Introduction to Platelet Disorders
Platelet disorders are conditions that affect the number or function of platelets, leading to abnormal clotting mechanisms in the body. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, play a crucial role in hemostasis and wound healing. Understanding the causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments of platelet disorders is essential to manage and prevent complications related to these conditions.
Definition and Overview
Platelet disorders involve abnormalities in the number or function of platelets in the blood, impacting the body’s clotting ability. When platelet count is too high or too low, or platelets do not function correctly, it can lead to bleeding or clotting problems. Understanding the causes and manifestations of platelet disorders is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and management.
Causes of Platelet Disorders
Primary bone marrow disorders, chronic inflammation in the body, and inherited platelet disorders can contribute to the development of platelet abnormalities.
Primary Bone Marrow Disorders
Primary bone marrow disorders can lead to platelet disorders such as essential thrombocytosis, where the bone marrow produces excess platelets, elevating the risk of blood clot formation.
Chronic Inflammation in the Body
Primary bone marrow disorders, chronic inflammation, and inherited factors can contribute to platelet disorders. Primary bone marrow disorders like essential thrombocytosis result in the overproduction of platelets, while chronic inflammation conditions can disrupt platelet function.
Inherited Platelet Disorders
Inherited platelet disorders, caused by genetic anomalies affecting platelet formation or function, present a range of clinical complications. These conditions stem from molecular irregularities in genes crucial for platelet processes, leading to various manifestations that can impact individuals differently.
Types of Platelet Disorders
Thrombocytosis and thrombocythemia, thrombocytopenia, and platelet dysfunction are key platelet disorder classifications.
Thrombocytosis and Thrombocythemia
Thrombocytosis and thrombocythemia refer to conditions where the body produces an excessive number of platelets, potentially leading to an increased risk of blood clot formation. Understanding these platelet disorders is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is characterized by a low platelet count in the blood, which heightens the risk of bleeding. Individuals with this disorder may experience bruising, petechiae, and mucosal bleeding due to insufficient platelets for proper clot formation.
Platelet Dysfunction
Platelet dysfunction can stem from issues within the platelets themselves or external factors affecting their normal function. Proper functioning platelets are vital for effective blood clotting mechanisms in the body, emphasizing the importance of addressing any dysfunction promptly.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Platelet Disorders
Symptoms of high platelet count and diagnosis through CBC and coagulation tests are vital for identifying platelet disorders accurately.
Symptoms of High Platelet Count
High platelet count symptoms are often due to blood clot formation and may include chest pain, heart palpitations, difficulty breathing, dizziness, vision changes, weakness, fatigue, headaches, and leg pain or swelling.
Diagnosis through CBC and Coagulation Tests
Platelet disorders are often diagnosed through a complete blood count (CBC) to assess platelet levels and coagulation tests to evaluate blood clotting function. These diagnostic tools help healthcare providers determine the nature and severity of platelet abnormalities.
Bleeding Disorders and Risk of Hemorrhage
Platelet disorders can lead to bleeding issues, increasing the risk of hemorrhage, which can have serious consequences on an individual’s health.
Platelet disorders can disrupt the normal blood clotting mechanism, leading to an increased risk of bleeding and clotting complications that can impact overall health and well-being.
Platelet disorders disrupt the body’s blood clotting mechanism, leading to an increased risk of bleeding and clotting issues that can have significant repercussions on an individual’s health and well-being.

Platelet disorders disrupt the body’s blood clotting mechanism, increasing the risk of bleeding and clotting issues.
Medication and Therapeutic Approaches
Managing platelet disorders often involves medications and therapeutic approaches aimed at regulating platelet levels and improving blood clotting function. These treatment strategies play a crucial role in controlling the complications associated with platelet abnormalities.
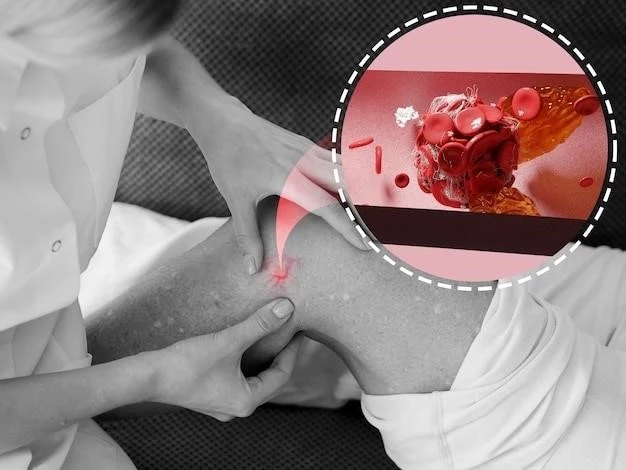
Impact on Blood Clotting Mechanism
Platelet disorders often disrupt the blood clotting mechanism, increasing the risk of bleeding and clotting complications that can affect an individual’s health significantly.
Managing platelet disorders involves adopting lifestyle changes and following specific dietary recommendations to support overall health and mitigate the impact of the condition.
Monitoring Platelet Counts and Regular Check-ups
Regular monitoring of platelet counts and consistent check-ups are essential in managing and preventing complications associated with platelet disorders.
Lifestyle Changes and Dietary Recommendations
Managing platelet disorders includes adopting healthy lifestyle changes and following specific dietary recommendations to support overall well-being and optimize platelet function.
Ongoing research and clinical trials aim to advance the treatment options for platelet disorders, exploring innovative approaches to managing these conditions effectively.
Current Studies and Clinical Trials
Ongoing research and clinical trials are exploring innovative approaches to advance the treatment of platelet disorders, aiming to enhance management strategies and outcomes for individuals impacted by these conditions.
Future Prospects for Platelet Disorder Management
Ongoing research and advancements in platelet disorder treatment hold promising prospects for enhancing management strategies and improving outcomes for individuals affected by these conditions in the future.
Platelet disorders can have psychological and emotional impacts on individuals, affecting their quality of life and well-being.
Social Support and Coping Strategies
Dealing with platelet disorders can have emotional impacts, highlighting the importance of social support and effective coping strategies to enhance quality of life.
Psychological and Emotional Effects
Dealing with platelet disorders can have psychological and emotional effects on individuals, emphasizing the need for social support and effective coping strategies to enhance quality of life.
In conclusion, platelet disorders can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, affecting their physical and emotional well-being. It is crucial to address the psychological and emotional effects, seek social support, and employ effective coping strategies to navigate the challenges associated with these conditions.
Summary of Key Points
Platelet disorders can significantly impact individuals’ quality of life by affecting both physical and emotional well-being. Proper management includes seeking social support and employing effective coping strategies to navigate the challenges associated with these conditions successfully. It is essential to address the psychological and emotional effects of platelet disorders to enhance overall quality of life.
