Gray matter heterotopia (GMH) is a group of neurological disorders characterized by ectopic neurons, including periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH) and subcortical band heterotopia. This article focuses on the clinical aspect of subependymal nodular heterotopia, the most common subtype of GMH.
Definition and Characteristics
Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia (SNH) is a common neurological disorder characterized by clusters of gray matter nodules located along the lateral ventricular walls. These nodules are often associated with epilepsy and cerebral malformations, with X-linked inheritance patterns observed in some cases. SNH can be diagnosed using imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans, allowing for appropriate management and treatment strategies.
Types and Classification
Gray matter heterotopia manifests as periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH) or subcortical band heterotopia (SBH), with different characteristics and locations.
Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia (PNH)
Periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH), also known as subependymal nodular heterotopia, is a common type of gray matter heterotopia characterized by gray matter nodules lining the walls of the lateral ventricles.
Subcortical Band Heterotopia (SBH)
Subcortical band heterotopia (SBH) is a type of gray matter heterotopia characterized by a band of neurons located below the cortex. This condition, also known as double cortex or band heterotopia, presents unique characteristics and implications for affected individuals.
Clinical Presentation
Gray matter heterotopia can manifest as periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH) or subcortical band heterotopia (SBH) with distinct clinical features.
Symptoms and Associated Conditions
Subependymal nodular heterotopia can present with a variety of symptoms, including epilepsy, cognitive impairments, and developmental delays. Associated conditions may include other malformations of cortical development and X-linked inheritance patterns in some cases.
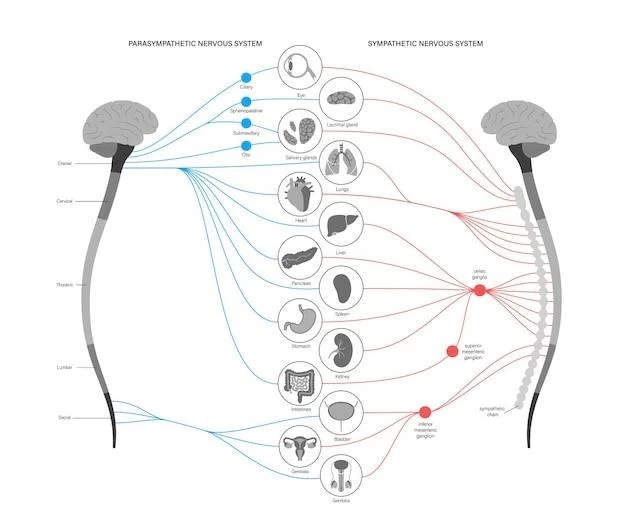
Diagnosis of Subependymal Nodular Heterotopia
Diagnosis of subependymal nodular heterotopia is usually achieved through imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans as well as genetic testing for precise identification.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans play a crucial role in diagnosing subependymal nodular heterotopia by visualizing gray matter nodules along the lateral ventricles and guiding treatment decisions.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing plays a vital role in diagnosing subependymal nodular heterotopia, helping identify specific genetic mutations or variations that contribute to the development of this condition.
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management strategies for subependymal nodular heterotopia involve various medical interventions and surgical options tailored to individual cases.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions for subependymal nodular heterotopia may involve pharmacological treatments to manage epilepsy, cognitive impairments, and developmental delays associated with the condition. Additionally, supportive therapies may be implemented to address specific symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Surgical Options
Surgical interventions for subependymal nodular heterotopia may include resection of abnormal gray matter nodules to alleviate seizures and improve neurological outcomes, particularly in cases refractory to medical management.
Prognosis and Complications
The prognosis of subependymal nodular heterotopia varies based on individual cases and the presence of associated complications, impacting the quality of life for affected individuals.
Impact on Quality of Life
The presence of subependymal nodular heterotopia can significantly impact the quality of life of affected individuals, resulting from associated symptoms, potential complications, and the need for ongoing management strategies.
Research and Advances in Understanding
Ongoing research on subependymal nodular heterotopia focuses on genetic mutations, neuronal migration disorders, and advancements in diagnostic imaging techniques to enhance understanding and improve patient care.
Genetic Mutations and Pathogenesis
Genetic mutations play a crucial role in the development of subependymal nodular heterotopia, with specific mutations identified in genes like filamin 1. Understanding the pathogenesis of these mutations is essential for elucidating the underlying mechanisms of the condition.
Patients and families affected by subependymal nodular heterotopia can benefit from specialized diagnostic teams and support from geneticists and neurologists for comprehensive care;
Support and Resources for Patients and Families
Patients and families impacted by subependymal nodular heterotopia can benefit from the specialized expertise of diagnostic teams comprising genetics and neurology professionals, providing comprehensive care and support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, subependymal nodular heterotopia presents a complex neurological condition with significant implications for patients. Enhancing diagnostic methods, understanding genetic mutations, and tailored treatment strategies are essential in managing this condition effectively.