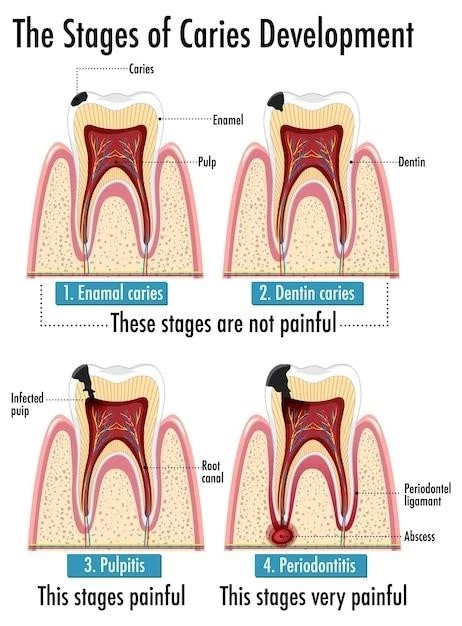
Disease ─ Dental Aberrations Due to Steroid Dehydrogenase Deficiency
Steroid hormones play a crucial role in tooth development, and enzyme dysfunction due to genetic mutations can lead to dental abnormalities. This article explores the impact of enzyme deficiency on oral health, focusing on dental diseases in individuals with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency.
Introduction
Individuals with genetic disorders affecting steroid metabolism may experience dental aberrations due to steroid dehydrogenase deficiency. This condition can impact tooth development and lead to various dental abnormalities, highlighting the intricate connection between steroid hormones and oral health; Understanding the role of enzymes in steroid metabolism is crucial in comprehending the mechanisms underlying dental anomalies in these patients. By delving into the genetic basis of enzyme deficiency, we can unravel the complexities of how genetic mutations contribute to dental issues. This article aims to shed light on the clinical presentation of dental anomalies in individuals with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency and explore the management strategies for addressing dental health concerns in these patients. Additionally, preventive measures for promoting dental health in the context of genetic disorders will be discussed, along with recent research advances in dental care for individuals with enzyme dysfunction. The psychosocial impact of dental abnormalities will also be highlighted, emphasizing the holistic care needed for patients with dental aberrations associated with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency. By examining the intersections of genetics, steroid metabolism, and dental health, this article strives to enhance awareness and understanding of dental diseases in the context of genetic disorders.
Understanding Steroid Metabolism
Steroid metabolism plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including tooth development. Steroid hormones, such as cortisol and testosterone, are essential for normal growth and development. The process of steroid metabolism involves the synthesis, transportation, and breakdown of these hormones in the body. Enzymes, particularly steroid dehydrogenases, are key players in regulating steroid metabolism by catalyzing the conversion of one steroid hormone into another. This intricate enzymatic process ensures the balance and proper functioning of steroid hormones in the body. A disruption in steroid metabolism, often caused by enzyme deficiencies, can have significant implications for overall health, including dental abnormalities. In the context of dental aberrations associated with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency, understanding the intricate pathways of steroid metabolism is crucial. By elucidating how genetic mutations or enzyme dysfunction can impact the synthesis and metabolism of steroid hormones, healthcare providers can better grasp the underlying mechanisms behind dental anomalies in affected individuals. Through a comprehensive understanding of steroid metabolism, researchers and clinicians can develop targeted interventions to address dental health issues arising from disruptions in steroid hormone regulation due to enzyme deficiency.
Role of Enzymes in Steroid Metabolism
Enzymes play a critical role in steroid metabolism by catalyzing the conversion of steroid hormones into their active forms or metabolites. Specifically, steroid dehydrogenases are a group of enzymes essential for the interconversion between different steroid hormones. These enzymes facilitate reactions that involve the removal or addition of hydrogen atoms, thereby influencing the biological activity of steroids. Through their enzymatic activities, steroid dehydrogenases regulate the levels of specific steroid hormones in the body, ensuring a delicate balance necessary for physiological functions. In the context of dental aberrations associated with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency, a disruption in the activity of these enzymes can result in imbalances in steroid hormone levels, which may adversely affect tooth development and oral health. Understanding the precise functions of steroid dehydrogenases in steroid metabolism is crucial in deciphering how enzyme dysfunction can lead to dental abnormalities in individuals with genetic disorders affecting steroid metabolism. Researchers continue to explore the intricate mechanisms by which these enzymes impact steroid hormone synthesis and metabolism, aiming to uncover novel therapeutic strategies for managing dental issues in patients with enzyme deficiencies. By unraveling the role of enzymes in steroid metabolism, healthcare professionals can enhance their understanding of the pathophysiology underlying dental anomalies in individuals with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency.
Genetic Basis of Enzyme Deficiency
The genetic basis of enzyme deficiency in steroid metabolism disorders is often attributed to mutations in the genes encoding specific enzymes involved in steroid hormone synthesis and metabolism. These genetic mutations can disrupt the normal function of enzymes, leading to deficiencies that impair the conversion of one steroid hormone to another. In the case of steroid dehydrogenase deficiency, mutations in the genes coding for dehydrogenase enzymes can result in enzymatic dysfunction, affecting the balance of steroid hormones crucial for various physiological processes, including tooth development. These genetic alterations can be inherited in an autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant manner, depending on the specific gene involved and the pattern of inheritance. Understanding the genetic basis of enzyme deficiency in steroid metabolism disorders is essential for diagnosing and managing dental aberrations in affected individuals. Genetic testing and molecular analyses play a crucial role in identifying specific gene mutations responsible for enzyme dysfunction, enabling healthcare providers to tailor treatment strategies accordingly. By elucidating the genetic mechanisms underlying enzyme deficiencies in steroid dehydrogenase disorders, researchers aim to develop targeted therapies that address the root cause of dental anomalies associated with these genetic conditions. Advances in genetic research continue to enhance our knowledge of the complex genetic landscape of enzyme deficiencies in steroid metabolism, paving the way for personalized approaches to managing dental health issues in patients with genetic disorders affecting steroid metabolism.
Dental Abnormalities in Steroid Dehydrogenase Deficiency
Steroid dehydrogenase deficiency can manifest in a variety of dental abnormalities that affect tooth development and oral health. Patients with this condition may experience delayed eruption of primary and permanent teeth, abnormal tooth morphology, enamel defects, and malocclusions. The disruption in steroid metabolism due to enzyme dysfunction can impact the mineralization process during tooth formation, leading to structural anomalies such as microdontia, hypodontia, or taurodontism. Additionally, alterations in steroid hormone levels resulting from enzyme deficiency may influence the development of dental tissues, contributing to abnormalities in tooth structure and morphology. Individuals with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency are also predisposed to periodontal issues, including gingival hyperplasia and increased susceptibility to periodontal disease. The combined effects of disrupted steroid metabolism on tooth development and oral health underscore the intricate relationship between genetic disorders affecting steroid hormones and dental anomalies. Recognizing and addressing these dental abnormalities in patients with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency is essential for providing comprehensive care that encompasses both systemic and oral health management. Dental professionals play a crucial role in early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of dental issues associated with enzyme deficiencies in steroid metabolism disorders, aiming to optimize oral health outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals. By understanding the spectrum of dental abnormalities in steroid dehydrogenase deficiency, healthcare providers can tailor personalized treatment plans that address the unique oral health needs of each patient.
Clinical Presentation of Dental Anomalies
The clinical presentation of dental anomalies in individuals with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency can vary widely, reflecting the diverse spectrum of dental abnormalities associated with this genetic disorder. Patients may present with a range of dental issues, including delayed tooth eruption, abnormal tooth shape and size, enamel defects, and malocclusions. Upon examination, dental professionals may observe structural irregularities such as microdontia, hypodontia, or taurodontism, which are indicative of disturbances in tooth development linked to enzyme dysfunction affecting steroid metabolism. Enamel hypoplasia, characterized by thin or pitted enamel, and increased incidence of cavities may also be observed in affected individuals. Moreover, patients with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency may exhibit gingival hyperplasia, inflamed or enlarged gums, and compromised periodontal health. The clinical features of dental anomalies in these individuals underscore the complex interplay between genetic mutations disrupting steroid metabolism and the resulting effects on oral health. Diagnosing and monitoring dental issues in patients with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency require a comprehensive evaluation of the oral cavity, including dental radiographs, intraoral examinations, and possibly genetic testing to confirm the underlying genetic etiology. By recognizing the distinctive clinical presentation of dental anomalies in individuals with enzyme deficiencies affecting steroid metabolism, dental providers can effectively plan and implement tailored treatment approaches to address the oral health needs of these patients.
Management of Dental Issues in Patients with Enzyme Dysfunction
The management of dental issues in patients with enzyme dysfunction associated with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency requires a multidisciplinary approach to address the complex interplay between genetic factors, enzymatic abnormalities, and oral health manifestations. Treatment strategies focus on preventing and treating dental abnormalities while promoting overall oral health and well-being in affected individuals. Dental interventions may include orthodontic treatments to correct malocclusions, dental restorations to address enamel defects and cavities, and periodontal therapies to manage gingival hyperplasia and periodontal disease. Regular dental examinations and cleanings are essential to monitor dental health status and detect issues early. In severe cases, surgical procedures such as dental extractions or gingivectomies may be necessary to address advanced periodontal problems. Moreover, adjunctive therapies like fluoride treatments and dental sealants can help strengthen enamel and prevent tooth decay in patients with compromised dental health due to enzyme deficiencies. Collaborating with medical specialists familiar with the systemic implications of steroid dehydrogenase deficiency is crucial to ensure comprehensive care that considers both genetic and oral health aspects. By tailoring treatment plans to the individual needs of each patient, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals with dental aberrations linked to enzyme dysfunction in steroid metabolism disorders.
Preventive Strategies for Dental Health in Genetic Disorders
Implementing preventive strategies is paramount in maintaining optimal dental health in individuals with genetic disorders, including those affecting steroid metabolism and enzyme function. Regular dental visits for comprehensive examinations and cleanings are essential for early detection and management of dental issues. Education on proper oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and fluoride use, can help mitigate the risk of dental caries and periodontal disease. In individuals with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency, special attention should be given to monitoring enamel defects, malocclusions, and other dental anomalies that may require intervention. Dietary counseling to promote a tooth-friendly diet low in sugary and acidic foods can also aid in preventing dental complications. Additionally, the use of mouthguards in patients with malocclusions or enamel defects can help protect teeth from damage during activities that pose a risk to oral health. Collaboration between dental professionals and genetic specialists is crucial in developing personalized preventive strategies that address the unique oral health needs of individuals with genetic disorders affecting steroid metabolism. By proactively managing dental health through preventive measures, individuals with enzyme deficiencies linked to steroid dehydrogenase deficiency can enhance their oral health outcomes and minimize the impact of dental abnormalities on their overall well-being.
Research Advances in Dental Care for Genetic Disorders
Ongoing research in the field of dental care for genetic disorders, such as those associated with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency, continues to drive innovations in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of dental abnormalities. Advances in genetic testing technologies have improved the identification of specific gene mutations responsible for enzyme deficiencies affecting steroid metabolism, enabling targeted therapies tailored to the individual genetic profile of each patient. Novel treatment modalities, including gene therapy and precision medicine approaches, show promise in addressing the root cause of dental aberrations in individuals with genetic disorders. Researchers are exploring innovative strategies to enhance enamel mineralization, promote proper tooth development, and mitigate the impact of enzyme dysfunction on oral health outcomes in affected individuals. Collaborative efforts between dental professionals, geneticists, and researchers aim to translate scientific discoveries into clinical applications that revolutionize the management of dental issues in genetic disorders. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and leveraging interdisciplinary expertise, the future of dental care for individuals with enzyme deficiencies linked to steroid dehydrogenase deficiency holds great potential for improving oral health outcomes and quality of life for patients affected by these genetic conditions.
Psychosocial Impact of Dental Abnormalities
The psychosocial impact of dental abnormalities in individuals with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency can be substantial, affecting self-esteem, social interactions, and overall quality of life. Dental issues such as enamel defects, malocclusions, and delayed tooth eruption can impact an individual’s confidence and self-image, leading to feelings of self-consciousness and embarrassment. These psychological effects may extend to social settings, affecting relationships and interpersonal interactions. Individuals with visible dental anomalies may experience stigma or discrimination, further exacerbating the psychosocial burden associated with their condition. Addressing the emotional and psychological aspects of dental abnormalities is integral to providing holistic care for patients with enzyme deficiencies linked to genetic disorders. Psychosocial support, counseling, and education can help individuals cope with the challenges posed by their dental anomalies and build resilience in facing societal perceptions and pressures. Encouraging open communication and empowering patients to voice their concerns can foster a sense of control and agency in managing the psychosocial impact of their condition. By recognizing and addressing the psychosocial aspects of dental abnormalities in individuals with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency, healthcare providers can offer comprehensive care that considers both the physical and emotional well-being of the patient, ultimately promoting a positive outlook and enhancing overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dental aberrations associated with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency highlight the intricate relationship between genetic disorders affecting steroid metabolism and oral health outcomes. Enzyme deficiencies can lead to a spectrum of dental abnormalities, including delayed tooth eruption, enamel defects, malocclusions, and periodontal issues, impacting the overall dental health and quality of life of affected individuals. Understanding the genetic basis of enzyme dysfunction in steroid metabolism disorders is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies. Managing dental issues in patients with enzyme deficiencies requires a multidisciplinary approach, encompassing preventive measures, early intervention, and personalized care plans. Research advances in dental care for genetic disorders are paving the way for innovative treatments that target the root cause of dental anomalies in affected individuals, offering new hope for improved oral health outcomes. Moreover, addressing the psychosocial impact of dental abnormalities is essential in providing holistic care that supports the emotional well-being of patients with steroid dehydrogenase deficiency. By integrating cutting-edge research, personalized treatments, and psychosocial support, healthcare providers can enhance the overall care and quality of life for individuals with genetic disorders affecting steroid metabolism and dental health.