Disease ‒ Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy
Lifestyle Recommendations
Conclusion
Introduction
Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the combination of palmoplantar keratoderma, a skin disorder causing thickening of the skin on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, and corneal dystrophy, a condition affecting the cornea of the eye.
This inherited condition is caused by a mutation in a specific gene and follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, meaning one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. Individuals with this syndrome typically exhibit palmoplantar keratoderma from early childhood, followed by the onset of eye abnormalities in adolescence or early adulthood.
The dystrophic changes in the cornea can lead to various eye problems, including vision impairment and discomfort. Diagnosis of Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy involves a thorough clinical examination, genetic testing, and ocular assessments to evaluate the extent of corneal involvement.
Management of this condition usually involves a multidisciplinary approach, addressing both the skin and eye manifestations. While there is currently no cure for this rare disease, treatment options focus on symptom management, such as the use of emollients for the skin and lubricating eye drops for the corneal abnormalities.
Researchers continue to study the underlying mechanisms of this hereditary disorder to develop more targeted therapies. Coping strategies and support networks play a crucial role in helping individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy navigate the challenges posed by the condition.
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of this rare genetic syndrome is essential for early detection, appropriate management, and ongoing support for affected individuals and their families.
Keratosis Palmoplantaris
Keratosis Palmoplantaris, also known as palmoplantar keratoderma, is a skin disorder characterized by thick, scaly plaques on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the context of Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy, this condition is a key feature that manifests in early childhood.
The thickening of the skin is due to abnormal keratinization, leading to the formation of calluses and fissures that can be painful and impact dexterity. While the severity of palmoplantar keratoderma can vary among individuals, it generally persists throughout life and may worsen over time.
In some cases, individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris may also experience hyperkeratotic lesions on other parts of the body, such as the knees, elbows, and waist. These additional skin manifestations can further contribute to the physical and psychological burden of the condition.
Treatment for palmoplantar keratoderma typically involves the use of keratolytic agents, moisturizers, and topical retinoids to help soften the thickened skin and reduce scaling. Regular exfoliation and proper foot care are essential in managing the symptoms and preventing complications such as infections.
Individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris often benefit from consulting dermatologists and podiatrists for specialized care tailored to their specific needs. Lifestyle modifications, including wearing comfortable footwear and avoiding friction, can also help alleviate discomfort associated with the skin disorder.
While the primary focus of treatment in Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy may be on the eye manifestations, addressing the challenges posed by palmoplantar keratoderma is an important aspect of comprehensive care for individuals with this rare genetic syndrome.
Corneal Dystrophy
Corneal dystrophy is a condition that affects the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. In the context of Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy, individuals with this rare genetic syndrome develop dystrophic changes in the cornea, leading to various eye abnormalities.
The cornea plays a crucial role in focusing light into the eye, and any abnormalities in its structure can result in vision problems. In corneal dystrophy, the cornea may become cloudy, swollen, or irregularly shaped, impacting visual acuity and causing discomfort.
Individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy may experience symptoms such as blurred vision, sensitivity to light, eye pain, and foreign body sensation. These symptoms can significantly impair daily activities and quality of life if left unmanaged.
Diagnosis of corneal dystrophy typically involves a comprehensive eye examination, including visual acuity tests, slit-lamp examination, and corneal topography to evaluate the extent of corneal involvement. Genetic testing may also be recommended to confirm the underlying hereditary cause.
Treatment options for corneal dystrophy focus on managing the symptoms and preserving visual function. Lubricating eye drops, ointments, and contact lenses can help alleviate dryness and discomfort associated with corneal abnormalities. In some cases, surgical interventions such as corneal transplantation may be considered.
Regular monitoring by ophthalmologists is essential to track the progression of corneal dystrophy and adjust treatment strategies accordingly. By addressing the eye manifestations of Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy, healthcare providers aim to improve the overall vision and well-being of affected individuals.
Relationship Between Keratosis Palmoplantaris and Corneal Dystrophy
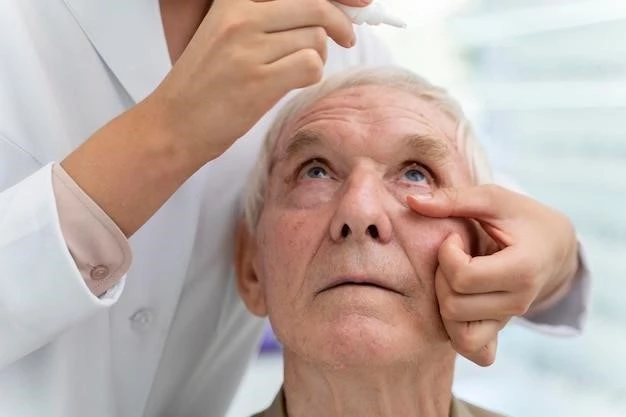
The relationship between Keratosis Palmoplantaris and Corneal Dystrophy in this genetic syndrome lies in their co-occurrence due to a shared underlying genetic mutation. While palmoplantar keratoderma affects the skin on the hands and feet, corneal dystrophy impacts the clarity and function of the cornea.
Both manifestations stem from the same autosomal dominant mutation, resulting in the development of distinctive symptoms in the skin and eyes of affected individuals. The close relationship between these two conditions underscores the complex nature of this rare genetic disorder.
Individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris often develop palmoplantar keratoderma in early childhood, which may precede the onset of corneal abnormalities later in life. The progression of these two features can vary among patients, with some experiencing more severe skin changes compared to eye complications.
Research indicates that the genetic mutation associated with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy affects the expression of proteins involved in skin and corneal development. Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind this relationship is crucial for advancing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes.
By exploring how the genetic defect leads to the concurrent presentation of palmoplantar keratoderma and corneal dystrophy, researchers aim to unravel the intricate interplay between skin and eye tissues in this hereditary disorder. This deeper understanding may pave the way for personalized treatment approaches that address both aspects of the syndrome.
Overall, the relationship between Keratosis Palmoplantaris and Corneal Dystrophy highlights the intricate connections between different organ systems affected by a common genetic abnormality, underscoring the need for multidisciplinary care and ongoing research to enhance management strategies for individuals with this complex syndrome.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy may experience a combination of symptoms affecting both the skin and eyes. Common symptoms of this rare genetic syndrome include palmoplantar keratoderma characterized by thickened skin on the palms and soles, as well as corneal abnormalities leading to vision disturbances and eye discomfort.
The skin symptoms typically manifest in early childhood, with the thickening of the palms and soles causing pain, cracking, and a significant impact on daily activities. Concurrently, dystrophic changes in the cornea may lead to blurred vision, light sensitivity, eye pain, and a feeling of foreign body presence.
Diagnosing Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy involves a comprehensive evaluation by dermatologists and ophthalmologists. Skin biopsies may be performed to assess the epidermal changes associated with palmoplantar keratoderma, while ocular examinations, including corneal imaging and visual field tests, aid in identifying corneal dystrophy.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis by detecting the specific mutation responsible for the syndrome. Understanding the clinical presentation of both skin and eye manifestations is essential for accurate diagnosis and subsequent management of the condition.
Given the variability in symptom severity and progression among affected individuals, a personalized approach to symptom management and monitoring is necessary. Close collaboration between dermatologists, ophthalmologists, and genetic counselors ensures a comprehensive evaluation of the syndrome and facilitates tailored treatment strategies.
Early detection and timely intervention are key in managing the symptoms of Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy, aiming to improve quality of life and preserve vision. By recognizing the diverse array of symptoms and employing specialized diagnostic tools, healthcare providers can deliver targeted care for individuals with this complex genetic disorder.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy focuses on managing the skin and eye manifestations to alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life for affected individuals. While there is no cure for this rare genetic syndrome, various treatment options aim to address specific aspects of the condition.
For palmoplantar keratoderma, therapeutic interventions include the use of moisturizing creams, keratolytic agents, and topical retinoids to soften the thickened skin, reduce scaling, and minimize discomfort. Regular exfoliation and proper foot care are essential components of skin management to prevent complications and improve skin texture.
In cases where palmoplantar keratoderma significantly impacts daily functioning or causes pain, physical or occupational therapy may be recommended to enhance hand dexterity and mobility. Customized orthotic devices can also help alleviate pressure on the affected areas and improve comfort.
Management of corneal dystrophy involves ophthalmologic care, with treatment options such as lubricating eye drops, ointments, or gels to address dryness and maintain corneal hydration. Contact lenses or glasses with special coatings may be prescribed to improve visual acuity and reduce discomfort caused by irregular corneal surfaces.
In more severe cases of corneal involvement, surgical procedures like corneal transplantation or phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) may be considered to improve vision and alleviate symptoms. These interventions are typically reserved for individuals with progressive corneal dystrophy that does not respond adequately to conservative measures.
Collaboration between dermatologists and ophthalmologists is essential in developing a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the skin and eye components of the syndrome. By tailoring interventions to the individual’s specific needs and monitoring response to treatment, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes and enhance the overall well-being of those living with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy.
Prognosis and Complications
The prognosis for individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy can vary depending on the severity of skin and eye involvement, as well as the individual’s response to treatment. While this rare genetic syndrome is chronic and typically persists throughout life, proactive management can help mitigate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Complications associated with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy may arise from both the skin and eye manifestations of the syndrome. Severe palmoplantar keratoderma can lead to pain, limited hand function, and an increased risk of infection if not properly managed. Chronic skin changes may also impact mobility and overall well-being.
In the context of corneal dystrophy, complications can include vision impairment, corneal scarring, and recurrent corneal erosions. These issues may result in visual disturbances, reduced quality of vision, and an increased risk of corneal infections. Without timely intervention, corneal complications can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
Long-term complications of Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy may require ongoing monitoring and intervention to prevent progression and alleviate symptoms. Regular follow-up visits with dermatologists and ophthalmologists are essential to assess treatment efficacy, monitor disease activity, and address any emerging complications promptly.
While the prognosis of this genetic syndrome cannot be definitively altered, early diagnosis, multidisciplinary care, and adherence to treatment regimens can positively influence outcomes and prevent potential complications. By recognizing and addressing both the skin and eye aspects of the disorder, healthcare providers can optimize management strategies and enhance the overall prognosis for individuals living with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy.
Research and Studies
Ongoing research and studies focusing on Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy aim to further elucidate the underlying genetic mechanisms, improve diagnostic approaches, and enhance treatment strategies for this complex genetic disorder. Investigators are exploring various aspects of the syndrome to advance clinical care and enhance patient outcomes.
Genetic studies play a crucial role in identifying the specific gene mutation responsible for Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy, allowing for precise diagnosis and targeted therapies. Understanding how this mutation affects skin and eye tissues at the molecular level is essential for developing personalized treatment approaches.
Researchers are investigating novel therapeutic interventions for managing the skin and eye manifestations of the syndrome. This includes exploring potential pharmacological agents, gene therapy techniques, and innovative surgical modalities to address both palmoplantar keratoderma and corneal dystrophy more effectively.
Clinical trials are essential in evaluating the safety and efficacy of new treatment modalities in individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy. These studies help researchers assess the impact of emerging therapies on symptom progression, quality of life, and long-term outcomes for affected patients.
Advancements in imaging technologies have enhanced the ability to visualize and monitor corneal changes in individuals with this genetic syndrome. High-resolution imaging modalities such as corneal topography and confocal microscopy provide valuable insights into the structural alterations within the cornea, guiding treatment decisions and prognostic assessments.
The collaborative efforts of dermatologists, ophthalmologists, geneticists, and researchers in the field of Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy are vital in driving progress and expanding our understanding of this rare genetic disorder. By leveraging interdisciplinary expertise and leveraging cutting-edge technologies, the scientific community strives to improve patient care and outcomes for individuals living with this complex syndrome.
Coping Strategies and Support
Coping with the challenges of Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and emotional impact of the syndrome. Individuals living with this rare genetic disorder, as well as their families, can benefit from various coping strategies and support resources to navigate the complexities of the condition.
Education and awareness play a crucial role in empowering individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy to understand their condition and actively participate in their care. Information about the genetic basis, symptom management, and available support services can help individuals make informed decisions regarding their health.
Mental health support is essential for individuals coping with the challenges posed by this complex syndrome. Counseling, therapy, and peer support groups provide a valuable outlet for expressing emotions, addressing anxiety or depression, and building resilience in the face of chronic illness.
Practical coping strategies, such as mindfulness techniques, stress management exercises, and relaxation therapies, can help individuals manage the emotional toll of living with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy. Engaging in hobbies, creative outlets, and social activities can also offer a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
Connecting with patient advocacy organizations and rare disease support networks can provide individuals and families affected by Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy with a sense of community and shared experiences. These networks offer a platform for sharing information, resources, and emotional support among those facing similar challenges.
Building a strong support network of healthcare providers, friends, family members, and other individuals impacted by rare diseases can create a supportive environment for those navigating the complexities of this genetic syndrome. Open communication, collaboration, and mutual understanding are key in fostering a resilient community of support.
By embracing a holistic approach to coping and seeking support from various channels, individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy can enhance their quality of life, promote emotional well-being, and foster a sense of empowerment in managing the challenges associated with this rare genetic disorder.
In conclusion, Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the co-occurrence of palmoplantar keratoderma and corneal dystrophy. This complex syndrome, driven by an autosomal dominant mutation, presents a unique set of challenges affecting both the skin and eyes of affected individuals.
The relationship between palmoplantar keratoderma and corneal dystrophy underscores the interplay between different organ systems impacted by a shared genetic abnormality. Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind these manifestations is crucial for developing targeted treatment strategies that address both skin and eye symptoms.
While there is currently no cure for Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy, proactive management focusing on symptom relief, regular monitoring, and multidisciplinary care can help individuals lead fulfilling lives despite the complexities of the syndrome. Advances in research, genetic studies, and therapeutic interventions hold promise for enhancing clinical outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals.
Coping with the challenges posed by this rare genetic disorder requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses education, mental health support, practical coping strategies, and community engagement. By fostering a supportive environment and leveraging available resources, individuals with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy can navigate the complexities of their condition with resilience and empowerment.
As research continues to unravel the complexities of this hereditary disorder, clinicians, researchers, and advocacy groups remain dedicated to advancing understanding, improving diagnostic approaches, and enhancing treatment modalities for individuals living with Keratosis Palmoplantaris with Corneal Dystrophy. By working collaboratively and embracing a holistic approach to care, the medical community strives to optimize outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this rare genetic syndrome.
