Abdominal neoplasms refer to abnormal growths in the abdomen, affecting organs like the stomach, liver, or intestines. Understanding these growths is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Symptoms of Abdominal Neoplasms
Common symptoms of abdominal neoplasms may include unexplained weight loss, abdominal pain or discomfort, bloating, changes in bowel habits, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. It’s essential to seek medical advice if experiencing persistent or worsening symptoms.
Other symptoms can vary based on the specific location and type of the neoplasm. For example, liver neoplasms may cause jaundice, while stomach neoplasms can lead to indigestion or difficulty swallowing. Understanding the symptoms can aid in prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options for Abdominal Neoplasms
Treatment for abdominal neoplasms depends on factors like the type, location, and stage of the neoplasm. Common approaches include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Surgery aims to remove the neoplasm and surrounding tissues. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells, while radiation therapy targets the cancer with high-energy rays. Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in tumor growth, and immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune response against the neoplasm.
Depending on the individual’s case, a combination of these treatments may be recommended. It’s important for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the most suitable treatment plan for their abdominal neoplasm.
Causes of Abdominal Neoplasms
Abdominal neoplasms can develop due to various factors. Some common causes include genetic mutations, exposure to carcinogens like tobacco smoke or certain chemicals, family history of cancer, obesity, unhealthy diet high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables, chronic inflammation, and certain infections like hepatitis B or C viruses.
Additionally, age, gender, and lifestyle choices such as alcohol consumption and lack of physical activity can also contribute to the development of abdominal neoplasms. Understanding the possible causes can help in taking preventive measures and making informed decisions regarding lifestyle changes and screenings.
Diagnosis of Abdominal Neoplasms
Diagnosing abdominal neoplasms typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, imaging tests like CT scans, MRIs, ultrasounds, and PET scans, as well as biopsy for tissue analysis. Blood tests may also be done to check for certain markers associated with neoplasms.
If a neoplasm is suspected, a healthcare provider may refer the patient to a specialist for further evaluation and management. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the type, stage, and extent of the neoplasm, which guides the treatment plan and prognosis.
Prevention of Abdominal Neoplasms
Reducing the risk of developing abdominal neoplasms can be achieved through lifestyle modifications and regular screenings. Maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, limiting alcohol intake, avoiding tobacco products, and staying physically active are key preventive measures.
Screening tests can help detect neoplasms at an early stage when treatment is more effective. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate screening schedule based on individual risk factors and family history. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and undergoing recommended screenings, one can take proactive steps in preventing abdominal neoplasms.
Types of Abdominal Neoplasms
Abdominal neoplasms encompass a wide range of tumor types that can affect different organs within the abdomen. Some common types include⁚
- Stomach Cancer⁚ Also known as gastric cancer, it originates in the lining of the stomach.
- Liver Cancer⁚ Hepatocellular carcinoma is a primary liver cancer that develops in the liver cells.
- Colon Cancer⁚ Arising in the colon or rectum, colorectal cancer is a common type of abdominal neoplasm.
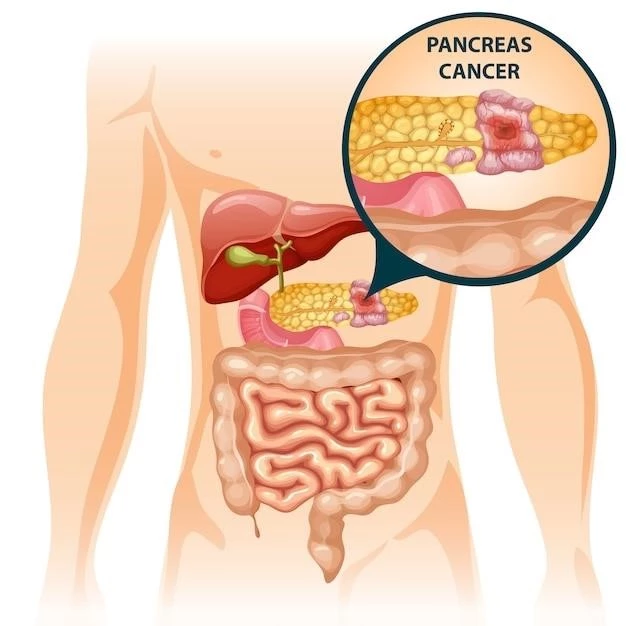
- Pancreatic Cancer⁚ This type affects the pancreas, an essential organ involved in digestion and hormone regulation.
- Ovarian Cancer⁚ Neoplasms in the ovaries can be of different types, including epithelial ovarian cancer.
Other types of abdominal neoplasms include gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), renal cell carcinoma affecting the kidneys, and neuroendocrine tumors that arise in various organs like the pancreas or intestines. Understanding the specific type of neoplasm is crucial for devising an appropriate treatment approach.

Risk Factors for Abdominal Neoplasms
Several risk factors may contribute to the development of abdominal neoplasms. These include⁚
- Age⁚ The risk of neoplasms tends to increase with age.
- Family History⁚ A family history of certain cancers can elevate an individual’s risk.
- Obesity⁚ Being overweight or obese is a known risk factor for various cancers, including abdominal neoplasms.
- Smoking⁚ Tobacco use is linked to an increased risk of developing abdominal neoplasms.
- Alcohol Consumption⁚ Excessive alcohol intake can raise the risk of certain neoplasms like liver cancer.
- Environmental Factors⁚ Exposure to toxins or carcinogens in the environment can play a role.
By understanding these risk factors, individuals can make informed choices to reduce their risk of developing abdominal neoplasms through lifestyle changes and proactive health management.