Disease ─ Hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia is a condition characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Understanding lipoprotein, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery plaque formation is crucial. Explore genetic risk factors, diet influence, statins, and the benefits of exercise in managing cholesterol levels.
Introduction
Hypercholesterolemia, commonly known as high cholesterol, is a significant health concern affecting millions worldwide. Cholesterol is a fatty substance crucial for the body’s normal function, but when levels become elevated, it can lead to serious health risks. Understanding the roles of lipoproteins, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), in cholesterol transport is essential in managing this condition. A key consequence of high cholesterol is atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in arteries, which can restrict blood flow and lead to heart-related complications. Genetic factors play a role in predisposing individuals to hypercholesterolemia, but lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, also significantly impact cholesterol levels. This article delves into the causes, risks, diagnosis, and treatment options for hypercholesterolemia. By exploring the impact of diet and exercise on cholesterol levels, individuals can gain insight into ways to mitigate the risks associated with high cholesterol and promote heart health.
Understanding Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in every cell of the body, vital for hormone production, digestion, and cell structure. It travels through the bloodstream in lipoproteins, including low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL, known as the ″bad″ cholesterol, carries cholesterol from the liver to cells, while HDL, the ″good″ cholesterol, transports excess cholesterol back to the liver for elimination. Imbalances in LDL and HDL levels can lead to the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries, contributing to atherosclerosis and plaque formation. Monitoring cholesterol levels through blood tests is crucial for assessing heart disease risk. Genetic factors can influence cholesterol levels, but lifestyle choices like diet and exercise play a significant role in managing cholesterol levels. By understanding the functions of cholesterol and its carriers, individuals can make informed decisions to maintain a healthy balance and reduce the risk of hypercholesterolemia.
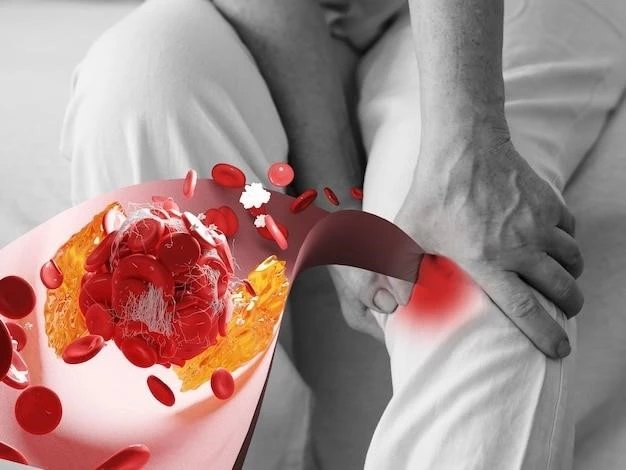
Atherosclerosis and Plaque Formation
Atherosclerosis is a condition where the arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of plaque, consisting of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances. High levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood can lead to the accumulation of this plaque on the artery walls. Over time, the arteries become narrowed, restricting blood flow and potentially leading to serious complications such as heart attacks and strokes. Plaque formation is a gradual process and often does not cause symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage. Factors like smoking, high blood pressure, and diabetes can exacerbate atherosclerosis. Understanding the role of cholesterol in plaque formation is crucial in preventing atherosclerosis. By managing cholesterol levels, individuals can reduce the risk of plaque buildup and maintain cardiovascular health.
Risk Factors for Hypercholesterolemia
Several risk factors contribute to the development of hypercholesterolemia. Genetics plays a significant role, as individuals with a family history of high cholesterol are more likely to experience it themselves. Poor diet, rich in saturated fats and trans fats, can elevate LDL cholesterol levels. Lack of physical activity and sedentary lifestyle also increase the risk of developing hypercholesterolemia. Obesity and excess body weight are linked to higher cholesterol levels and a higher risk of heart disease. Age and gender also influence cholesterol levels, with men typically having higher cholesterol earlier in life. Other factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions like diabetes can further exacerbate the risk of hypercholesterolemia. Understanding these risk factors is essential for adopting preventive measures and managing cholesterol levels to reduce the likelihood of developing complications associated with high cholesterol.
Health Risks Associated with High Cholesterol
High cholesterol levels pose significant health risks, primarily due to their association with atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. When LDL cholesterol accumulates in the arteries, it can form plaque, leading to narrowed and hardened arteries. This increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. Atherosclerosis can also affect other vital organs by reducing blood flow to the kidneys, legs, and even the brain. In severe cases, atherosclerosis can result in life-threatening conditions such as coronary artery disease. High cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease, one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Individuals with untreated hypercholesterolemia have a higher likelihood of developing these cardiovascular complications. Managing cholesterol levels through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring is crucial in reducing the risks associated with high cholesterol and promoting heart health.
Diagnosis of Hypercholesterolemia
Diagnosing hypercholesterolemia typically involves a blood test to measure cholesterol levels, specifically LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol. These tests provide valuable information about an individual’s cholesterol profile and the associated risks. The ideal values for LDL and HDL cholesterol are determined based on overall cardiovascular health. High LDL cholesterol levels are a concern as they are associated with a higher risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. Additionally, the ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol is often assessed to evaluate heart disease risk. It is important to diagnose hypercholesterolemia early to prevent the progression of plaque buildup in the arteries and minimize the risks of cardiovascular complications. Regular cholesterol screenings, along with discussions with healthcare providers, are vital in monitoring cholesterol levels and implementing appropriate interventions to manage hypercholesterolemia effectively.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hypercholesterolemia aims to reduce cholesterol levels and lower the risk of cardiovascular complications; One common approach involves lifestyle modifications, including adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats and trans fats. Regular exercise is also essential in managing cholesterol levels and promoting overall cardiovascular health. In cases where lifestyle changes are not sufficient, medications such as statins may be prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol levels. Statins work by inhibiting an enzyme involved in cholesterol production in the liver, thus reducing circulating cholesterol. Other medications, like bile acid sequestrants and PCSK9 inhibitors٫ may also be used to improve cholesterol levels. Combining medication with lifestyle changes can be highly effective in controlling hypercholesterolemia and reducing the risks associated with high cholesterol. Regular monitoring and follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial to track progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Importance of LDL and HDL Levels
LDL and HDL play crucial roles in cholesterol transport and cardiovascular health. LDL cholesterol, often referred to as ″bad″ cholesterol, can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. High levels of LDL cholesterol are a significant risk factor for cardiovascular complications. In contrast, HDL cholesterol, known as ″good″ cholesterol, helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transport it to the liver for excretion. Higher levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. Maintaining a balance between LDL and HDL cholesterol levels is essential for cardiovascular health. Individuals with hypercholesterolemia often focus on lowering LDL cholesterol while increasing HDL cholesterol through lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication. Understanding the roles of LDL and HDL cholesterol and their impact on heart health is key to effectively managing hypercholesterolemia and reducing the risks of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular complications.
Impact of Diet on Cholesterol Levels
Diet plays a significant role in influencing cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. Consuming a diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and dietary cholesterol can elevate LDL cholesterol levels, contributing to the development of hypercholesterolemia. On the other hand, incorporating heart-healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins can help lower LDL cholesterol and improve overall cholesterol profiles. Foods rich in soluble fiber, like oats and legumes, can also aid in reducing LDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel can help increase HDL cholesterol levels. Limiting the intake of processed foods٫ sugary beverages٫ and refined carbohydrates is beneficial for managing cholesterol levels. Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet plays a critical role in preventing and managing hypercholesterolemia. Individuals with high cholesterol can work with healthcare providers and nutritionists to develop personalized dietary plans that support optimal cholesterol levels and promote heart health.
Role of Exercise in Managing Hypercholesterolemia
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in managing hypercholesterolemia and improving overall cardiovascular health. Exercise helps increase HDL cholesterol levels, which can have a protective effect against heart disease. Engaging in aerobic activities such as brisk walking, running, cycling, swimming, or dancing can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis. Strength training exercises utilizing weights or resistance bands can also be beneficial in improving cardiovascular fitness and cholesterol profiles. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week to maintain heart health. Physical activity not only influences cholesterol levels but also helps control body weight, reduce blood pressure, and enhance overall well-being. Making exercise a regular part of one’s routine is essential in managing hypercholesterolemia and mitigating the risks associated with high cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle Changes for Preventing Hypercholesterolemia
Preventing hypercholesterolemia involves adopting healthy lifestyle practices that support optimal cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Making dietary changes like reducing saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol-rich foods while increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help prevent the development of high cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity is crucial in maintaining cardiovascular health and managing cholesterol levels. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is also important in preventing hypercholesterolemia and its associated risks. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, adequate sleep, and a healthy work-life balance can positively impact heart health. Regular cholesterol screenings and health check-ups enable early detection and intervention to prevent hypercholesterolemia. By incorporating these lifestyle changes into daily routines, individuals can promote heart health, reduce the risks of high cholesterol, and maintain overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hypercholesterolemia poses significant health risks due to high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Understanding the roles of LDL and HDL cholesterol, atherosclerosis, and plaque formation is crucial in managing this condition. Genetic factors, diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices all play key roles in influencing cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health. Regular screenings, diagnosis, and early intervention are essential in preventing the progression of hypercholesterolemia and reducing the risks of heart disease. By making dietary modifications, engaging in physical activity, and adopting healthy habits, individuals can effectively manage cholesterol levels and promote overall well-being. With a comprehensive approach that combines medication, if necessary, and lifestyle changes, individuals can control hypercholesterolemia and improve heart health outcomes. It is imperative to prioritize heart health, monitor cholesterol levels regularly, and work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan to mitigate the risks associated with high cholesterol.
