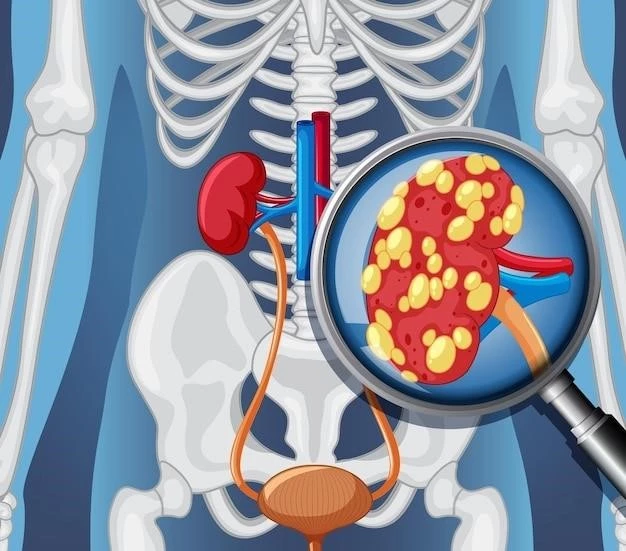
Introduction
Primary tumors of the spleen are rare and often asymptomatic. Some neoplasms are linked to blood disorders.
Primary tumors of the spleen can be asymptomatic until complications arise. These neoplasms can be linked to blood disorders such as myeloproliferative neoplasms. Common types include lymphomas, hemangiomas, and angiosarcomas. Biopsy is often necessary for a suspected tumor. Metastases to the spleen are rare, with primary angiosarcoma being extremely uncommon.
Overview of Spleen Neoplasm
Primary spleen tumors are rare, often asymptomatic until complications like rupture occur. Myeloproliferative neoplasms can cause an enlarged spleen.
Primary spleen tumors are rare and often asymptomatic until complications like rupture, bleeding, or compression. Myeloproliferative neoplasms can lead to an enlarged spleen. Lymphomas and vascular tumors are common types, while metastases to the spleen are rare compared to primary tumors.
Primary spleen tumors are rare and often asymptomatic until complications like rupture, bleeding, or compression. Myeloproliferative neoplasms can lead to an enlarged spleen. Lymphomas, vascular tumors, and metastases from other cancers are common types of primary spleen neoplasms.
Primary spleen tumors are rare, often asymptomatic until complications like rupture, bleeding, or compression. Myeloproliferative neoplasms can lead to an enlarged spleen. Lymphomas, vascular tumors, and metastases from other cancers are common types of primary spleen neoplasms.
Primary vs. Metastatic Tumors
Primary tumors of the spleen, including lymphomas, are rare but can lead to symptoms like abdominal pain. Metastases to the spleen are infrequent compared to primary malignancies, often originating from melanoma, breast, or lung cancers.
Benign vs. Malignant Neoplasms
The spleen can develop a range of neoplasms, from benign hemangiomas to malignant conditions like splenic lymphomas and angiosarcomas. Imaging plays a crucial role in identifying these neoplasms accurately.
Primary spleen tumors are rare, often asymptomatic until complications like rupture, bleeding, or compression. Myeloproliferative neoplasms can lead to an enlarged spleen. Lymphomas, vascular tumors, and metastases from cancers are common types.
Need for Biopsy in Suspected Cases
If a tumor is suspected or if the cause of an enlarged spleen is unknown, a biopsy is usually required. Aspirate and splenectomy are common methods to obtain diagnostic samples and prevent complications. Understanding the underlying condition is crucial for appropriate treatment.
Role of Aspirate and Splenectomy
When a tumor is suspected or the cause of an enlarged spleen is unknown, a biopsy is typically required. Although methods like aspirate with an ultrasound-guided needle can be used, splenectomy ─ the removal of the spleen ─ is often recommended to prevent complications and ensure an accurate diagnosis for appropriate treatment.
Primary spleen tumors are rare, often asymptomatic until complications like rupture, bleeding, or compression. Myeloproliferative neoplasms can lead to an enlarged spleen. Lymphomas, vascular tumors, and metastases from cancers are common types.
Lymphomas and Vascular Tumors
Lymphomas and vascular tumors are common types of neoplasms in the spleen. Splenic lymphomas are the most frequently encountered malignant tumors involving the spleen, originating from the white pulp. On the other hand, vascular tumors such as hemangiomas and angiosarcomas are among the benign and malignant neoplasms found in the spleen.
Hemangiomas and Angiosarcomas
Splenic hemangiomas are among the most common benign neoplasms found in the spleen and are typically asymptomatic. In contrast, angiosarcomas are malignant tumors originating from the endothelial lining of blood vessels and can present with vague symptoms like abdominal discomfort. Differentiating between these vascular tumors is crucial for appropriate management.
Primary spleen tumors are rare, often asymptomatic until complications like rupture, bleeding, or compression. Myeloproliferative neoplasms can lead to an enlarged spleen. Lymphomas, vascular tumors, and metastases from cancers are common types.
Myeloproliferative neoplasms, a group of blood disorders, can lead to an enlarged spleen. Enlargement may cause symptoms like a full feeling in the abdomen, highlighting the interconnected nature of splenic neoplasms and blood disorders.
The majority of metastatic tumors to the spleen originate from cancers such as melanoma, breast, lung, ovary, colon, stomach, and pancreas. Splenic metastases are typically seen as solitary or multiple masses, and diffuse infiltration is uncommon. Differentiated imaging characteristics aid in identifying splenic metastases accurately.
Relation to Blood Disorders
Myeloproliferative neoplasms, a group of blood disorders, can lead to an enlarged spleen. Enlargement may cause symptoms like a full feeling in the abdomen, indicating an interconnected relationship between splenic neoplasms and blood disorders.
Metastases and Associated Cancers
Metastatic tumors to the spleen are rare compared to primary malignancies. Common primary sites that give rise to splenic metastases include melanoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, and cancers of the colon, stomach, and pancreas. Differentiating between primary and metastatic tumors is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment decisions.
The management of splenic neoplasms is often determined by the staging of the disease. Depending on the extent of the tumor and potential spread, treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. Staging helps healthcare providers tailor the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual case.
Management Based on Staging
The staging of splenic neoplasms is crucial in determining the appropriate course of treatment. Depending on the tumor’s stage, healthcare providers may recommend surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. Staging aids in tailoring individualized treatment plans for optimal outcomes.
Spleen neoplasms can have varying effects on overall health, depending on the type and stage of the tumor. Complications such as splenic rupture or compression can impact the body’s functioning, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain and discomfort. Managing the neoplasm effectively is vital to minimize health implications and ensure a better quality of life.
Impact on Overall Health
Spleen neoplasms can have varying effects on overall health, depending on the type and stage of the tumor. Complications such as splenic rupture or compression can impact the body’s functioning, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain and discomfort. Managing the neoplasm effectively is vital to minimize health implications and ensure a better quality of life.
Primary Tumors of the Spleen
Primary spleen tumors are rare, often asymptomatic until complications like rupture, bleeding, or compression. Myeloproliferative neoplasms can cause an enlarged spleen. Common types include lymphomas, vascular tumors, and metastases from other cancers.
Research on spleen neoplasms focuses on understanding the classification and treatment options for these rare tumors. Studies explore the impact of various neoplasms on overall health and aim to improve survival rates through innovative therapies and personalized treatment approaches. Researchers are also investigating the potential recurrence risks associated with different types of spleen neoplasms to enhance patient outcomes.
Ongoing research on spleen neoplasms aims to enhance classification accuracy and treatment efficacy. Investigative studies focus on refining diagnostic approaches, evaluating treatment outcomes, and exploring novel therapeutic strategies to improve patient survival rates. Researchers are dedicated to advancing the understanding of spleen neoplasms through cutting-edge research initiatives.
Current Studies on Spleen Neoplasms
Ongoing research on spleen neoplasms focuses on understanding the classification and treatment options for these rare tumors. Studies explore the impact of various neoplasms on overall health and aim to improve survival rates through innovative therapies and personalized treatment approaches. Researchers are also investigating the potential recurrence risks associated with different types of spleen neoplasms to enhance patient outcomes.
Early signs of spleen neoplasms may go unnoticed, but symptoms like abdominal discomfort, fullness, or unexplained weight loss must be promptly evaluated. Early detection through regular check-ups and awareness of potential warning signs can lead to timely diagnosis and better treatment outcomes for individuals at risk of spleen tumors.
Awareness of early signs of spleen neoplasms is crucial. Symptoms like abdominal discomfort, fullness, or unexplained weight loss should be promptly addressed. Regular check-ups play a significant role in early detection, potentially leading to timely diagnosis and better treatment outcomes for individuals at risk of developing spleen tumors.
Symptom Recognition and Early Detection
Awareness of early signs of spleen neoplasms is crucial. Symptoms like abdominal discomfort, fullness, or unexplained weight loss should be promptly addressed. Regular check-ups play a significant role in early detection, potentially leading to timely diagnosis and better treatment outcomes for individuals at risk of developing spleen tumors.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are essential in the early detection of spleen neoplasms. Keeping up with routine health evaluations can aid in identifying potential warning signs, allowing for timely intervention and improved treatment outcomes. Being proactive about health screenings contributes to overall well-being and assists in the prompt management of any emerging health concerns.
Genetic Counseling and Screening
Genetic counseling and screening can play a crucial role in identifying individuals at risk of developing spleen neoplasms. Understanding familial predispositions and genetic markers associated with these tumors can aid in early detection and preventive strategies. By incorporating genetic counseling and screening practices, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and potentially mitigate the risk of developing spleen neoplasms.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of developing spleen neoplasms. Avoiding tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption may also play a role in preventing certain types of cancers. Incorporating these lifestyle modifications can support overall health and potentially lower the risk of spleen tumors.
Joining patient support groups can provide individuals with spleen neoplasms a sense of community, emotional support, and valuable resources. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can foster empowerment, shared experiences, and helpful information exchange. These groups offer a platform for individuals to navigate their journey, gain insights, and find encouragement throughout their treatment and recovery process.
Patient Support Groups
Engaging with patient support groups can provide individuals affected by spleen neoplasms with emotional support, shared experiences, and valuable resources. Connecting with others who face similar challenges can offer a sense of community, empowerment, and access to information. These groups serve as a platform for individuals to navigate their journey, exchange insights, and find encouragement throughout their treatment and recovery process.
Counseling Services for Patients and Families
Seeking counseling services can provide valuable support for patients and families navigating the challenges of spleen neoplasms. Counseling can offer emotional guidance, coping strategies, and a safe space to express concerns and fears. Professional counselors assist individuals and their loved ones in addressing the psychological and emotional impact of the diagnosis, treatment, and recovery process.
Spleen neoplasms can impact both physical and emotional health. Symptoms like abdominal discomfort and anemia can affect physical well-being, while the emotional toll of a cancer diagnosis may be significant. Maintaining balance in both aspects is essential for overall health and quality of life during the treatment and recovery journey.
Challenges Faced by Patients
Patients with spleen neoplasms may encounter various challenges, both physically and emotionally. From managing symptoms like abdominal discomfort to coping with the psychological impact of a cancer diagnosis, individuals may face difficulties in navigating their treatment journey. Understanding and addressing these challenges can help individuals and their families cope effectively during the course of the illness.
Physical and Emotional Well-being
Spleen neoplasms can impact both physical and emotional health. Symptoms like abdominal discomfort and anemia can affect physical well-being, while the emotional toll of a cancer diagnosis may be significant. Maintaining balance in both aspects is essential for overall health and quality of life during the treatment and recovery journey.
While primary tumors of the spleen are rare, they can present unique diagnostic and management challenges. Understanding the incidence rates and disparities in treatment approaches can aid in providing optimized care for individuals with spleen neoplasms worldwide. Access to advanced treatments and standardized care can impact patient outcomes and overall prognosis.
Research Collaborations and International Efforts
Collaborative research efforts and international collaborations are essential in advancing the understanding and treatment of spleen neoplasms. By fostering partnerships among healthcare professionals, researchers, and institutions worldwide, valuable insights can be gained, leading to improved diagnostic techniques, treatment modalities, and patient outcomes. Sharing knowledge and resources on a global scale can enhance the management of spleen neoplasms and drive innovation in the field.
Incidence and Treatment Disparities
Primary spleen tumors, though rare, present unique challenges in diagnosis and management. Understanding treatment disparities and incidence rates globally can improve care strategies for individuals with spleen neoplasms. Enhanced access to advanced treatments and standardized care can significantly impact patient outcomes and overall prognosis.
Summary of Key Points
Spleen neoplasms, whether primary or metastatic, present various diagnostic and management challenges. Understanding the incidence rates, treatment disparities, and global collaborative efforts can greatly impact patient outcomes. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, genetic counseling, and support resources play vital roles in addressing these complex diseases.