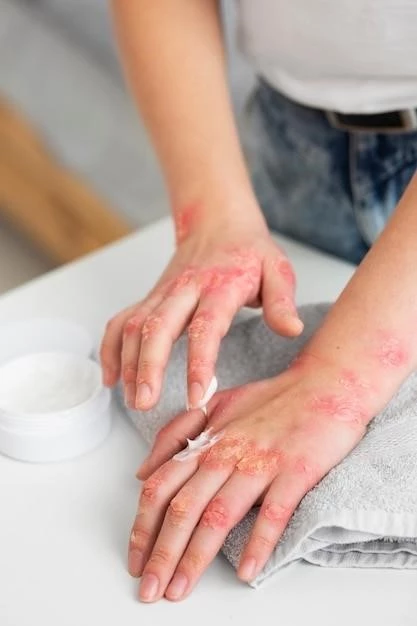
Introduction to Nonallergic Atopic Dermatitis
INTRODUCTION. Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic pruritic relapsing inflammatory skin disease with variable clinical features. AD has been categorized into two types‚ the classic IgE-mediated allergic (extrinsic form; eAD)‚ and non-allergic (intrinsic form⁚ iAD or atopiform dermatitis). The European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology nomenclature task force has proposed the distinction to better understand and manage this condition.
Definition and Background Information
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease with a complex genetic background. It often manifests as itchy‚ dry‚ and inflamed skin‚ affecting individuals of all ages. Understanding the distinction between allergic and non-allergic forms of AD is crucial for proper management and treatment. The condition’s genetic predisposition and impact on the immune system play a significant role in its development and progression.
Clinical Features of Nonallergic Atopic Dermatitis
The chronic pruritic nature of nonallergic atopic dermatitis presents with varying clinical features‚ emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis and tailored management strategies based on individual symptoms and triggers.
Chronic Pruritic Nature of the Disease
Nonallergic atopic dermatitis is characterized by its chronic pruritic nature‚ leading to continuous discomfort and the risk of complications. Understanding the persistent itch and its impact on daily life is essential for effective management and improving quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Variability in Clinical Presentation
Nonallergic atopic dermatitis exhibits a wide range of clinical presentations‚ making it essential for healthcare providers to recognize and address the individualized nature of each patient’s symptoms. This variability underscores the importance of personalized treatment approaches tailored to specific manifestations of the disease.
Comorbidities Associated with Nonallergic Atopic Dermatitis
The consequences of atopic dermatitis reach beyond the skin and past childhood. Patients with atopic dermatitis are at risk of developing allergic comorbidities‚ but less is known about the associations between atopic dermatitis and non-allergic conditions. Understanding these non-allergic comorbidities has the potential to improve patient outcomes.
Understanding Allergic vs. Non-Allergic Comorbidities
Atopic dermatitis often coexists with other allergic conditions such as asthma and allergic rhinitis due to shared genetic factors and immune responses. However‚ recognizing the distinctions between allergic and non-allergic comorbidities is vital for comprehensive care and tailored treatment plans to address individual patient needs effectively.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
The impact of nonallergic atopic dermatitis on patient outcomes can be profound‚ influencing quality of life‚ mental well-being‚ and overall health. By recognizing and addressing these implications‚ healthcare providers can improve treatment strategies and enhance the long-term management of this chronic skin condition.
Management and Treatment of Nonallergic Atopic Dermatitis
To effectively manage nonallergic atopic dermatitis‚ it is crucial to prioritize regular moisturizing and establish self-care habits. Additionally‚ considering the use of medicated creams and exploring other treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and improve skin health.
Importance of Regular Moisturizing and Self-Care Habits
Regular moisturizing is key in managing nonallergic atopic dermatitis‚ as it helps improve skin hydration and prevent flare-ups. Establishing self-care habits like gentle cleansing and avoiding harsh products can further support skin health and reduce itching and inflammation.
Role of Medicated Creams and Other Treatment Options
Medicated creams play a vital role in managing nonallergic atopic dermatitis by controlling itching and aiding in skin repair. Understanding the diverse treatment options available‚ such as topical medications and advanced therapies‚ can significantly improve symptom management and overall skin health.
Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Nonallergic Atopic Dermatitis
Understanding the genetic background and skin barrier impairment associated with nonallergic atopic dermatitis sheds light on the links to immune system responses and inflammation‚ emphasizing the importance of addressing these factors in managing the condition effectively.
Genetic Background and Skin Barrier Impairment
The genetic background and skin barrier impairment in nonallergic atopic dermatitis play essential roles in the immune system response and inflammation‚ highlighting the need to address these factors for effective management of the condition.
Link to Immune System Response and Inflammation
In nonallergic atopic dermatitis‚ there is a notable connection between the skin barrier impairment‚ immune system response‚ and inflammation. Understanding how these factors interact is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and managing the condition successfully.
Risk Factors and Triggers for Nonallergic Atopic Dermatitis
Understanding genetic predisposition and family history is crucial‚ as well as identifying and avoiding common triggers and irritants that can exacerbate nonallergic atopic dermatitis. By managing these risk factors effectively‚ individuals can better control their condition and prevent flare-ups.
Genetic Predisposition and Family History
Genetic predisposition and family history play a significant role in the development of nonallergic atopic dermatitis. Understanding these factors is essential for identifying individuals at risk and implementing preventive measures to manage the condition effectively.
Common Triggers and Irritants to Avoid
Identifying and avoiding common triggers and irritants‚ such as certain foods‚ allergens‚ harsh chemicals‚ and environmental factors‚ is crucial in managing nonallergic atopic dermatitis. By minimizing exposure to these triggers‚ individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups‚ promoting better skin health and overall well-being.
Implementing tips for preventing eczema flares and maintaining adequate skin hydration through regular moisturizing are essential for managing nonallergic atopic dermatitis effectively. Consistent skincare routines can help minimize irritation and support skin health.
Prevention Strategies and Basic Skin Care Routine
Adopting tips to prevent eczema flares and focusing on adequate skin hydration through regular moisturizing are key strategies in managing nonallergic atopic dermatitis effectively. Consistent skincare routines play a crucial role in minimizing skin irritation and promoting overall skin health.
Importance of Moisturizing and Skin Hydration
Prioritizing skin hydration through regular moisturizing is crucial for managing nonallergic atopic dermatitis. Consistent use of moisturizers helps maintain the skin’s natural barrier function‚ reduce dryness‚ and alleviate discomfort associated with the condition.
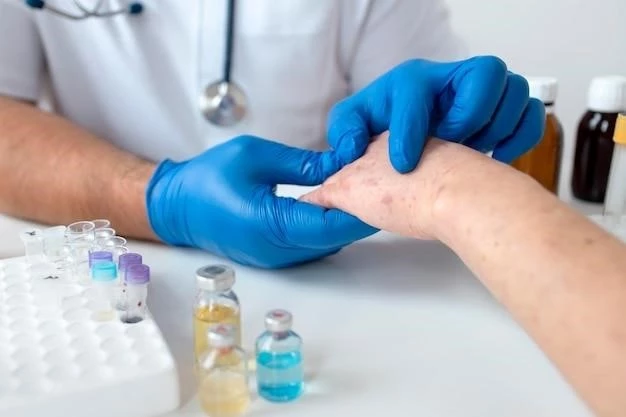
Complications and Long-Term Outlook
Potential complications of nonallergic atopic dermatitis can impact quality of life. Therefore‚ managing symptoms effectively and preventing flare-ups are essential for improving long-term outcomes and maintaining skin health.
Potential Complications of Nonallergic Atopic Dermatitis
Nonallergic atopic dermatitis may lead to potential complications that can affect the quality of life. Proper management and flare prevention strategies are essential to mitigate these complications and ensure optimal long-term skin health.
Management of Symptoms and Flare Prevention
Effective management of symptoms and preventive measures are vital in controlling nonallergic atopic dermatitis. By implementing strategies to address flare triggers and maintaining a consistent skincare routine‚ individuals can better manage their condition and improve long-term skin health.
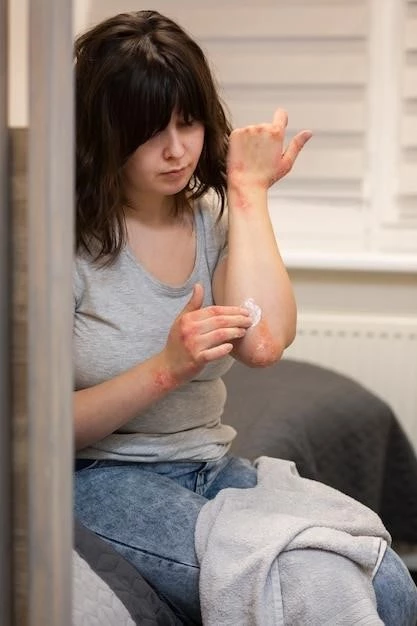

Research and Advancements in Nonallergic Atopic Dermatitis
Current evidence highlights the importance of understanding non-allergic comorbidities to improve patient outcomes and enhance the management of nonallergic atopic dermatitis effectively. Stay informed about advancements in treatment approaches to optimize skin health.
Overview of Systematic Reviews on Nonallergic Comorbidities
Systematic reviews provide valuable insights into nonallergic comorbidities associated with atopic dermatitis. Understanding the comprehensive evidence gathered from these reviews can guide healthcare professionals in optimizing patient care strategies and improving outcomes for individuals with nonallergic atopic dermatitis.
Current Evidence and Future Directions in Treatment Approaches
Staying informed about current evidence and exploring future directions in treatment approaches for nonallergic atopic dermatitis is crucial. Advancements in therapeutic strategies can lead to more effective management of the condition‚ enhancing skin health and overall well-being in individuals affected by this chronic skin disease.