Introduction to Quinckes Edema
Isolated angioneurotic edema of the uvula is termed Quinckes disease․ It is a rare clinical disorder of acute onset with few known causes․ It may be encountered in any emergency setup and must be dealt with rapidly and with utmost vigilance for prevention of progression and complications․ Quinckes disease, or isolated uvular angioedema, was first described in 1882 and has since been a relatively rare form of angioedema of the upper airway․ Although it is typically caused by an immediate Type I hypersensitivity reaction, uvular edema can also be caused by trauma, thermal injury, and infections․
Isolated angioneurotic edema of the uvula is named Quinckes disease, a rare disorder characterized by acute onset swelling․ First described in 1882, this condition primarily results from hypersensitivity reactions but can also be triggered by trauma, thermal injury, and infections․ Notably, Quinckes edema can lead to severe manifestations, particularly in the upper airway, necessitating prompt and vigilant management to avert complications․
Description and Background Information
Isolated angioneurotic edema of the uvula, known as Quinckes disease, is a rare clinical disorder onset․ First described in 1882, it is primarily triggered by hypersensitivity reactions but can also result from trauma, thermal injury, and infections․ Management of this condition requires prompt attention due to potential complications, especially in the upper airway;
Quinckes disease, or isolated uvular angioedema, is a rare clinical disorder first described in 1882․ This condition٫ characterized by acute onset swelling٫ primarily results from hypersensitivity reactions but can also be triggered by trauma٫ thermal injury٫ and infections․ The historical context of Quinckes edema underscores its significance as a relatively uncommon form of angioedema with potential severe manifestations٫ especially in the upper airway․
Clinical Presentation and Rareness
Quinckes edema, characterized by acute onset swelling primarily due to hypersensitivity reactions but also trauma, thermal injury, and infections, presents rare clinical manifestations, particularly in the upper airway․ Prompt recognition and management are crucial to prevent progression and complications associated with this unique condition․
Quinckes disease, or isolated uvular angioedema, is a rare clinical disorder first described in 1882․ This condition, characterized by acute onset swelling, primarily results from hypersensitivity reactions but can also be triggered by trauma, thermal injury, and infections․ The historical context of Quinckes edema underscores its significance as a relatively uncommon form of angioedema with potential severe manifestations, especially in the upper airway․
Quinckes disease, or isolated uvular angioedema, may be triggered by various factors such as hypersensitivity reactions, trauma, thermal injury, and infections․ Additionally, the condition can result from specific causes like allergic reactions to medications, food allergens, and genetic predispositions․ Understanding these diverse triggers is essential for effective management and prevention strategies․
Etiological Factors and Triggers
Quinckes disease, also known as isolated uvular angioedema, can be triggered by various factors such as hypersensitivity reactions, trauma, thermal injury, and infections․ Allergies to medications, food allergens, genetic predispositions, and specific triggers like insect venom are also known to contribute to the development of this condition․ Understanding these diverse etiological factors and triggers is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of Quinckes edema․
Definition and Historical Context
Quinckes disease, or isolated uvular angioedema, is a rare clinical disorder first described in 1882․ This condition, characterized by acute onset swelling, primarily results from hypersensitivity reactions but can also be triggered by trauma, thermal injury, and infections․ The historical context of Quinckes edema underscores its significance as a relatively uncommon form of angioedema with potential severe manifestations, especially in the upper airway․
Quinckes edema, also known as angioedema, manifests as swelling in the deeper skin layers, particularly around the eyes and lips․ While often harmless and manageable with antihistamine medication, severe cases of Quinckes edema can pose life-threatening risks, especially if the swelling affects the airway, potentially leading to airway obstruction․
Common Areas Affected by the Swelling
Quinckes edema commonly affects deeper skin layers, particularly around the eyes and lips, leading to visible swelling․ While manageable with antihistamine medication in most cases, severe manifestations of Quinckes edema can pose life-threatening risks, especially if the swelling obstructs the airway, necessitating urgent medical intervention․
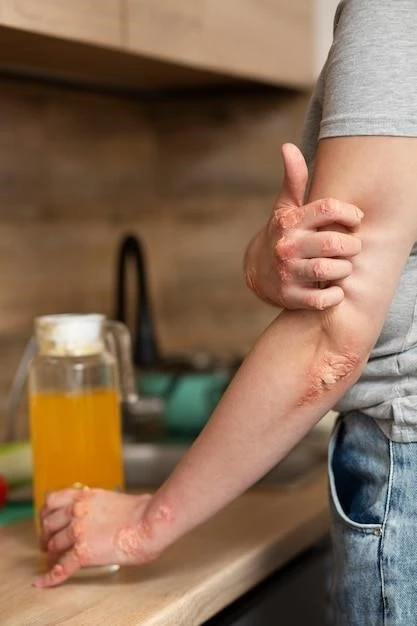
Quinckes edema typically presents as swelling in deeper skin layers, commonly around the eyes and lips․ Although manageable with antihistamine medication in many cases, severe forms can pose life-threatening risks, especially if the swelling affects the airway, potentially leading to airway obstruction and necessitating urgent medical attention․
Medical Evaluation and Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing Quinckes edema typically involves a physical examination to assess swelling in deeper skin layers, especially around the eyes and lips․ Diagnostic procedures may include allergy testing, blood tests for underlying conditions, and imaging studies to evaluate airway involvement․ Distinguishing Quinckes edema from other similar conditions is crucial for appropriate treatment planning and management․
Distinguishing Quinckes Edema from Other Conditions
Quinckes edema, characterized by localized skin or mucous membrane swelling, typically differentiates from other conditions through its association with allergic reactions and specific medical backgrounds․ Proper diagnosis of Quinckes edema is crucial to differentiate it from similar presentations and ensure appropriate management based on the underlying cause․
Physical Indicators and Manifestations
Quinckes edema typically manifests as swelling in deeper skin layers, notably around the eyes and lips․ While usually manageable with antihistamines, severe cases may lead to life-threatening airway obstruction․
Management Strategies and Medication
Treatment approaches for Quinckes edema often involve the use of antihistamine medication to manage symptoms related to swelling․ In severe cases where the airway is compromised, emergency interventions such as intubation or tracheostomy may be necessary to ensure adequate breathing and prevent life-threatening complications․
Potential Complications and Emergency Interventions
In severe cases, Quinckes edema may lead to life-threatening complications such as airway obstruction․ Emergency interventions like intubation or tracheostomy might be necessary to ensure proper breathing and prevent adverse outcomes․ Prompt medical attention is vital to manage these emergent situations effectively․
The prognosis for Quinckes edema is generally favorable with prompt treatment․ Recurrence risks vary depending on the underlying cause and management effectiveness․ Monitoring and addressing potential triggers can help mitigate the likelihood of future episodes, enhancing long-term outcomes and quality of life․
Recovery Rates and Recurrence Risks
Management of Quinckes edema typically leads to favorable recovery rates․ Recurrence risks vary based on the specific triggers and individual responses to treatment․ Monitoring potential allergens and triggers can help mitigate the recurrence of episodes, thus improving long-term outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals․
Impact on Quality of Life
Quinckes edema can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, especially during acute episodes that may restrict breathing or interfere with daily activities․ Recurrent episodes can lead to psychological distress and fear of potential severe complications, highlighting the importance of effective management strategies to improve overall well-being and peace of mind for those affected by this condition․
In distinguishing hereditary vs․ non-hereditary forms of Quinckes edema, clinical features and genetic testing play a crucial role․ Identifying specific genetic components helps tailor treatment approaches and provide better prognostic insights․ Proper diagnosis is essential to address the condition effectively and ensure optimal outcomes for individuals affected by Quinckes edema․
Differentiating Factors and Genetic Components
When distinguishing between hereditary and non-hereditary forms of Quinckes edema, clinical features and genetic testing are essential․ Identifying specific genetic components aids in tailoring treatment plans and providing prognostic insights․ Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and improved outcomes for individuals with Quinckes edema․
Importance of Proper Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of Quinckes edema is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment and management strategies tailored to the underlying cause․ Proper identification allows for targeted interventions to alleviate symptoms effectively and prevent potential complications associated with this condition․
Recent studies have highlighted advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of Quinckes edema, emphasizing the role of personalized medicine based on genetic components․ Innovative therapies offer targeted approaches for managing this condition effectively, showcasing promising developments in the field of angioedema research․
Recent Findings and Medical Advances
Recent studies have highlighted advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of Quinckes edema, emphasizing personalized medicine based on genetic components․ Innovative therapies offer targeted approaches for managing this condition effectively, showcasing promising developments in angioedema research․
Case Studies Illustrating Quinckes Edema Management
No additional information was available for the requested topic at this time․
Preventing Quinckes edema involves avoiding known triggers such as allergens, trauma, and certain medications․ Risk reduction strategies may include allergen identification, lifestyle modifications, and prompt medical intervention upon early symptoms to prevent the onset of severe episodes․ Educating individuals on potential triggers is essential for reducing the likelihood of Quinckes edema occurrence․
Avoidance Measures and Risk Reduction

Preventing Quinckes edema involves avoiding known triggers such as allergens, trauma, and certain medications․ Risk reduction strategies may include allergen identification, lifestyle modifications, and prompt medical intervention upon early symptoms to prevent the onset of severe episodes․ Educating individuals on potential triggers is essential for reducing the likelihood of Quinckes edema occurrence․
Educational Initiatives and Public Awareness Campaigns
Public education plays a crucial role in raising awareness about Quinckes edema, emphasizing the importance of recognizing early symptoms, avoiding triggers, and seeking prompt medical attention․ Initiatives focusing on allergen identification, emergency response training, and community engagement can enhance public knowledge and promote timely intervention strategies to manage this condition effectively․
