Managing Interstitial Cystitis
Understanding Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic bladder pain condition that can cause pelvic pain, urinary urgency, and frequency. It is characterized by discomfort or pressure in the bladder and pelvic area due to inflammation of the bladder wall. This condition can lead to painful urination and discomfort in the urethra.
Patients with interstitial cystitis may experience discomfort that ranges from mild to severe and can significantly impact their quality of life. The cause of this condition is not well understood, but it is believed to involve a defect in the bladder lining that allows irritating substances in the urine to reach the bladder wall and trigger inflammation.
Understanding the symptoms of interstitial cystitis is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. If you experience persistent pelvic pain, urinary discomfort, or increased urinary frequency, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation. A urologist specializing in bladder conditions can help diagnose interstitial cystitis through tests like cystoscopy;
By understanding the nature of interstitial cystitis and its impact on your daily life, you can take proactive steps to manage the condition effectively. Educating yourself about the treatment options available can empower you to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized care plan tailored to your needs.
Diagnosis of Interstitial Cystitis
Diagnosing interstitial cystitis can be challenging due to the overlapping symptoms with other conditions. A urologist specializing in bladder disorders is crucial for an accurate diagnosis. The diagnosis typically starts with a detailed medical history and physical examination to assess symptoms like chronic bladder pain, urinary urgency, and frequency.
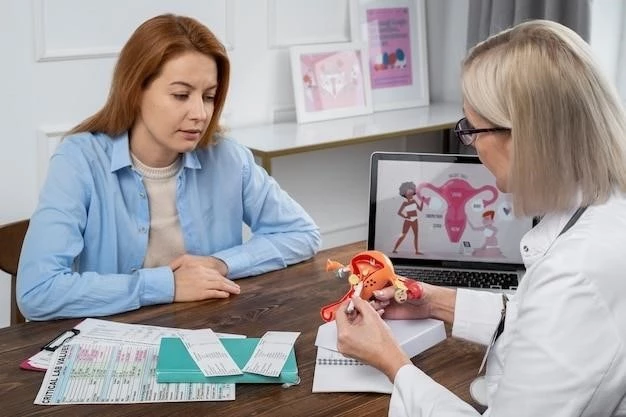
Diagnostic tests may include a urine sample analysis to rule out infections and cystoscopy to examine the bladder lining for signs of inflammation or other abnormalities. During cystoscopy, a thin tube with a camera is inserted through the urethra to visualize the bladder interior, providing valuable insights for diagnosis.
Urodynamic testing can also be utilized to evaluate how the bladder and urethra are functioning. This test helps assess issues like urinary incontinence, incomplete bladder emptying, or abnormal bladder contractions. Furthermore, your healthcare provider may recommend additional tests like bladder ultrasounds or urinary cytology to rule out other potential causes of your symptoms.
It is important to communicate openly with your healthcare team about your symptoms, concerns, and medical history to aid in the diagnostic process. Keeping a bladder diary to track your daily fluid intake, urinary frequency, and symptom severity can provide valuable information for your healthcare provider.
Treatment Options for Interstitial Cystitis
Managing interstitial cystitis involves a combination of treatment approaches tailored to your specific symptoms and needs. Treatment options focus on relieving chronic bladder pain, pelvic discomfort, and urinary urgency while addressing inflammation of the bladder wall. Here are some common strategies⁚
- Pain Relievers⁚ Over-the-counter pain medications may help alleviate discomfort associated with interstitial cystitis. However, consult your healthcare provider before taking any medication to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- Physical Therapy⁚ Pelvic floor physical therapy can be beneficial for improving bladder function and reducing pelvic pain. A trained therapist can provide exercises to strengthen pelvic floor muscles and improve bladder control.
- Bladder Training⁚ Learning techniques to control urinary urgency and frequency through scheduled voiding and relaxation exercises can help manage interstitial cystitis symptoms.
- Nerve Stimulation⁚ Procedures like sacral nerve stimulation or pudendal nerve stimulation may be recommended for controlling bladder function and reducing pain in some cases.
- Surgery⁚ In severe cases where conservative treatments have not been effective, surgical interventions like bladder augmentation or cystectomy (bladder removal) may be considered as a last resort.
It is essential to work closely with a urologist specializing in interstitial cystitis to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your condition. Your healthcare provider will consider the severity of your symptoms, your response to previous treatments, and your overall health before recommending a course of action.
By exploring various treatment options and actively participating in your care, you can effectively manage interstitial cystitis and improve your quality of life. Remember that finding the right treatment approach may involve a trial-and-error process, so communicate openly with your healthcare team to address any concerns or adjustments needed.
Medications for Interstitial Cystitis
Medications play a vital role in managing the symptoms of interstitial cystitis and reducing bladder pain and discomfort. Working closely with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most appropriate medication regimen for your specific condition. Here are some commonly prescribed medications for interstitial cystitis⁚
- Oral Medications⁚ Pain relievers like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help reduce pain and inflammation associated with interstitial cystitis. However, these medications may have side effects and should be used under medical supervision.
- Bladder Coating Agents⁚ Medications like pentosan polysulfate sodium form a protective layer on the bladder lining, reducing irritation and improving symptoms. These agents help restore the protective lining of the bladder.
- Antihistamines⁚ Some antihistamines may provide relief from urinary urgency and frequency by targeting the inflammatory response in the bladder. Discuss with your healthcare provider about the appropriate antihistamine for your condition.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants⁚ Low doses of tricyclic antidepressants can help manage chronic pain and improve sleep quality in patients with interstitial cystitis. These medications work by affecting neurotransmitters that modulate pain signals.
- Antispasmodics⁚ Medications like oxybutynin or tolterodine can help relax the bladder muscles, reducing urinary urgency and frequency. They are commonly used to manage overactive bladder symptoms.
It is essential to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance regarding medication dosage, frequency, and potential side effects. Keep track of your symptoms and any changes you experience while on medication to discuss with your healthcare team during follow-up appointments.
Remember that medications are just one aspect of managing interstitial cystitis, and they are often combined with other treatment modalities to optimize symptom relief and improve bladder function; Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to ensuring that your medication regimen effectively addresses your individual needs and preferences.
Non-Invasive Therapies for Interstitial Cystitis
Non-invasive therapies can complement traditional treatments and provide additional relief for individuals with interstitial cystitis. These therapies aim to reduce symptoms, promote bladder health, and improve overall quality of life. Here are some non-invasive options to consider⁚
- Physical Therapy⁚ Pelvic floor physical therapy focuses on strengthening pelvic floor muscles, improving bladder control, and reducing pelvic pain. A skilled therapist can provide personalized exercises and techniques to alleviate symptoms.
- Bladder Retraining⁚ Bladder training involves scheduling bathroom visits at regular intervals to gradually increase bladder capacity and reduce urinary urgency. This technique can help manage symptoms of interstitial cystitis and improve bladder function.
- Heat Therapy⁚ Applying heat to the pelvic area can help relax muscles, reduce discomfort, and alleviate pelvic pain associated with interstitial cystitis. Warm baths, heating pads, or warm compresses may offer relief.
- Dietary Modifications⁚ Certain foods and beverages can irritate the bladder and worsen interstitial cystitis symptoms. Consider working with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to identify and eliminate potential triggers from your diet;
- Stress Management⁚ Stress can exacerbate interstitial cystitis symptoms. Engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
Non-invasive therapies provide safe and effective alternatives to managing interstitial cystitis symptoms without the need for invasive procedures or medications. However, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new therapy to ensure that it aligns with your treatment plan and overall health goals.
By integrating non-invasive therapies into your comprehensive treatment approach, you can address interstitial cystitis from various angles and enhance the effectiveness of your overall management strategy. Remember to communicate openly with your healthcare team about your experiences with non-invasive therapies to optimize your treatment outcomes.
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
For individuals with severe interstitial cystitis symptoms that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options may be considered to alleviate pain and improve bladder function. Surgical interventions aim to address the underlying causes of interstitial cystitis and provide long-term relief. Here are some surgical options for severe cases⁚
- Bladder Augmentation⁚ Bladder augmentation surgery involves enlarging the bladder using a segment of the bowel or synthetic material. This procedure increases bladder capacity, reduces urinary urgency, and can improve overall bladder function for individuals with severe interstitial cystitis.
- Cystectomy (Bladder Removal)⁚ In extreme cases where other treatments have not been successful, cystectomy may be considered as a last resort. During this surgery, the bladder is removed, and alternative methods for urine storage and elimination, such as a urinary diversion, are created.
- Hunner’s Lesion Removal⁚ For individuals with Hunner’s ulcers, a subtype of interstitial cystitis characterized by bladder lesions, endoscopic surgery can be performed to remove the ulcers and improve symptoms. This procedure aims to eliminate sources of inflammation and pain within the bladder.
- Nerve Stimulation⁚ Sacral nerve stimulation (neuromodulation) involves implanting a device that delivers electrical impulses to the sacral nerves, which can help regulate bladder function and reduce urinary urgency in some cases of interstitial cystitis.
- Fulguration⁚ Fulguration is a surgical procedure used to treat Hunner’s ulcers by burning or cauterizing the lesion with a specialized instrument. This technique aims to remove the ulcer and promote healing of the bladder lining.
Surgical options for severe interstitial cystitis cases should be discussed thoroughly with a urologist specializing in bladder disorders to weigh the risks, benefits, and potential outcomes. It is essential to consider the impact of surgery on your quality of life, recovery process, and long-term bladder health before making a decision.
By exploring surgical options under the guidance of a knowledgeable healthcare team, individuals with severe interstitial cystitis can make informed decisions about their treatment pathway and work towards improving their bladder function and overall well-being.
Consulting a Urologist for Interstitial Cystitis
Seeking guidance from a urologist specializing in interstitial cystitis is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment. A urologist has the expertise to evaluate your symptoms, perform diagnostic tests, and recommend an appropriate management plan tailored to your specific needs. When considering consulting a urologist for interstitial cystitis, keep the following points in mind⁚
- Specialized Knowledge⁚ Urologists are trained in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the urinary tract, including interstitial cystitis. Their specialized knowledge enables them to identify the underlying causes of bladder pain, urinary urgency, and frequency.
- Diagnostic Expertise⁚ A urologist can perform various diagnostic tests such as cystoscopy, urodynamic testing, and bladder ultrasounds to assess bladder health and rule out other potential conditions. These tests provide valuable insights for accurate diagnosis.
- Treatment Recommendations⁚ Based on your symptoms, medical history, and test results, a urologist can recommend personalized treatment options ranging from medications and physical therapy to surgical interventions for severe cases. Their expertise ensures that you receive the most effective and up-to-date treatments.
- Long-Term Management⁚ Urologists play a crucial role in long-term management of interstitial cystitis by monitoring your symptoms, adjusting treatment plans as needed, and providing ongoing support and guidance. Regular follow-up appointments with a urologist can help track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your care.
When scheduling an appointment with a urologist, be prepared to discuss your symptoms, medical history, and any previous treatments you have tried. Bringing a detailed list of medications, supplements, and symptoms you are experiencing can help the urologist make an accurate assessment of your condition. Additionally, don’t hesitate to ask questions and seek clarification on any aspect of your diagnosis or treatment plan.
By collaborating with a skilled urologist specializing in interstitial cystitis, you can receive comprehensive care, effective treatments, and valuable support to manage your condition and improve your quality of life. Remember that open communication and a strong patient-provider relationship are key to successful outcomes in the management of interstitial cystitis.
Coping Strategies and Support for Interstitial Cystitis
Coping with interstitial cystitis involves a holistic approach that includes not only medical treatment but also strategies to manage the emotional and psychological impact of the condition. Additionally, seeking support from healthcare providers, peers, and mental health professionals can enhance your ability to cope effectively. Consider the following coping strategies and support options⁚
- Stress Management⁚ Stress can exacerbate interstitial cystitis symptoms. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness to promote relaxation and well-being.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices⁚ Maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated, get regular exercise, and prioritize quality sleep. Healthy lifestyle habits can support overall well-being and may positively impact interstitial cystitis symptoms.
- Support Groups⁚ Joining interstitial cystitis support groups or online communities can provide a sense of belonging, empathy, and shared experiences. Connecting with individuals facing similar challenges can offer emotional support and practical advice.
- Communication⁚ Openly communicate with your healthcare team about your symptoms, concerns, and treatment preferences. Effective communication can help ensure that your needs are understood and addressed in your care plan.
- Mental Health Support⁚ Consider seeking support from a therapist or counselor to address emotional challenges, anxiety, or depression that may arise from living with a chronic condition like interstitial cystitis. Therapy can provide coping strategies and emotional resilience.
- Self-Care Practices⁚ Practice self-care activities that promote relaxation and self-compassion, such as journaling, hobbies, spending time in nature, or engaging in activities you enjoy. Taking time for yourself is essential for mental and emotional well-being.
Remember that coping with interstitial cystitis is a journey that may have ups and downs. Be patient with yourself, stay informed about your condition, and advocate for your needs. By incorporating coping strategies, seeking support, and prioritizing self-care, you can navigate the challenges of interstitial cystitis with resilience and strength.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare providers, support networks, and mental health professionals for assistance as you navigate the complexities of interstitial cystitis. Together, you can develop a comprehensive approach to managing the condition and improving your quality of life.
