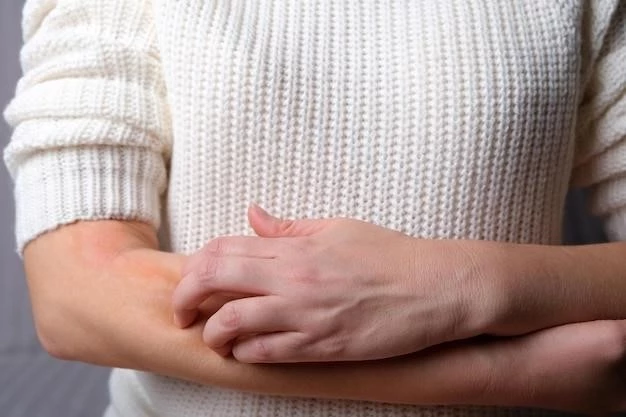
Introduction
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a common skin disorder characterized by red, raised, itchy bumps on the skin. It affects around 20% of the general population.
Overview of Urticaria
Urticaria, or hives, is a common skin disorder characterized by red, raised, itchy bumps known as wheals. The lesions can be intensely pruritic and may be accompanied by angioedema, causing swelling deeper in the skin. It is a prevalent condition affecting a significant portion of the population worldwide.
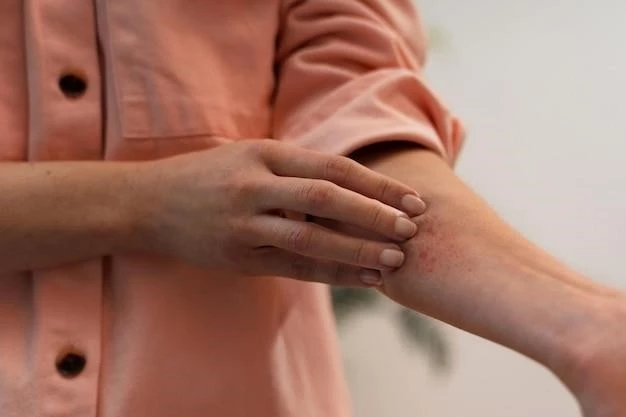
Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of urticaria typically involves red, raised, and itchy bumps on the skin known as wheals. These wheals can be accompanied by angioedema, causing swelling in deeper skin layers.
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, manifests as red, raised, and itchy bumps on the skin, termed wheals. These wheals can be accompanied by angioedema, resulting in deeper skin swelling. The condition is prevalent globally, affecting a significant portion of the population.
Causes and Triggers
Urticaria, also known as hives, can be triggered by various factors such as allergens, medications, infections, and physical stimuli like pressure or temperature changes.
Characteristics of Urticaria
Urticaria, also known as hives, presents as red, raised, itchy wheals on the skin. These wheals may be accompanied by angioedema, resulting in deeper tissue swelling. It is a common condition affecting a significant percentage of the population worldwide.
Diagnosis and Treatment
To diagnose and manage urticaria, healthcare providers may perform physical exams, allergy tests, blood tests, and suggest treatments such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, or immune system modulators.
Approaches to Diagnosing and Managing Urticaria
Diagnosing urticaria involves physical exams, allergy tests, and blood tests to identify triggers. Treatment may include antihistamines, corticosteroids, or immune system modulators based on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Chronic Urticaria
Chronic urticaria, characterized by the presence of wheals or angioedema, can persist for more than six weeks and reappear intermittently over months or years, often with unidentified causes.
Understanding Chronic Urticaria
Chronic urticaria is characterized by the persistent presence of wheals or angioedema for more than six weeks, often reoccurring intermittently over months or even years. The causes of chronic urticaria are frequently unknown, making its management challenging.
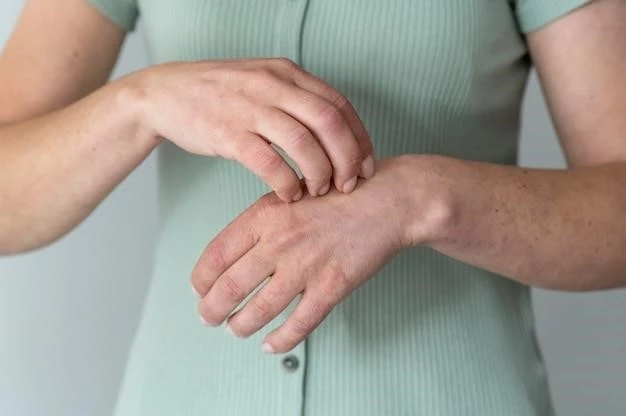
Prevention and Management
Managing and preventing urticaria involves identifying triggers like allergens, infections, or medications, and employing treatments such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, or immune system modulators.
Strategies for Preventing and Managing Urticaria
Preventing and managing urticaria involves identifying triggers like allergens, infections, or medications, and employing treatments such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, or immune system modulators based on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
