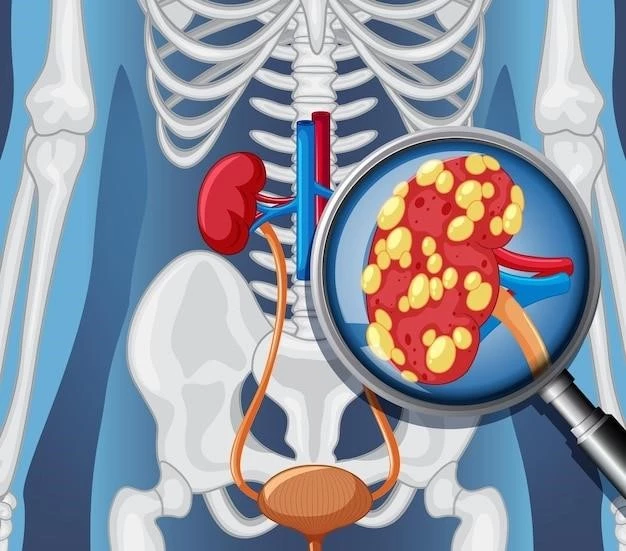
Introduction to Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD or PCKD) is a genetic disorder where multiple cysts develop within the kidneys. These cysts can lead to complications like high blood pressure and kidney failure. Consult a healthcare professional for more information.
Definition and Overview
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD)‚ also known as polycystic kidney syndrome‚ is a genetic disorder characterized by the development of multiple cysts within the kidneys. These cysts can lead to complications such as high blood pressure and kidney failure. PKD may present at different stages of life‚ and early diagnosis and management are essential in addressing its impact on kidney function and overall health.
Types of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) includes autosomal dominant PKD and autosomal recessive PKD‚ both leading to chronic kidney disease and potential kidney failure.
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is the most common genetic cause of renal failure worldwide‚ characterized by cyst formation and progressive kidney enlargement. Early diagnosis and management are crucial to addressing complications across multiple organs.
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects infants and children‚ leading to kidney and liver cysts. Early detection and management are crucial in improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals with ARPKD.
Symptoms and Complications of ADPKD
Common signs and symptoms of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) include blood in the urine‚ back pain‚ urinary tract infections‚ kidney stones‚ and an increased risk of kidney failure. Regular monitoring and early intervention are essential.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Most individuals with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) may experience symptoms such as blood in the urine‚ back or flank pain‚ recurring urinary tract infections‚ kidney stones‚ and an increased risk of developing kidney failure. Regular monitoring and prompt medical attention are crucial for managing these symptoms effectively.
Consult healthcare providers for accurate diagnosis using imaging tests like ultrasounds and CT scans. Treatments focus on managing symptoms and complications effectively‚ including controlling high blood pressure and developing personalized care plans to address kidney function decline.

Diagnosis and Treatment Options
For accurate diagnosis of Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)‚ healthcare providers may use imaging tests like ultrasounds or CT scans. Treatment focuses on symptom management‚ including controlling high blood pressure and developing personalized care plans to address kidney function decline effectively.
Treatment Approaches‚ including Tolvaptan
Treatment options for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) may include medications like tolvaptan‚ which can help slow kidney function decline. Consult your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan for managing ADPKD effectively.
Epidemiology and Genetic Factors
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder causing cyst growth in the kidneys‚ affecting around 500‚000 people in the U.S. The main types are autosomal dominant PKD and autosomal recessive PKD‚ with various genetic origins and manifestation ages.
Prevalence and Inheritance Patterns
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a common inherited disorder‚ affecting approximately 1 in 400 to 1 in 1‚000 individuals. The disease is passed down through family members and often diagnosed between ages 30 and 50‚ leading to kidney complications. Understanding the genetic inheritance of ADPKD is crucial for early detection and management.
A healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD). Follow dietary guidelines‚ engage in regular exercise‚ and stay hydrated to support kidney health. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Lifestyle Recommendations for Managing PKD
Diet plays a crucial role in managing Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD). Following dietary guidelines‚ particularly a low-salt‚ low-fat diet‚ and staying hydrated are essential. Regular physical exercise‚ as recommended by healthcare providers‚ can also help maintain overall health and manage PKD symptoms effectively.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing studies are exploring potential breakthroughs in understanding and managing Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD). Stay informed about research advancements and emerging treatment options by connecting with healthcare professionals and reputable organizations in the field.
Ongoing Studies and Potential Breakthroughs
Research studies are investigating potential breakthroughs in understanding and treating Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD). Stay engaged with ongoing research advancements to stay informed about new treatment options and potential breakthroughs in managing PKD effectively.
Support and Resources for Individuals with PKD
For support and resources related to Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)‚ consider reaching out to helplines‚ organizations‚ and patient communities for guidance and assistance. Stay informed and connected to better manage PKD.
Helplines‚ Organizations‚ and Patient Communities
Access valuable support resources for Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) by connecting with dedicated helplines‚ reputable organizations‚ and engaging with patient communities for guidance‚ information‚ and a supportive network. Stay connected for holistic assistance in managing PKD.