Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects joints, causing pain and stiffness. It is an autoimmune disorder that can lead to joint damage and systemic effects. Learn more from trusted sources.
Definition and Overview
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. It can lead to joint damage and systemic effects beyond the joints. Learn about the anatomy, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies for RA to improve your quality of life.

Anatomy and Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that affects joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. It involves the inflammation of joint tissues, leading to joint damage. Understanding the anatomy and pathophysiology is crucial in managing this condition effectively.
Autoimmune Nature of RA
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissues, especially the synovium in joints. This autoimmune response leads to inflammation, joint damage, and systemic effects. Understanding the autoimmune nature of RA is crucial for proper management and treatment.
Impact on Joints and Surrounding Tissues
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has a significant impact on joints and surrounding tissues, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. The inflammation can cause damage to cartilage and bone, affecting joint function. It’s essential to understand how RA affects the entire joint structure to implement appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Clinical Presentation of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understand the chronic inflammatory nature of rheumatoid arthritis, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness in joints. Learn about its systemic effects and seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Symptoms and Signs
Rheumatoid arthritis may present with joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and deformity. Understanding these common symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management. Seek medical advice if you experience these signs to enhance your quality of life.
Systemic Effects Beyond Joints
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is not only limited to joint inflammation but can also affect other organs in the body, leading to systemic complications. Understanding these systemic effects is important for comprehensive management and treatment. Consult a healthcare professional to address the holistic impact of RA on your health.
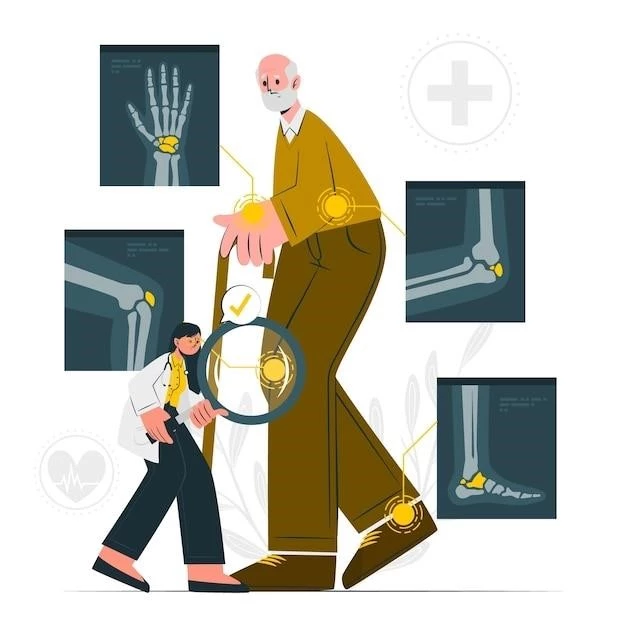
Diagnosis and Assessment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Learn about diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis through medical history, physical exams, lab tests, and imaging studies. Find effective treatment options and management strategies to improve your well-being.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis involves a detailed medical history review and a comprehensive physical examination focusing on joint pain, inflammation, and function. These assessments help healthcare providers identify key symptoms and signs essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Laboratory Tests and Imaging Studies
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis often involves laboratory tests to detect specific antibodies and imaging studies like X-rays and MRIs to assess joint damage. These diagnostic tools aid in confirming RA and guiding treatment decisions. Seek medical advice for a comprehensive evaluation if RA is suspected;
Treatment Approaches for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Discover effective medication options, physical therapy, surgical interventions, and complementary therapies to manage rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and improve your quality of life. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans.
Medication Options
Discover various medications used in treating rheumatoid arthritis, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, steroids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These medications aim to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and slow disease progression. Consult healthcare providers to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your condition.
Physical Therapy and Surgical Interventions
Explore the role of physical therapy in managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and improving joint mobility. Surgical interventions like joint replacement may be considered for severe joint damage. Consult with a healthcare provider to discuss personalized options to enhance your quality of life.
Complementary Therapies
Explore complementary therapies to support rheumatoid arthritis treatment, including acupuncture, dietary supplements, and mind-body techniques. These adjunctive approaches can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Consult your healthcare provider before incorporating complementary therapies into your treatment plan for RA.
Management Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Implement symptom management techniques and joint protection strategies to prevent damage and maintain functionality. Enhance your quality of life through personalized care and lifestyle adjustments. Consult healthcare professionals for tailored guidance.
Symptom Management and Joint Protection
Apply optimal symptom management strategies to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and enhance joint function. Implement joint protection techniques to prevent further damage and maintain mobility. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance on managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively.
Prevention of Joint Damage and Disability
Implement strategies to prevent joint damage and disability associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Early diagnosis, timely treatment, and ongoing management can help minimize complications and preserve joint function. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized care and guidance.
Improving Quality of Life
Enhance your quality of life while living with rheumatoid arthritis by managing symptoms, seeking appropriate treatment, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments. Consult healthcare providers for personalized advice to improve your well-being and overall health.
