneys and Liver
Polycystic kidney disease type 3 (PKD3) can progress, leading to renal and liver cysts, impacting organ function over time. Learn about managing the consequences of cyst formation in the kidneys and liver in individuals with PKD3.
Diagnosis and Staging of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3) can be diagnosed through imaging tests to observe renal and liver cysts. Additionally٫ staging of chronic kidney disease in PKD3 is done based on specific criteria to assess the progression and severity of the condition.
Diagnostic Tests for PKD3
Diagnosing Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3) involves imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI to visualize cysts in the kidneys and liver. Genetic testing may also be utilized to confirm the diagnosis and assess the risk of passing on the condition to offspring.
Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease in PKD3
In polycystic kidney disease type 3 (PKD3), the staging of chronic kidney disease involves assessing the kidney’s function using tests like estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). This staging helps determine the severity of kidney dysfunction and guides treatment decisions for individuals with PKD3.
Treatment Options for Polycystic Kidney Disease, Type 3
Explore management strategies such as lifestyle modifications, medication, and dialysis for individuals with PKD3. Learn about novel treatment techniques under investigation.
Management Strategies for PKD3
Effective management of Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3) involves lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, along with medications to help alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression. Consulting with healthcare providers and specialists for personalized treatment plans is essential for individuals with PKD3.
Research on New Treatment Techniques
Ongoing research is focusing on innovative techniques for treating Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3). Recent studies have identified potential therapies aimed at slowing disease progression and improving outcomes for individuals with PKD3. Stay informed about emerging treatment options through reputable sources and healthcare professionals.
Genetic Aspects of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3) is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, presenting with renal and liver cysts that may impact organ function. Understanding the genetic basis of PKD3 is crucial for diagnosis and management.
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance of PKD3
Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3) follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, with renal and liver cysts leading to organ dysfunction. Understanding the genetic inheritance of PKD3 is crucial for both diagnosis and management of the condition.
Comparison with Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)
When comparing Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3) with Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)٫ PKD3 is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner and typically manifests with renal and liver cysts. In contrast٫ ARPKD is a recessive genetic disorder characterized by the formation of cysts in the kidneys and liver٫ usually presenting in infancy or childhood. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of each condition;
Prevalence and Risk Factors of PKD3
Polycystic kidney disease type 3 (PKD3) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder. It is characterized by renal cysts often associated with liver cysts, which can lead to organ dysfunction. PKD3 typically presents in mid to late adulthood with progressive cyst formation in the kidneys and liver. Understanding the prevalence and risk factors of PKD3 is essential for early detection and management.
Incidence Rates of PKD3
PKD3٫ an autosomal dominant genetic disorder٫ has varying incidence rates globally. Understanding the prevalence of PKD3 can aid in early detection and tailored management plans. Consult healthcare providers for personalized guidance based on family history and risk factors.
Factors Contributing to the Development of PKD3
The development of Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3) is influenced by genetic factors due to its autosomal dominant inheritance. Additionally, lifestyle choices, environmental influences, and underlying health conditions can influence the progression of PKD3. Understanding these factors can guide personalized management approaches and improve outcomes for individuals affected by PKD3.
Awareness and Support for Individuals with PKD3
Understand the characteristics and progression of polycystic kidney disease type 3 (PKD3) for better awareness and seek support from relevant organizations and healthcare providers. Stay informed and connected during your PKD3 journey.
National Kidney Month and Kidney Disorders Awareness
March is National Kidney Month, promoting awareness of kidney disorders like Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3). Stay informed about kidney health, support available, and ways to manage and cope with PKD3. Join the conversation to raise awareness of kidney diseases and the importance of early detection and treatment.
Support Organizations for PKD3 Patients
Connect with support organizations dedicated to assisting individuals with Polycystic Kidney Disease Type 3 (PKD3). These organizations offer valuable resources, educational materials, and community support to help patients navigate their PKD3 journey. Accessing support networks can provide emotional assistance, information on treatment options, and empower individuals with PKD3 to manage their condition effectively.
