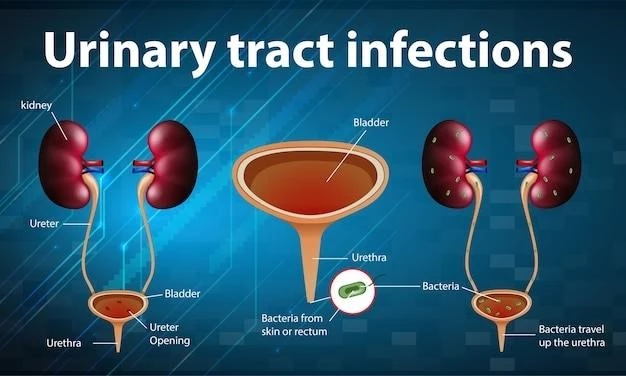
Perlman syndrome (PS)‚ also known as nephroblastomatosis–fetal ascites–macrosomia–Wilms tumor syndrome‚ is a rare overgrowth syndrome caused by genetic mutations in the DIS3L2 gene․ PS is characterized by various clinical features and an increased risk for Wilms tumor․
Definition and Characteristics
Perlman syndrome‚ also known as nephroblastomatosis-fetal ascites-macrosomia-Wilms tumor syndrome‚ is an autosomal recessive overgrowth syndrome caused by genetic mutations in the DIS3L2 gene․ This syndrome is characterized by macrocephaly‚ neonatal macrosomia‚ nephromegaly‚ renal dysplasia‚ dysmorphic facial features‚ and an increased risk for Wilms tumor․
Understanding Fetal Ascites
Fetal ascites can be a manifestation of Perlman syndrome‚ a rare genetic disorder associated with various abnormalities like nephroblastomatosis and Wilms tumor․ As Perlman syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition‚ understanding its implications is crucial in clinical practice․
Relationship with Perlman Syndrome
Fetal ascites can be a manifestation of Perlman syndrome‚ a rare genetic disorder associated with various abnormalities like nephroblastomatosis and Wilms tumor․ As Perlman syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition‚ understanding its implications is crucial in clinical practice․

Macrosomia⁚ Causes and Implications
In the context of Perlman syndrome‚ macrosomia can be a significant clinical feature associated with nephroblastomatosis‚ fetal ascites‚ and Wilms tumor․ Understanding the causes of macrosomia is crucial in assessing the implications of this condition․
Association with Wilms Tumor
Fetal macrosomia‚ a condition observed in Perlman syndrome‚ is often linked to an increased risk of Wilms tumor․ Understanding this association is crucial for early detection and effective management of Wilms tumor in individuals with Perlman syndrome․
Insight into Wilms Tumor
Wilms tumor‚ commonly associated with Perlman syndrome‚ is a rare kidney cancer primarily affecting children․ Understanding the nature of Wilms tumor and its relationship with syndromes like Perlman syndrome is vital in clinical management․
Development and Risk Factors
Wilms tumor‚ associated with Perlman syndrome‚ often originates from nephroblastomatosis‚ a precursor lesion․ Understanding the developmental trajectory and identifying risk factors for Wilms tumor are crucial in early diagnosis and intervention․
Perlman Syndrome⁚ An Overgrowth Syndrome
Perlman syndrome (PS)‚ also known as nephroblastomatosis-fetal ascites-macrosomia-Wilms tumor syndrome‚ is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by overgrowth and associated with increased risk of Wilms tumor․ Understanding the complexities of Perlman syndrome is essential for proper diagnosis and management․
Clinical Features and Diagnosis
Perlman syndrome‚ also known as nephroblastomatosis-fetal ascites-macrosomia-Wilms tumor syndrome‚ presents with various clinical features including overgrowth‚ renal abnormalities‚ dysmorphic facial characteristics‚ and an increased risk of Wilms tumor․ Diagnosis involves recognizing these clinical manifestations and genetic testing to confirm the presence of DIS3L2 gene mutations․
Genetic Aspects of Nephroblastomatosis
Recent research has identified the DIS3L2 gene mutations as the underlying genetic cause of Perlman syndrome‚ a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by nephroblastomatosis‚ fetal ascites‚ macrosomia‚ and Wilms tumor․ Understanding the genetic aspects of nephroblastomatosis is crucial for diagnosing and managing this complex condition effectively․
Inheritance Patterns and Genetic Mutations
Perlman syndrome‚ characterized by genetic mutations in the DIS3L2 gene‚ follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern․ The identified mutations play a crucial role in the development of this rare syndrome‚ which is associated with nephroblastomatosis‚ fetal ascites‚ macrosomia‚ and Wilms tumor․ Understanding the genetic aspects of Perlman syndrome aids in both diagnosis and potential therapeutic interventions․
Prevalence of Wilms Tumor in Perlman Syndrome
Perlman syndrome‚ characterized by nephroblastomatosis‚ fetal ascites‚ macrosomia‚ and Wilms tumor‚ presents a high incidence of Wilms tumor in affected individuals․ Understanding the prevalence and associations of Wilms tumor in Perlman syndrome is crucial for clinical management․
Incidence Rates and Age of Diagnosis
Individuals with Perlman syndrome have a 64% incidence of Wilms tumor‚ diagnosed at an earlier age compared to sporadic cases; The bilateral occurrence in over half of cases emphasizes the necessity of early surveillance and intervention․ Understanding the age of onset and frequency of Wilms tumor in Perlman syndrome aids in implementing appropriate monitoring strategies․
Diagnostic Challenges and Screening Recommendations
Perlman syndrome presents diagnostic challenges due to its association with nephroblastomatosis‚ fetal ascites‚ macrosomia‚ and Wilms tumor․ Screening individuals at risk‚ especially for Wilms tumor‚ requires vigilant monitoring and utilization of imaging techniques like renal ultrasounds for early detection and management․
Importance of Renal Ultrasounds
Renal ultrasounds play a critical role in the early detection and monitoring of conditions such as nephroblastomatosis‚ fetal ascites‚ macrosomia‚ and Wilms tumor in individuals at risk‚ including those with Perlman syndrome․ Regular renal ultrasounds are essential for screening‚ diagnosing‚ and managing these complex conditions effectively․
Perlman Syndrome and High Neonatal Mortality
Perlman syndrome is associated with high neonatal mortality rates and a predisposition to developmental delays and an elevated risk of Wilms tumor‚ emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and comprehensive management strategies in affected individuals․
Developmental Delays and Tumor Risks
Perlman syndrome‚ a complex condition‚ can lead to developmental delays and an increased risk of Wilms tumor‚ highlighting the need for early intervention and thorough management strategies to address these challenges effectively․
Research and Treatment Strategies
Evolving research on Perlman syndrome focuses on identifying genetic mutations and developing targeted treatment strategies to mitigate the risk of Wilms tumor and manage associated challenges․ Collaborative studies aim to enhance diagnostic methods and implement tailored interventions‚ ultimately improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals with this rare overgrowth syndrome․
Management Approaches and Future Directions
Management of Perlman syndrome involves a multidisciplinary approach‚ including genetic counseling‚ regular monitoring for developmental delays‚ tumor surveillance‚ and supportive care․ Collaborative research focuses on identifying targeted therapeutic strategies based on genetic insights to improve outcomes for affected individuals․ Future directions aim to enhance early detection methods‚ refine treatment modalities‚ and provide tailored support for individuals with Perlman syndrome․