Disease ─ Infundibulopelvic Stenosis Multicystic Kidney
Overview of the Condition
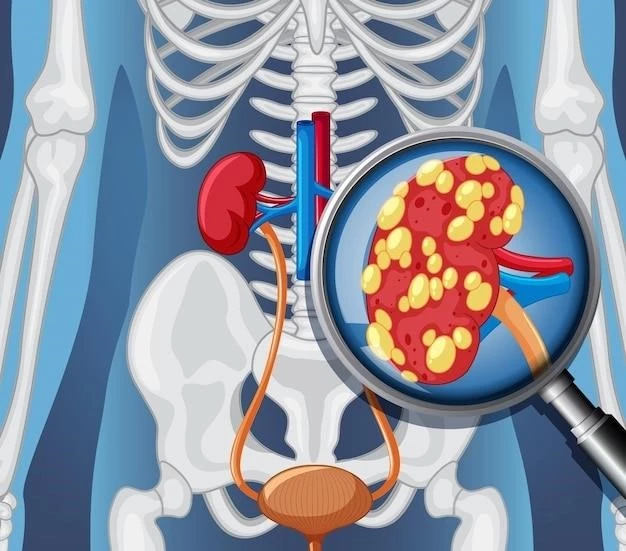
Infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney is a rare congenital condition characterized by the presence of multiple fluid-filled sacs in the affected kidney. The condition typically results from abnormal development of the kidney during fetal growth, leading to the formation of cysts. These cysts can cause blockage of the kidney pelvis and obstructed urinary system function.
One of the underlying causes of this condition is pelviureteric junction obstruction, where there is a narrowing of the renal artery at the point where the renal pelvis meets the ureter. This narrowing can lead to difficulties in urine flow, contributing to the formation of cysts within the kidney.
Individuals with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney may experience a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, high blood pressure, urinary tract infections, and even kidney failure in severe cases. Diagnosis often involves imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the cysts and assess kidney function.
Treatment options for this condition may include medications to manage symptoms, drainage procedures to alleviate blockages, or in severe cases, surgical interventions to remove the affected kidney. Early detection and appropriate management are crucial in preventing complications and improving the prognosis for individuals with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney.
Causes and Risk Factors
Infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney is primarily caused by abnormal development of the kidney during fetal growth, leading to the formation of multiple fluid-filled sacs within the kidney. One of the key contributing factors to this condition is a congenital disorder known as pelviureteric junction obstruction.
Pelviureteric junction obstruction involves a narrowing or blockage at the point where the renal pelvis connects to the ureter. This blockage can impede the flow of urine from the kidney, resulting in the buildup of fluid and the formation of cysts within the kidney tissue.
While the exact mechanisms underlying the development of this condition are not fully understood, there are certain risk factors that may increase the likelihood of infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney. These risk factors may include genetic predisposition, family history of kidney disorders, and certain environmental factors that could impact fetal kidney development.
Individuals born with a narrow renal artery or other anatomical variations in the urinary system may also be at a higher risk of developing this condition. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney is essential for early detection and appropriate management to prevent complications and improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney can present with a variety of symptoms that may vary in severity depending on the extent of kidney involvement. Common symptoms of this condition include abdominal pain, particularly in the flank area where the affected kidney is located. Individuals may also experience recurrent urinary tract infections due to the obstructed urinary system.
Some individuals with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney may develop high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, as a result of compromised kidney function. In severe cases where kidney function is significantly impaired, symptoms of kidney failure such as swelling, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating may occur.
Diagnosing infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests. Ultrasound imaging is often used to visualize the structure of the kidney and identify the presence of multiple fluid-filled sacs within the kidney tissue.
Additional imaging modalities such as CT scans or MRI scans may be utilized to further assess the extent of kidney involvement and evaluate renal function. Laboratory tests, including urine analysis and blood tests, can help assess kidney function and detect any abnormalities that may indicate the presence of infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney depends on the severity of symptoms, the extent of kidney involvement, and the overall health of the individual. In some cases, conservative management may be sufficient to address mild symptoms and slow the progression of the condition.
Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms such as pain, urinary tract infections, or high blood pressure associated with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney. Antibiotics are commonly used to treat and prevent infections, while pain medications can help alleviate discomfort.
In situations where there is significant blockage in the urinary system or if complications arise, more invasive treatment options may be considered. Drainage procedures, such as the insertion of a stent to promote urine flow or the placement of a nephrostomy tube to drain excess fluid from the kidney, may be recommended.
In severe cases where the affected kidney is non-functioning or causing persistent symptoms, surgical intervention to remove the kidney (nephrectomy) may be necessary. Surgical removal of the affected kidney can help alleviate symptoms, prevent further complications, and improve overall kidney function.
Regular monitoring and follow-up care may also be recommended to assess kidney function, manage symptoms, and address any potential complications that may arise. The goal of treatment for infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney is to optimize kidney health, alleviate symptoms, and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Complications and Prognosis
Infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney can lead to various complications if left untreated or if the condition progresses. Persistent blockage of the urinary system can result in recurrent urinary tract infections, which may lead to kidney damage over time. In severe cases, kidney failure may occur, necessitating interventions such as dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Individuals with this condition may also be at an increased risk of developing hypertension (high blood pressure) due to impaired kidney function. Uncontrolled hypertension can further exacerbate kidney damage and increase the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Long-term complications of infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney can impact the overall quality of life and may require ongoing medical management. Regular monitoring of kidney function, blood pressure, and urinary health is essential to detect and address any complications promptly.
The prognosis for individuals with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney varies depending on the severity of kidney involvement, the presence of complications, and the response to treatment. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can help alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve outcomes.
With timely intervention and comprehensive care, many individuals with this condition can achieve a good quality of life and maintain adequate kidney function. Close collaboration between healthcare providers, including urologists and nephrologists, is essential in managing complications, optimizing kidney health, and providing long-term support for individuals with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney.
Prevention and Management
While infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney is a congenital condition that cannot be completely prevented, there are measures that can help reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes for individuals with this condition. Early detection and prompt intervention are key elements in the effective management of this disorder.
Regular prenatal care is essential for identifying any abnormalities in fetal development that may indicate the presence of infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney. Prenatal ultrasound screenings can help detect structural anomalies in the kidneys and urinary system, allowing for timely intervention if necessary.
For individuals diagnosed with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney, close monitoring by healthcare providers is crucial to assess kidney function, manage symptoms, and prevent complications. Compliance with prescribed medications, follow-up appointments, and lifestyle modifications can all contribute to effective disease management.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate hydration can help support overall kidney health and reduce the risk of complications. Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption is also important in maintaining kidney function and overall well-being.
Engaging in open communication with healthcare providers, asking questions, and seeking support from medical professionals and support groups can help individuals with infundibulopelvic stenosis multicystic kidney better understand their condition and actively participate in their care plan. By taking proactive steps in prevention and management, individuals can optimize their quality of life and maintain kidney health.