Disease Overview ─ Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose
Research and Innovations
Quality of Life Considerations
Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to this comprehensive overview of the complex condition known as Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose. This condition encompasses a unique combination of cranial‚ facial‚ and neurological abnormalities‚ presenting challenges in diagnosis and management;
Hydrocephalus‚ characterized by an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain’s cavities‚ is often associated with craniosynostosis‚ a condition where the skull’s sutures prematurely fuse‚ leading to abnormal skull development. Bifid nose deformity‚ involving a cleft or widening of the nasal tip‚ further complicates the presentation of this rare disorder.
The intricate interplay between these three components necessitates a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and treatment. Individuals affected by this condition may experience a range of symptoms‚ including cognitive impairment‚ malformations of the skull and facial structures‚ and neurological deficits.
Understanding the genetic basis of this disorder is crucial for providing personalized care and identifying individuals at risk. Effective management strategies‚ including surgical interventions such as ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement‚ aim to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life for affected individuals.
This article will delve into the intricate details of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose‚ exploring the nuances of each component‚ diagnostic challenges‚ treatment modalities‚ genetic implications‚ and the latest advancements in research. By shedding light on this complex disorder‚ we aim to enhance awareness and foster better outcomes for individuals grappling with this condition.
Understanding Hydrocephalus
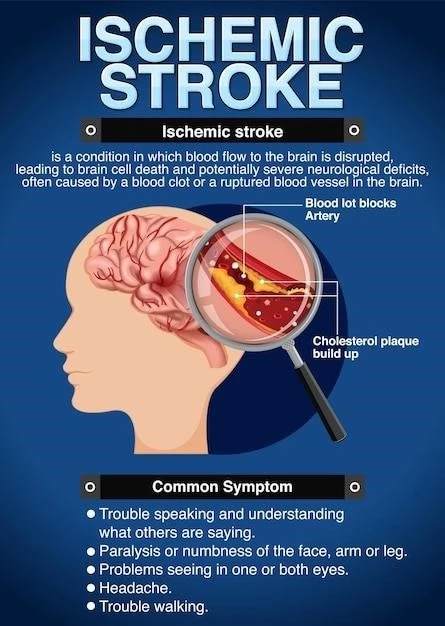
Hydrocephalus is a neurological condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain’s ventricles‚ leading to increased intracranial pressure. This buildup can result from an imbalance in the production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid‚ obstruction of its flow‚ or impaired drainage mechanisms.
Individuals with hydrocephalus may experience a range of symptoms‚ including headaches‚ nausea‚ visual disturbances‚ gait disturbances‚ and cognitive impairments. Infants with hydrocephalus may present with an enlarged head circumference‚ bulging fontanelles‚ and developmental delays.
The diagnosis of hydrocephalus involves imaging studies such as MRI and CT scans to assess the ventricular enlargement and the underlying cause. Treatment approaches vary depending on the etiology and severity of the condition. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery is a common intervention to divert excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain to the abdominal cavity‚ relieving intracranial pressure.
Long-term management of hydrocephalus may involve regular monitoring‚ shunt revisions‚ and addressing associated complications such as infections or shunt malfunctions. The impact of hydrocephalus on cognitive function can vary widely‚ ranging from mild cognitive deficits to more significant impairments in memory‚ attention‚ and executive functioning.
Understanding the underlying causes of hydrocephalus‚ whether congenital or acquired‚ is essential for guiding treatment and optimizing outcomes. Advancements in imaging technology‚ surgical techniques‚ and shunt technology continue to improve the management of hydrocephalus‚ enhancing the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
Craniosynostosis in Detail
Craniosynostosis is a congenital condition characterized by the premature fusion of one or more cranial sutures in an infant’s skull. This fusion restricts normal skull growth perpendicular to the affected suture and can lead to abnormal head shape and potential neurological implications.
The early closure of the skull sutures can result in increased intracranial pressure due to limited space for brain growth‚ affecting brain development and potentially leading to cognitive impairment. The diagnosis of craniosynostosis often involves physical examination‚ imaging studies like CT scans‚ and consultation with craniofacial specialists.
Surgical intervention is frequently necessary to release the fused sutures and allow space for the brain to grow normally. The goal of surgery is to correct the head shape deformity‚ relieve intracranial pressure‚ and prevent potential neurological complications. Postoperative care and monitoring are crucial to ensure optimal outcomes and early intervention for any issues that may arise.
While the exact causes of craniosynostosis can vary‚ genetic factors play a significant role in some cases. Syndromic forms of craniosynostosis‚ associated with genetic disorders such as Apert syndrome or Crouzon syndrome‚ often present with additional craniofacial anomalies beyond skull fusion. Understanding the genetic underpinnings of craniosynostosis is vital for appropriate management and genetic counseling.
Addressing craniosynostosis early in infancy is essential to optimize cranial growth and neurodevelopment. Multidisciplinary care involving neurosurgeons‚ craniofacial surgeons‚ geneticists‚ and pediatric specialists is key to providing comprehensive treatment for individuals with craniosynostosis‚ ensuring the best possible outcomes for their long-term health and well-being.
Bifid Nose Deformity
Bifid nose deformity is a rare craniofacial anomaly characterized by a central cleft or widening of the nasal tip. This condition can occur in isolation or in association with other craniofacial abnormalities‚ such as craniosynostosis and midline defects.
The presentation of bifid nose deformity varies from subtle widening of the nasal tip to a more pronounced cleft that extends towards the nasal bridge. The diagnosis of bifid nose deformity typically involves clinical examination by a craniofacial specialist and may include imaging studies to assess the extent of the anomaly.
Surgical correction of bifid nose deformity may be considered to improve nasal symmetry and restore normal nasal anatomy. The surgical approach often involves reshaping the nasal cartilage and tissues to achieve a more harmonious nasal appearance. Close postoperative monitoring is essential to ensure optimal healing and aesthetic outcomes.
Bifid nose deformity can have a significant impact on facial aesthetics and may contribute to psychosocial challenges for affected individuals. Multidisciplinary care involving plastic surgeons‚ otolaryngologists‚ and other specialists is crucial to address the aesthetic and functional aspects of the deformity.
Understanding the underlying causes of bifid nose deformity‚ whether genetic or acquired‚ is essential for guiding treatment strategies and providing appropriate support for individuals affected by this condition. Through a comprehensive and personalized approach to care‚ individuals with bifid nose deformity can achieve improved facial symmetry and function‚ enhancing their quality of life and well-being.
Diagnosis of the Condition
Diagnosing the complex condition of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose requires a meticulous and multidisciplinary approach. Clinical evaluation by neurosurgeons‚ craniofacial specialists‚ geneticists‚ and other healthcare providers plays a crucial role in identifying and assessing the components of this rare disorder.
For hydrocephalus‚ diagnostic modalities such as MRI and CT scans are utilized to visualize the enlargement of the brain ventricles and assess the underlying cause of cerebrospinal fluid accumulation. Clinical symptoms and signs‚ such as increased head circumference in infants or neurological deficits in older individuals‚ also aid in the diagnosis of hydrocephalus.
Craniosynostosis diagnosis involves physical examination to detect abnormal skull shapes‚ imaging studies like CT scans to identify premature sutural fusion‚ and consultation with craniofacial specialists to evaluate the extent of cranial abnormalities. Genetic testing may be warranted in cases where syndromic forms of craniosynostosis are suspected.
Bifid nose deformity is diagnosed through clinical assessment of nasal anatomy‚ including the presence of a central cleft or widening of the nasal tip. Nasal imaging studies may be performed to characterize the deformity and plan for surgical correction if needed. A comprehensive evaluation by plastic surgeons and otolaryngologists guides the diagnosis and management of bifid nose deformity.
Integrated diagnostic approaches that consider the collective impact of hydrocephalus‚ craniosynostosis‚ and bifid nose deformity are essential for providing tailored treatment plans and improving outcomes for affected individuals. By accurately diagnosing each component of this complex condition‚ healthcare professionals can deliver targeted and effective interventions to address the diverse challenges presented by Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose.
Treatment Approaches
The management of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose necessitates a comprehensive and individualized treatment approach tailored to address the complex interplay of cranial‚ facial‚ and neurological abnormalities. Treatment strategies often involve a combination of surgical interventions‚ multidisciplinary care‚ and long-term monitoring.
For hydrocephalus‚ the primary treatment modality is the placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. This surgical procedure involves the insertion of a catheter to divert excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain’s ventricles to the abdominal cavity‚ relieving intracranial pressure. Regular follow-up and monitoring are crucial to detect shunt malfunctions or infections promptly.
Craniosynostosis management typically requires surgical correction to release the fused cranial sutures and reshape the skull to allow for normal brain growth. Craniofacial surgeons perform these intricate procedures to address head shape deformities and prevent potential complications associated with increased intracranial pressure.
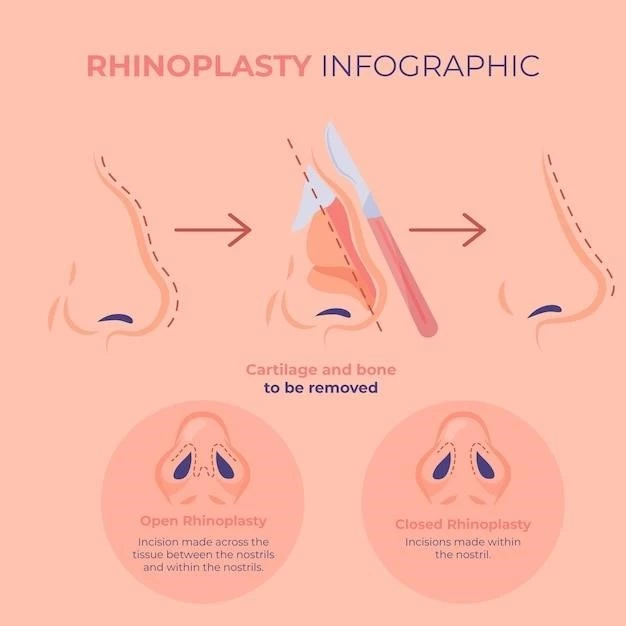
Individuals with bifid nose deformity may undergo surgical reconstruction to achieve nasal symmetry and restore normal nasal anatomy. Plastic surgeons and otolaryngologists collaborate to reshape the nasal structures‚ improving both aesthetic appearance and functional outcomes.
Genetic counseling and testing may be recommended for individuals with syndromic forms of the condition to understand the underlying genetic factors and provide appropriate support and guidance. Early intervention and close collaboration between specialists are essential to optimize treatment outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals with Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose.
By integrating surgical interventions‚ genetic considerations‚ and ongoing monitoring‚ healthcare professionals can address the unique challenges posed by this complex disorder. Through a comprehensive and coordinated treatment approach‚ individuals affected by Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose can receive the specialized care needed to promote their health and well-being.
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Surgery
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt surgery is a fundamental intervention in the management of hydrocephalus‚ a key component of the complex condition encompassing Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose. This neurosurgical procedure aims to alleviate the increased intracranial pressure caused by abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain’s ventricles.
During VP shunt surgery‚ a thin‚ flexible catheter is implanted into one of the brain’s ventricles to divert excess cerebrospinal fluid away from the brain. The distal end of the catheter is then tunneled under the skin to the peritoneal cavity‚ where the fluid is absorbed by the body. This diversion pathway helps regulate and maintain the appropriate balance of cerebrospinal fluid within the central nervous system.
The placement of a VP shunt requires precision and expertise to ensure accurate positioning and optimal functioning. Neurosurgeons meticulously select appropriate shunt components‚ including valves to control the flow of fluid‚ to tailor the treatment to each individual’s needs. Postoperatively‚ ongoing monitoring and regular follow-up evaluations are essential to check for any complications‚ such as infection‚ blockage‚ or overdrainage;
VP shunt surgery carries risks‚ including infection‚ shunt malfunction‚ overdrainage‚ or underdrainage‚ which may necessitate surgical revisions or adjustments. Close collaboration between neurosurgeons‚ neurologists‚ and other healthcare professionals is crucial to ensure prompt detection and management of any shunt-related issues.
By effectively relieving intracranial pressure and managing the symptoms of hydrocephalus‚ VP shunt surgery plays a vital role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose. Through meticulous surgical techniques‚ vigilant postoperative care‚ and ongoing monitoring‚ healthcare providers strive to optimize outcomes and provide comprehensive support for patients undergoing this critical neurosurgical intervention.
Impact on Cognitive Function
The complex condition of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose can exert a profound impact on cognitive function‚ influencing various aspects of neurodevelopment and mental processing. Individuals affected by this rare disorder may experience cognitive impairments of varying degrees‚ stemming from the interplay of cranial‚ facial‚ and neurological abnormalities.
Hydrocephalus‚ characterized by increased intracranial pressure due to abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid‚ can result in cognitive deficits such as impaired memory‚ attention‚ and executive functioning. The pressure exerted on the brain structures by excess fluid may disrupt neural pathways vital for cognitive processes‚ potentially leading to learning difficulties and developmental delays.
Craniosynostosis poses additional challenges to cognitive function‚ as premature fusion of skull sutures can impact brain growth and development. The restrictive nature of craniosynostosis on brain expansion may contribute to cognitive delays or intellectual disabilities‚ particularly if left untreated and unmanaged.
Bifid nose deformity‚ while primarily a facial anomaly‚ can also affect cognitive function indirectly through its psychosocial implications. Individuals with conspicuous facial differences may face challenges in social interactions and self-esteem‚ which can impact cognitive and emotional well-being.
Understanding the multifaceted impact of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose on cognitive function is crucial for designing comprehensive management approaches. Early detection‚ intervention‚ and ongoing cognitive assessments are essential components of holistic care for individuals affected by this complex condition.
Through personalized treatment strategies‚ including surgical interventions‚ cognitive therapy‚ and educational support‚ healthcare professionals strive to optimize cognitive outcomes and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals grappling with the cognitive challenges associated with Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose.
Genetic Aspects
Genetic factors play a pivotal role in the etiology and manifestation of the intricate condition encompassing Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose. The interplay of genetic variations can contribute to the development of each component of this complex disorder‚ influencing its presentation‚ severity‚ and associated complications.
In some cases‚ hydrocephalus can have a genetic basis‚ with mutations in genes related to cerebrospinal fluid dynamics or brain development contributing to its onset. Familial patterns of hydrocephalus suggest a hereditary component‚ highlighting the importance of genetic screening and counseling for affected families.
Craniosynostosis is also influenced by genetic factors‚ with syndromic forms of the condition often linked to specific gene mutations. Disorders such as Apert syndrome‚ caused by mutations in the FGFR2 gene‚ or Crouzon syndrome‚ associated with mutations in the FGFR3 gene‚ exemplify the genetic underpinnings of craniosynostosis.
Genetic analysis can aid in identifying individuals at risk of developing bifid nose deformity as part of a genetic syndrome or complex craniofacial anomaly. Understanding the genetic determinants of bifid nose deformity can inform treatment decisions‚ prognostic assessments‚ and genetic counseling for affected individuals and their families.
The integration of genetic testing and counseling into the diagnostic and management framework of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose is essential for providing tailored and personalized care. Genetic insights not only guide treatment approaches but also offer valuable information on recurrence risks‚ family planning considerations‚ and potential therapeutic targets.
By delving into the genetic aspects of this complex disorder‚ healthcare professionals can enhance their understanding of its underlying mechanisms and tailor interventions to address the unique genetic profiles of individual patients. Through collaborative efforts between geneticists‚ neurologists‚ and other specialists‚ the genetic dimension of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose can be elucidated to optimize patient care and outcomes.
Managing Malformations
The management of malformations associated with Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose requires a multidisciplinary and holistic approach to address the diverse cranial and facial abnormalities present in affected individuals. Effective management strategies aim to correct deformities‚ alleviate symptoms‚ and optimize functional and aesthetic outcomes.
For individuals with hydrocephalus‚ ongoing monitoring and timely adjustments to ventriculoperitoneal shunts are crucial to manage fluid drainage and prevent complications such as overdrainage or infections. Close collaboration between neurosurgeons and neurologists ensures comprehensive care and early intervention for shunt-related issues.
Craniosynostosis management involves surgical correction to release fused cranial sutures‚ reshape the skull‚ and promote normal brain growth. Craniofacial surgeons meticulously perform these procedures to address head shape deformities and mitigate the risk of increased intracranial pressure‚ which can impact cognitive and neurological function.
Addressing bifid nose deformity may require surgical reconstruction to enhance nasal symmetry and restore normal nasal anatomy. Plastic surgeons and otolaryngologists collaborate to reshape the nasal structures and improve both aesthetic appearance and functional outcomes‚ addressing the facial component of the complex disorder.
Comprehensive management of malformations associated with Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose involves psychosocial support‚ cognitive therapy‚ and educational interventions to optimize overall well-being and quality of life. The integration of genetic insights‚ surgical interventions‚ and long-term monitoring ensures a tailored approach to address the intricate challenges posed by this rare and multifaceted condition.
Through a coordinated and personalized management strategy‚ healthcare professionals strive to maximize outcomes‚ minimize complications‚ and improve the overall health and functioning of individuals facing the complex malformations associated with Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose.
In conclusion‚ the intricate interplay of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose presents a unique challenge in the realm of cranial‚ facial‚ and neurological disorders. This rare condition requires a multidisciplinary approach involving neurosurgeons‚ craniofacial specialists‚ geneticists‚ and other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive and individualized care.
From the abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in hydrocephalus to the premature fusion of cranial sutures in craniosynostosis and the facial deformity of bifid nose‚ each component demands careful consideration and tailored interventions. Genetic aspects play a significant role‚ guiding diagnosis‚ treatment strategies‚ and genetic counseling for affected individuals and their families.
The impact on cognitive function underscores the importance of early detection‚ cognitive assessments‚ and cognitive therapy to address learning difficulties and developmental delays. Managing malformations associated with this complex disorder requires ongoing monitoring‚ surgical interventions‚ and psychosocial support to optimize functional and aesthetic outcomes.
By recognizing the genetic‚ cognitive‚ and malformative intricacies of Hydrocephalus Craniosynostosis Bifid Nose‚ healthcare professionals can enhance their understanding of the condition and deliver personalized care that addresses the diverse needs of affected individuals. Through ongoing research‚ innovative treatments‚ and collaborative efforts‚ the management of this rare disorder continues to evolve‚ offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those impacted by this complex condition.