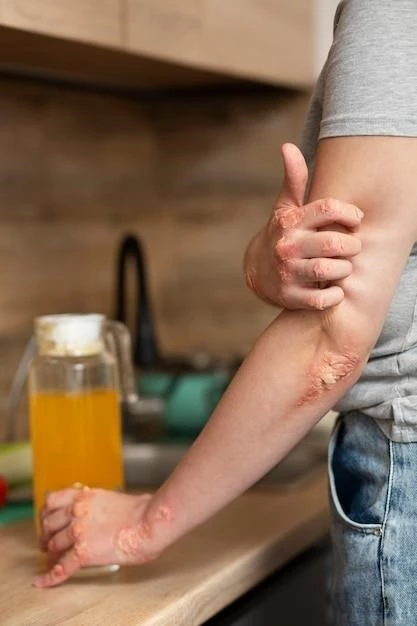
Disease ‒ Flesh Eating Bacteria
Learn about the alarming infection caused by flesh-eating bacteria. Discover the devastating effects on tissue and the importance of early intervention. Understand the risk factors and treatment options available to combat this severe condition.
Introduction
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on flesh-eating bacteria, a rare yet serious infection known as necrotizing fasciitis. This condition rapidly deteriorates soft tissue and can lead to life-threatening complications like sepsis. Understanding the nature of this disease is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Stay informed to protect yourself and your loved ones from the devastating consequences of this aggressive infection.
Necrotizing fasciitis, often caused by invasive bacteria, requires immediate medical attention to prevent extensive tissue damage. Learn about the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available. Explore the risk factors that increase susceptibility to this infection and the potential outcomes if not addressed promptly. By educating yourself about flesh-eating bacteria, you empower yourself to recognize the signs early and seek timely medical intervention.
Throughout this article, we will delve into the intricacies of flesh-eating bacteria, shedding light on the essential information needed to navigate this challenging medical condition. From understanding the different types of bacteria responsible for necrotizing fasciitis to discussing the implications of severe tissue damage, we aim to equip you with the knowledge required to make informed decisions in the face of this rare but serious infectious disease. Stay tuned for valuable insights into prevention strategies, treatment advancements, and the critical role of early intervention in combating flesh-eating bacteria.
Understanding Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis, commonly referred to as flesh-eating bacteria, is a rare but serious infection that affects the deeper layers of skin and subcutaneous tissues. This aggressive condition can rapidly progress, leading to extensive tissue damage and potentially life-threatening complications such as sepsis. It is crucial to recognize the early signs and symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis to seek immediate medical attention.
The bacteria responsible for necrotizing fasciitis can enter the body through a break in the skin, such as a cut, surgical incision, or insect bite. Once inside, the bacteria release toxins that destroy soft tissue, including muscle and fat. This rapid destruction of tissue can result in severe pain, redness, swelling, and a fever that worsens rapidly.
Diagnosing necrotizing fasciitis often requires a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and sometimes surgical exploration to assess the extent of tissue damage. Early diagnosis is key to preventing the spread of infection and minimizing the risk of complications. Prompt initiation of treatment, which may include surgery and intravenous antibiotics, is essential to halt the progression of the infection and save the affected tissue.
Understanding the nature of necrotizing fasciitis is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public. By familiarizing yourself with the symptoms and risk factors associated with this condition, you can improve your chances of early detection and intervention. Stay vigilant, and seek prompt medical attention if you suspect you or someone you know may be experiencing symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis.
Types of Bacteria
Several types of bacteria can cause necrotizing fasciitis, each with its own distinct characteristics and methods of infection. Common culprits include Group A Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium perfringens, and Vibrio vulnificus, among others. These bacteria thrive in different environments and can enter the body through various means, leading to the development of necrotizing fasciitis.
Group A Streptococcus, a bacteria frequently found in the throat and on the skin, is a common cause of necrotizing fasciitis. This bacterium can rapidly spread and release toxins that damage tissue. Staphylococcus aureus, another prevalent bacteria, is known for causing skin infections that can progress to necrotizing fasciitis under certain conditions. Clostridium perfringens, commonly found in soil and the intestines of humans and animals, is a less common but potent cause of this condition.
Vibrio vulnificus, often associated with contaminated water, particularly in warmer coastal regions, can lead to necrotizing fasciitis when it enters the body through cuts or wounds exposed to seawater. Understanding the types of bacteria that can cause necrotizing fasciitis is essential for recognizing the source of infection and determining the appropriate treatment approach. By staying informed about these bacteria, you can take proactive steps to reduce your risk of developing this severe and potentially life-threatening condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis is crucial for early intervention and improved outcomes. Common signs include severe pain beyond the area of the skin wound, rapidly worsening redness, swelling, and a fever. As the infection progresses, skin may become discolored, and the affected area may develop blisters or ulcers.
Diagnosing necrotizing fasciitis often requires a combination of clinical assessment, imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs, blood tests to check for signs of infection, and sometimes surgical exploration to confirm the extent of tissue damage. Healthcare providers will also consider the rapid onset and progression of symptoms when determining a diagnosis.
If you experience symptoms such as intense pain, swelling, or redness following a skin injury or wound, seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in managing necrotizing fasciitis and preventing complications. Do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect you may be at risk for this severe infection.
By staying vigilant and aware of the symptoms associated with necrotizing fasciitis, you can act swiftly to address the infection and minimize tissue damage. Remember that timely diagnosis and treatment are essential in combating this aggressive disease. Trust your instincts and prioritize your health by seeking medical evaluation if you suspect you may be experiencing symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis.
Tissue Damage and Progression
The progression of necrotizing fasciitis involves rapid and extensive tissue damage that can have severe consequences if left untreated. As the infection spreads, the bacteria release toxins that break down the skin, fat, and muscle tissues. This process leads to the formation of dead, necrotic tissue that must be removed to prevent further spread of the infection.
The damage caused by necrotizing fasciitis can result in the loss of blood supply to the affected area, leading to tissue death and the formation of deep ulcers or open wounds. Without prompt medical intervention, the infection can rapidly progress, affecting larger areas of soft tissue and increasing the risk of complications such as sepsis, organ failure, and limb loss.
Monitoring the progression of tissue damage is essential in managing necrotizing fasciitis. Healthcare providers may need to perform surgical debridement, a procedure to remove dead tissue, to prevent the spread of infection and promote healing. In severe cases, amputation of affected limbs or tissue may be necessary to save the patient’s life.
Understanding the implications of tissue damage in necrotizing fasciitis underscores the importance of early diagnosis and intervention. By recognizing the signs of tissue necrosis and seeking timely medical care, individuals can improve their chances of recovering from this aggressive infection. Stay vigilant, and do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect tissue damage or necrosis associated with necrotizing fasciitis.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing necrotizing fasciitis, a serious infection caused by flesh-eating bacteria. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, cancer, or chronic illnesses, are more susceptible to infection due to reduced immune response. People with compromised skin barriers, such as cuts, wounds, or surgical incisions, are also at higher risk of bacteria entering the body and causing necrotizing fasciitis.
Chronic conditions like obesity and peripheral vascular disease can impair blood flow and wound healing, creating an environment conducive to bacterial infection. Intravenous drug use and alcoholism can weaken the body’s defenses, making individuals more vulnerable to invasive infections like necrotizing fasciitis. Additionally, older adults and the elderly are at increased risk due to age-related immune system changes.
Engaging in activities that involve exposure to natural bodies of water, especially in warm coastal regions, raises the risk of infection with bacteria like Vibrio vulnificus, a common cause of necrotizing fasciitis. Poor hygiene practices, inadequate wound care, and a history of skin conditions can also contribute to the development of this serious soft tissue infection.
Understanding the risk factors associated with necrotizing fasciitis is essential in taking proactive measures to reduce susceptibility to infection. By addressing underlying health conditions, practicing good wound care hygiene, and seeking prompt medical attention for skin injuries, individuals can lower their risk of developing this potentially life-threatening disease. Stay informed, and consult healthcare professionals if you have concerns about your risk factors for necrotizing fasciitis.
Treatment Options
Timely and aggressive treatment is essential in managing necrotizing fasciitis, a severe infection caused by flesh-eating bacteria. The primary goal of treatment is to eradicate the infection, minimize tissue damage, and prevent life-threatening complications. A multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals from various specialties is often necessary to address the complexities of necrotizing fasciitis.
Surgical intervention plays a crucial role in the treatment of necrotizing fasciitis. Debridement, the surgical removal of dead or infected tissue, is often performed to halt the spread of infection and promote healing. In severe cases, amputation of affected limbs or tissue may be required to save the patient’s life and prevent the infection from spreading further.
Antibiotics are commonly used in combination with surgical procedures to combat the bacterial infection. Intravenous antibiotics are administered to target the specific bacteria responsible for necrotizing fasciitis and prevent further tissue destruction. Close monitoring of the patient’s response to antibiotics is essential to ensure the effectiveness of treatment.
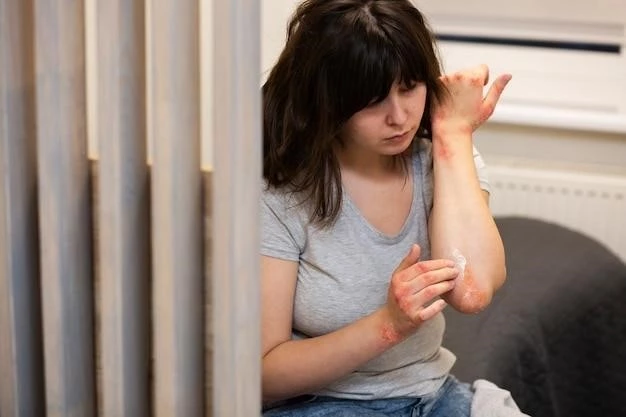

In some cases, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be utilized to enhance tissue oxygenation and promote healing. This adjunctive therapy can help improve wound healing and tissue recovery in individuals with necrotizing fasciitis. Intensive care support may also be necessary to stabilize patients with severe infections and manage potential complications like sepsis.
Understanding the treatment options available for necrotizing fasciitis is vital for patients and healthcare providers alike. By exploring surgical interventions, antibiotic therapies, and supportive care measures, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their treatment plan. Trust in the expertise of your healthcare team and follow their recommendations to maximize the chances of recovery from this challenging and potentially life-threatening infection.
Amputation and Mortality
In severe cases of necrotizing fasciitis, amputation may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection and save the individual’s life. Amputation involves the surgical removal of affected limbs or tissue that cannot be salvaged due to extensive tissue damage or the presence of necrotic tissue. While amputation is a drastic measure, it can be life-saving in the context of necrotizing fasciitis.
The decision to amputate is made based on several factors, including the extent of tissue damage, the risk of sepsis and organ failure, and the patient’s overall health and prognosis. Healthcare providers carefully assess the benefits and risks of amputation to determine the most appropriate course of action for each individual. Rehabilitation and support services are often provided to help patients adjust to life after amputation.
Mortality rates associated with necrotizing fasciitis can be significant, especially in cases where diagnosis and treatment are delayed or the infection is particularly aggressive. The risk of death from necrotizing fasciitis underscores the importance of early intervention, prompt diagnosis, and aggressive treatment to minimize the impact of this devastating infection.
It is essential for individuals to be aware of the potential consequences of necrotizing fasciitis, including the risk of amputation and mortality. By recognizing the severity of the infection and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can improve their chances of a successful outcome. Trust in the expertise of your healthcare team and follow their guidance to address necrotizing fasciitis effectively and minimize the risk of complications.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is paramount in the management of necrotizing fasciitis, a fast-progressing infection caused by flesh-eating bacteria. Prompt recognition of symptoms, immediate medical evaluation, and early initiation of treatment can significantly impact the outcome of this serious condition. Timely intervention can help prevent the rapid spread of infection, reduce tissue damage, and improve the chances of recovery.
Delaying medical care for necrotizing fasciitis can have devastating consequences, including the need for extensive surgical interventions like amputation and an increased risk of mortality. By recognizing the signs of necrotizing fasciitis early on and seeking immediate medical attention, individuals can avoid potentially life-threatening complications and improve their prognosis.
Healthcare providers emphasize the importance of early intervention in necrotizing fasciitis due to its aggressive nature and potential for rapid deterioration. Being proactive about seeking medical help at the first signs of infection, such as severe pain, redness, and swelling, is crucial in managing this challenging disease. Do not hesitate to contact healthcare professionals if you suspect you may have necrotizing fasciitis.
Educating yourself about the urgency of early intervention in necrotizing fasciitis empowers you to take swift action in response to potential symptoms. By prioritizing early detection and treatment, you can optimize your chances of a successful outcome and minimize the risk of severe tissue damage or complications associated with this dangerous infection. Act promptly, trust your instincts, and seek medical assistance without delay in suspected cases of necrotizing fasciitis.
Post-Treatment Care
Post-treatment care plays a crucial role in the recovery process following treatment for necrotizing fasciitis, a severe infection caused by flesh-eating bacteria. After medical interventions such as surgery and antibiotic therapy, it is essential to follow healthcare providers’ guidance to promote healing, prevent complications, and regain optimal health.
Patients recovering from necrotizing fasciitis may require ongoing wound care to facilitate proper healing of surgical incisions and affected areas. This may involve changing dressings, keeping the wound clean, and monitoring for signs of infection. Following post-operative instructions carefully is paramount in reducing the risk of wound complications.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation may be recommended to help patients regain strength, mobility, and function after treatment for necrotizing fasciitis. These therapies can aid in restoring muscle strength, improving range of motion, and enhancing overall quality of life following the challenges of infection and surgical interventions.
Emotional support and counseling may be beneficial for individuals recovering from necrotizing fasciitis, as the experience of facing a life-threatening infection can be mentally and emotionally challenging. Seeking support from mental health professionals or support groups can help individuals cope with the psychological impact of the infection and adjust to life post-treatment.
Adhering to follow-up appointments with healthcare providers is crucial in monitoring recovery progress, addressing any concerns or complications that may arise, and ensuring the effectiveness of treatment. By actively participating in post-treatment care and maintaining open communication with your healthcare team, you can support your recovery journey and optimize the outcomes of treatment for necrotizing fasciitis.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research and advancements in the field of necrotizing fasciitis play a vital role in improving the understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of this severe infection caused by flesh-eating bacteria. Scientific studies aim to uncover new insights into the mechanisms of the disease, develop more effective diagnostic tools, and explore innovative treatment approaches to enhance patient outcomes.
Researchers are investigating potential biomarkers and diagnostic techniques that can aid in the early detection of necrotizing fasciitis, allowing for prompt intervention and improved prognosis. Advancements in imaging technologies, such as MRI and ultrasound, are being explored to enhance accuracy in diagnosing the extent of tissue damage associated with the infection.
In the realm of treatment, antimicrobial strategies, including novel antibiotic combinations and targeted therapies, are being studied to combat antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria responsible for necrotizing fasciitis. Immunotherapy and adjunctive therapies like hyperbaric oxygen are also under investigation for their potential to boost the immune response and promote tissue healing.
Clinical trials and collaborative research efforts are essential for evaluating the safety and efficacy of new treatment modalities for necrotizing fasciitis. These studies play a critical role in advancing medical knowledge, refining treatment protocols, and ultimately improving patient outcomes in the battle against this life-threatening infection.
By supporting research initiatives and staying informed about the latest advancements in the field, both healthcare professionals and individuals affected by necrotizing fasciitis can contribute to the collective effort to enhance understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of this challenging disease. Engage with healthcare providers, participate in clinical trials when appropriate, and advocate for continued research to drive progress in the fight against flesh-eating bacteria.
Prevention Strategies
Implementing effective prevention strategies is key to reducing the risk of necrotizing fasciitis, a serious infection caused by flesh-eating bacteria. Practicing good wound care hygiene, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and taking precautions in high-risk environments can help minimize the chances of developing this rare yet potentially life-threatening condition.
Proper wound care is essential in preventing infections that can lead to necrotizing fasciitis. Clean cuts, scrapes, and any open wounds promptly with soap and water, apply antiseptic agents, and cover them with sterile bandages. Avoid exposing wounds to contaminated water or soil, especially in environments where bacterial pathogens thrive.
Maintaining good overall health is crucial in bolstering the immune system and reducing vulnerability to infections like necrotizing fasciitis. Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients, staying physically active, and managing chronic conditions effectively can enhance immunity and reduce the risk of complications from bacterial infections.
Individuals engaging in activities that involve potential exposure to flesh-eating bacteria should take precautions to protect themselves; Wear protective gear, such as appropriate footwear and clothing, when in areas where bacterial pathogens may be present. Be cautious when swimming in natural bodies of water, especially in warm coastal regions known for bacterial contamination.
Education and awareness are fundamental in preventing necrotizing fasciitis. Stay informed about the symptoms of the infection, risk factors, and preventive measures. Educate others in your community about proper wound care, hygiene practices, and the importance of seeking medical attention promptly if an infection is suspected. By promoting awareness and taking proactive steps to prevent necrotizing fasciitis, individuals can reduce their risk of encountering this severe bacterial infection.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness and promoting education about necrotizing fasciitis, a severe infection caused by flesh-eating bacteria, are crucial in preventing the onset and complications of this rare disease. Educating individuals about the risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures associated with necrotizing fasciitis can empower communities to recognize and address the infection promptly.
Engaging in community initiatives, public health campaigns, and educational programs can help disseminate accurate information about necrotizing fasciitis to a broader audience. By collaborating with healthcare professionals, advocacy groups, and local organizations, communities can work together to raise awareness about the signs of infection and the importance of seeking timely medical care.
Utilizing various communication channels, such as social media, public service announcements, and informational websites, can facilitate the dissemination of educational materials related to necrotizing fasciitis. Providing accessible resources that outline the risks of the infection, preventive strategies, and steps to take if infection is suspected can empower individuals to protect themselves and their loved ones.
Healthcare providers play a vital role in educating patients, caregivers, and the general public about necrotizing fasciitis. By offering accurate information, preventive guidance, and resources for early intervention, healthcare professionals can contribute to the overall awareness and understanding of this potentially life-threatening infection. Encouraging open dialogue and addressing concerns about necrotizing fasciitis can help dispel misconceptions and foster a proactive approach to infection prevention.
By prioritizing public awareness and education initiatives surrounding necrotizing fasciitis, communities can work together to minimize the impact of this aggressive infection. Empowering individuals with knowledge about the infection, its risk factors, and preventive measures is essential in building resilient communities that are prepared to recognize and respond to the challenges posed by flesh-eating bacteria.
In conclusion, necrotizing fasciitis, commonly known as flesh-eating bacteria, is a rare yet life-threatening infection that requires swift intervention and comprehensive treatment. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and importance of early diagnosis is crucial in addressing this aggressive disease. Timely medical attention, including surgical intervention, antibiotic therapy, and supportive care, is essential in managing necrotizing fasciitis effectively.
Prevention strategies, such as practicing good wound care hygiene, maintaining overall health, and promoting public awareness, play a significant role in reducing the risk of necrotizing fasciitis. By staying informed, taking preventive measures, and seeking prompt medical care when needed, individuals can minimize their susceptibility to this serious bacterial infection.
Advancements in research and treatment offer hope for improved outcomes in the management of necrotizing fasciitis. Collaborative efforts, ongoing studies, and innovative approaches are shaping the future of care for individuals affected by flesh-eating bacteria. By supporting research initiatives and staying actively engaged in healthcare, we can work towards better understanding and combating this challenging infection.
Through education, awareness, and proactive measures, we can empower individuals and communities to recognize the signs of necrotizing fasciitis, take preventive actions, and advocate for early intervention. By fostering a culture of preparedness and resilience, we can work together to mitigate the impact of necrotizing fasciitis and protect the well-being of those at risk. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against flesh-eating bacteria.