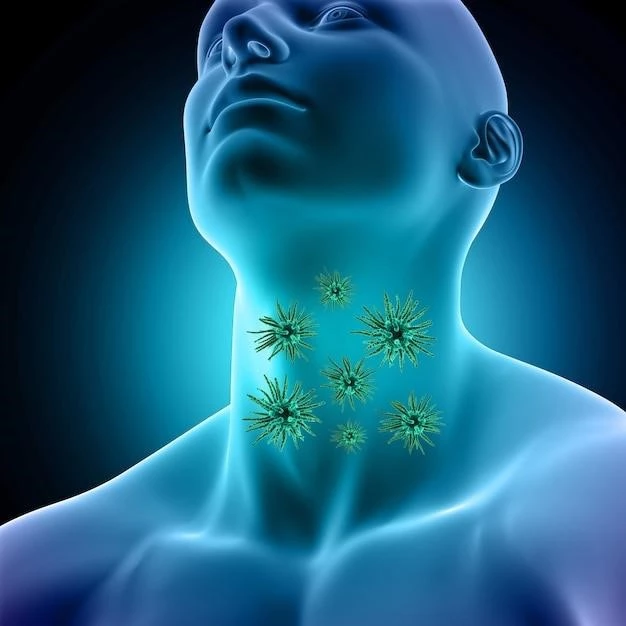
Disease ⏤ Lympha-Lymphe
When the Lymphatic System faces infection by bacteria or virus, the immune response triggers swelling and inflammation in the lymph nodes. The treatment involves antibiotics to combat the disease progression.
Introduction
Welcome to the world of Lympha-Lymphe disease, where the delicate balance of the lymphatic system can be disrupted by the invasion of harmful bacteria and viruses. This condition can set off a cascade of events, culminating in a series of immune responses that lead to swelling and inflammation in the lymph nodes. Understanding how infections impact the lymphatic system is crucial in battling this disease effectively. The use of antibiotics plays a key role in fighting off these pathogens and preventing the disease from progressing further. Join us as we delve deeper into the intricate workings of the lymphatic system when faced with infections, and explore the mechanisms behind the immune response, swelling, inflammation, and the treatment methods employed to combat the Lympha-Lymphe disease. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of this intricate interplay between the lymphatic system and infectious agents.
Role of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in the body’s defense against infections. It consists of a network of vessels and lymph nodes that help filter out harmful substances, including bacteria and viruses. When pathogens enter the body, the lymphatic system works to trap and destroy them, preventing further spread of infection. Lymph nodes act as checkpoints, where immune cells detect and mount responses to invaders. This process helps in initiating the immune response, which includes producing antibodies and activating immune cells to eradicate the pathogens. Additionally, the lymphatic system aids in the removal of cellular waste and excess fluid from tissues, maintaining a healthy balance within the body. Understanding the intricate functions of the lymphatic system is essential in comprehending how infections can disrupt its normal processes, leading to diseases like Lympha-Lymphe. By exploring how the lymphatic system responds to pathogens, we can appreciate its crucial role in protecting the body from harmful invaders and maintaining overall health.
Infection by Bacteria and Virus
When the body encounters bacteria or viruses, the delicate balance of the lymphatic system can be disrupted, leading to potential infections. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that can enter the body through various means, causing harm and triggering an immune response; On the other hand, viruses are infectious agents that invade cells and use their machinery to replicate, often resulting in illness. Both bacteria and viruses can target the lymphatic system, infiltrating lymph nodes and disrupting their normal functions. The immune system recognizes these invaders and initiates a defense mechanism to combat the infection. Understanding the differences between bacterial and viral infections is crucial in diagnosing and treating Lympha-Lymphe disease effectively. By exploring how these pathogens interact with the lymphatic system, we can gain insights into the complexities of the disease progression and the immune responses involved in fighting off these microbial invaders.
Immune Response in Lympha-Lymphe Disease
When faced with Lympha-Lymphe disease, the immune system springs into action to combat the bacterial or viral invasion. The immune response involves a coordinated effort of various immune cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages, working together to identify and eliminate the pathogens. Lymphocytes recognize specific antigens presented by the invaders and launch targeted attacks to neutralize them. Macrophages engulf and digest the foreign particles, assisting in clearing the infection. The immune response also triggers the release of inflammatory molecules to recruit more immune cells to the site of infection, leading to swelling and inflammation in the lymph nodes. This inflammatory process is a sign that the immune system is actively fighting off the pathogens. Understanding the intricate mechanisms of the immune response in Lympha-Lymphe disease is essential in developing effective treatment strategies to restore the lymphatic system’s normal functioning and combat the infection.
Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling and inflammation are common manifestations of the immune response in Lympha-Lymphe disease. When the lymphatic system detects an infection by bacteria or virus, it triggers a series of events that lead to the enlargement of the lymph nodes and surrounding tissues. The accumulation of immune cells and fluid in these areas causes swelling, a visible sign of the body’s defense mechanism at work. Inflammation occurs as a result of immune cells releasing cytokines and other inflammatory molecules to combat the pathogens. This inflammatory response helps create an inhospitable environment for the invaders and signals the immune system to mount a robust defense. While swelling and inflammation can be uncomfortable, they are essential components of the immune response in fighting off infections. Understanding how these processes contribute to the body’s ability to ward off harmful pathogens is crucial in managing Lympha-Lymphe disease and promoting recovery.
Treatment with Antibiotics
Antibiotics play a crucial role in treating Lympha-Lymphe disease caused by bacterial infections. These medications work by targeting and inhibiting the growth of bacteria, allowing the immune system to more effectively combat the infection. Different classes of antibiotics target specific types of bacteria, ensuring targeted treatment. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare provider to eradicate the infection completely and prevent antibiotic resistance. While antibiotics are not effective against viral infections, supportive care and antiviral medications may be recommended based on the type of virus causing the illness. Understanding the importance of proper antibiotic use in bacterial infections is key to managing Lympha-Lymphe disease and preventing its progression. Consulting a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and treatment is vital in ensuring successful recovery from bacterial infections affecting the lymphatic system.
Disease Progression
In Lympha-Lymphe disease, the progression can vary depending on the underlying cause, whether bacterial or viral. If left untreated, bacterial infections can lead to complications such as abscess formation or systemic spread of the infection. The inflammation and swelling in the lymph nodes may worsen, affecting their ability to fight off pathogens effectively. In the case of viral infections, the disease progression may involve the virus spreading to other tissues and organs, causing widespread damage. Without timely intervention, both bacterial and viral infections can result in severe illness and long-term consequences. Monitoring the signs and symptoms of Lympha-Lymphe disease is crucial in assessing the disease progression and initiating appropriate treatment. Early detection and management of the infection can help prevent further complications and promote a faster recovery, highlighting the importance of prompt medical attention in combating this lymphatic system disorder.
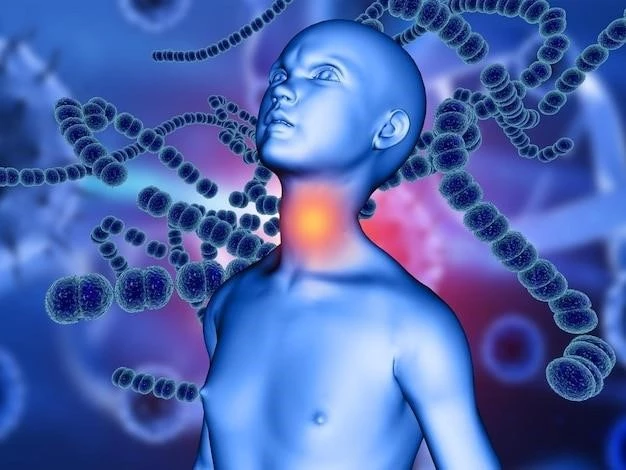
Prevention and Management
Preventing Lympha-Lymphe disease involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support the immune system. Vaccinations can help prevent certain infections that may affect the lymphatic system. Early detection of symptoms, such as persistent swelling or inflammation in the lymph nodes, is crucial for prompt medical evaluation and treatment. Managing Lympha-Lymphe disease requires a comprehensive approach, including the use of appropriate antibiotics for bacterial infections, supportive care for viral infections, and monitoring for any signs of disease progression. Following healthcare provider recommendations, completing prescribed treatments, and attending follow-up appointments are essential in managing the condition effectively. By taking preventive measures and actively participating in the management of Lympha-Lymphe disease, individuals can reduce the risk of infections and complications, promoting overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lympha-Lymphe disease poses a significant challenge to the lymphatic system when faced with bacterial and viral infections. The immune response triggered by these pathogens leads to swelling and inflammation in the lymph nodes, highlighting the system’s role in combating infections. Treatment with antibiotics is crucial for bacterial infections, while supportive care is essential for viral causes. Disease progression can have serious consequences if left unchecked, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention. Prevention through hygiene practices, vaccinations, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to reducing the risk of Lympha-Lymphe disease. By understanding the intricacies of the lymphatic system’s response to infections and actively participating in prevention and management strategies, individuals can better protect their health and well-being from the impacts of this challenging disease.