Introduction
Pharyngitis is a common infection causing sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. This article explores its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Pharyngitis is the inflammation of the mucous membranes of the throat, commonly causing symptoms such as sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. It can be bacterial or viral in origin, with streptococcal and respiratory viruses being common culprits. Understanding the cause of pharyngitis is crucial for appropriate treatment and management of this condition.
Clinical Features of Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an infection causing sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. It can be viral or bacterial, with distinct symptoms and treatment approaches.
Definition and Overview of Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is the inflammation of the mucous membranes of the throat, commonly causing symptoms such as sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. It can be bacterial or viral in origin, with streptococcal and respiratory viruses being common culprits. Understanding the cause of pharyngitis is crucial for appropriate treatment and management of this condition.
Symptoms and Signs of Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis commonly presents with symptoms such as sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. Other signs may include redness and swelling in the throat, swollen lymph nodes, and occasionally white patches on the tonsils. It is important to differentiate between viral and bacterial pharyngitis based on these symptoms for appropriate treatment.
Causes of Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis can be caused by viral infections like common cold, flu, or bacterial infections such as strep throat. Other causes include allergies, trauma, environmental factors, and certain toxins.
Bacterial Causes⁚ Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes is a common bacterial cause of pharyngitis, particularly in children and adolescents. It is crucial to differentiate streptococcal pharyngitis from viral infections for appropriate treatment with antibiotics and to prevent complications such as rheumatic fever.
Viral Causes⁚ Common Cold and Flu
Pharyngitis can be caused by viral infections like the common cold and flu. These viruses lead to inflammation in the throat, resulting in symptoms such as sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. Understanding the viral origins of pharyngitis is essential for appropriate management and treatment.

Diagnosis of Pharyngitis
Diagnosing pharyngitis involves a physical examination, medical history review, and sometimes rapid antigen tests to determine the underlying cause of the throat infection.
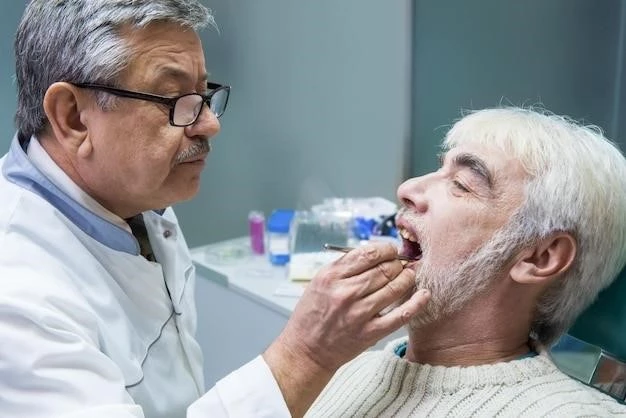
Physical Examination and Medical History
Diagnosing pharyngitis involves a physical examination to assess the throat, tonsils, and lymph nodes. Obtaining a detailed medical history helps identify possible causes and guides further diagnostic evaluations.
Diagnostic Tests⁚ Rapid Antigen Tests
Rapid antigen tests are often used to differentiate between bacterial and viral causes of pharyngitis quickly. These tests can identify the presence of specific antigens, such as Streptococcus pyogenes, aiding in the prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment of bacterial pharyngitis.
Treatment of Pharyngitis
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial pharyngitis, while antiviral medications are used for viral pharyngitis. Proper diagnosis aids in selecting the most effective treatment.
Antibiotics for Bacterial Pharyngitis
Antibiotics are frequently prescribed to treat bacterial pharyngitis caused by organisms like Streptococcus pyogenes. It is essential to complete the antibiotic course to prevent complications.
Antiviral Medications for Viral Pharyngitis
For viral pharyngitis, antiviral medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and shorten the duration of the illness. These medications target specific viruses causing the infection, aiding in recovery.
Complications of Pharyngitis
Tonsillitis can develop as a complication of pharyngitis, leading to swelling and inflammation of the tonsils. Long-term effects may include recurrent infections and potential impacts on the immune system.
Tonsillitis as a Complication
Tonsillitis can develop as a complication of pharyngitis, particularly when the infection affects the tonsils. This condition presents with symptoms such as swollen and inflamed tonsils, accompanied by throat discomfort and difficulty swallowing. Prompt identification and treatment are essential to prevent potential complications and ensure recovery.
Potential Long-Term Effects
Long-term complications of pharyngitis may include recurrent infections, chronic inflammation, and potential impacts on the immune system. Proper management and follow-up care are crucial in addressing these effects and preventing further complications.
Prevention of Pharyngitis
Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, can help prevent the spread of pharyngitis. Strengthening the immune system through a healthy diet and adequate rest is vital in reducing the risk of contracting the infection.
Hygiene Practices to Prevent Spread
Adopting good hygiene practices like washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with individuals displaying symptoms, and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing can help prevent the spread of pharyngitis-causing viruses and bacteria.
Strengthening Immune System
Boosting the immune system through a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, as well as maintaining adequate hydration and quality sleep, can help the body fight off infections like pharyngitis more effectively. Regular exercise and stress management are also crucial in supporting overall immune function.
Chronic Pharyngitis
Chronic pharyngitis can be caused by various factors such as infections, environmental pollutants, allergies, or acid reflux. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for effective management.
Causes and Management of Chronic Pharyngitis
Chronic pharyngitis can arise from persistent infections, exposure to environmental pollutants, underlying allergies, or conditions like acid reflux. Management involves addressing the root cause, providing symptomatic relief, and possibly lifestyle modifications to prevent recurrence.
Home remedies like saltwater gargles, honey lemon tea, and throat lozenges can provide relief from pharyngitis symptoms. Additionally, staying hydrated and getting ample rest can aid in recovery.
Alternative and Home Remedies
When dealing with pharyngitis, alternative and home remedies such as saltwater gargles, honey lemon tea, and throat lozenges can help alleviate symptoms and promote comfort. These non-medical approaches provide soothing relief and support healing without the use of pharmaceutical interventions.
Prognosis of Pharyngitis
Recovery from pharyngitis typically occurs within a week with appropriate treatment. Recurrence rates are low, but complications like tonsillitis may prolong symptoms and require additional management.
Recovery Time and Recurrence Rates
Typically, individuals with pharyngitis recover within a week, especially with appropriate treatment. Recurrence rates are low for acute cases, but chronic or repeated infections may require further evaluation and management to address underlying factors contributing to recurrent episodes.
Overall, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pharyngitis is crucial for effective management and recovery. By following appropriate medical advice and practicing preventive measures, individuals can navigate through episodes of pharyngitis more effectively.
Summary of Key Points on Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis, whether caused by viruses or bacteria, presents with symptoms like sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing. Treatment involves antibiotics for bacterial cases and antiviral medications for viral infections. Proper diagnosis, management, and preventive measures are essential to address pharyngitis effectively and reduce the risk of complications.
