Overview of Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral valve insufficiency, also known as mitral regurgitation, is a common cardiac disorder that causes blood to leak back into the left atrium during systole.
Causes and Diagnosis
Causes of mitral regurgitation may include mitral valve prolapse, rheumatic heart disease, connective tissue diseases, and cleft mitral valve. Diagnosis often involves echocardiogram and clinical evaluation to assess symptoms and identify the underlying cause.
Treatment and Prognosis
Treatment for mitral regurgitation depends on the severity of the condition and may include medications, lifestyle modifications, or surgical intervention such as mitral valve repair or replacement. Prognosis can vary but early diagnosis and appropriate management can improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with this disease.
Cardiospondylocarpofacial Syndrome, characterized by mitral regurgitation, conductive deafness, and skeletal anomalies, is a genetic disorder associated with specific gene pathways. Clinical features include growth retardation, fusion of cervical vertebrae, and cardiac anomalies.
Genetic Factors and Pathways
Cardiospondylocarpofacial Syndrome, a rare genetic disorder, is associated with specific gene pathways such as MAP3K7 (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase 7). This syndrome includes features like mitral regurgitation, conductive deafness, and various skeletal anomalies, highlighting the complex genetic factors contributing to its manifestation.
Cardiospondylocarpofacial Syndrome
Cardiospondylocarpofacial Syndrome, characterized by mitral regurgitation, conductive deafness, and skeletal anomalies, is a genetic disorder associated with specific gene pathways. Clinical features include growth retardation, fusion of cervical vertebrae, and cardiac anomalies.
Impact on Diagnosis and Treatment
The presence of skeletal anomalies in individuals with mitral regurgitation can complicate both diagnosis and treatment strategies. Understanding the relationship between these anomalies and cardiac issues is crucial for effective management.
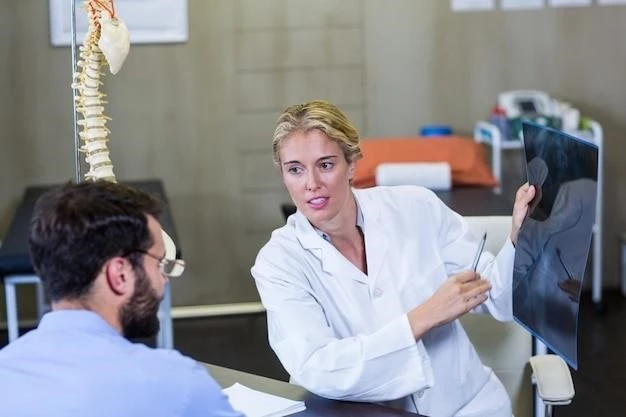

Skeletal Anomalies Associated with Mitral Regurgitation
The presence of skeletal anomalies in individuals with mitral regurgitation can impact both the diagnostic process and the chosen treatment pathways. Understanding how these anomalies relate to the cardiac condition is essential for effective management and care.
Relationship to Other Symptoms
The presence of skeletal anomalies in individuals with mitral regurgitation can offer important insights into the overall symptomatology of the condition. Understanding how these anomalies relate to other symptoms can aid in comprehensive management and treatment planning.
Types of Heart Valve Disease
Types of heart valve disease caused by mitral valve anomalies include mitral valve stenosis and mitral valve regurgitation. Mitral valve stenosis occurs when the valve opening is narrowed, reducing blood flow. Mitral valve regurgitation results in blood flowing back into the heart’s left atrium.
Mitral Valve Stenosis
Mitral valve stenosis is a condition where the mitral valve opening narrows, restricting blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. This narrowing can lead to increased pressure in the left atrium and lungs, causing symptoms and impacting heart function.
Mitral Valve Prolapse and Regurgitation
Mitral valve prolapse and regurgitation are common conditions characterized by the improper closure of the mitral valve. Mitral valve prolapse occurs when the valve’s flaps bulge into the left upper heart chamber during contractions, while regurgitation results in blood flowing backward due to a leaky valve, leading to potential complications and symptoms.
Echocardiogram and other imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosing mitral regurgitation. Transesophageal echocardiography offers detailed insights into the structure and function of the heart valves, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Echocardiogram and other imaging techniques are essential for diagnosing mitral regurgitation. Transesophageal echocardiography provides detailed insights into heart valve structure and function, aiding accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
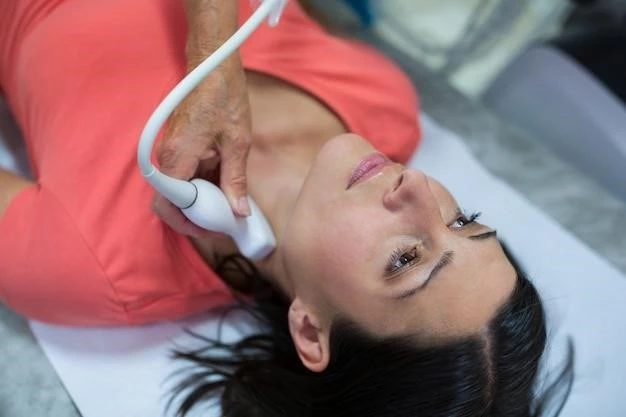
Diagnostic Procedures for Mitral Regurgitation
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) is a valuable diagnostic tool in evaluating mitral regurgitation. This imaging technique provides detailed visualization of the heart structures, allowing for a more precise assessment of the severity and mechanism of the regurgitation.
Complications of Mitral Valve Disease
Progression of mitral valve disease can lead to various complications, impacting heart function and potentially causing conditions like atrial fibrillation. Understanding these complications is crucial for effective management and treatment strategies.
Effects on Heart Function
Mitral valve disease can significantly impact heart function, leading to complications such as increased workload for the heart, enlargement of the left ventricle, and potential weakening of the heart muscle. Understanding these effects is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Associated Conditions like Atrial Fibrillation
Complications of mitral valve disease can include conditions such as atrial fibrillation. Understanding the potential association between mitral regurgitation and atrial fibrillation is essential for optimizing treatment and managing the overall health of individuals affected by these cardiac issues.
Mitral Regurgitation-Deafness-Skeletal Anomalies Syndrome
Forney syndrome, also known as Mitral regurgitation-deafness-skeletal anomalies syndrome, is a rare condition characterized by mitral insufficiency, conductive deafness, short stature, and skeletal abnormalities. Genetic factors play a significant role in the onset of this syndrome.
Description and Prevalence
Forney syndrome, also known as Mitral regurgitation-deafness-skeletal anomalies syndrome, is a rare genetic condition characterized by cardiac anomalies, conductive deafness, and skeletal abnormalities. The prevalence of this syndrome is low, and it is crucial to understand its unique features for accurate diagnosis and management.
Inheritance Patterns and Onset Age
The Mitral Regurgitation-Deafness-Skeletal Anomalies syndrome exhibits an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, with an onset that can occur at any age. Understanding the genetic transmission and age of onset is essential for proper counseling and management of individuals affected by this rare syndrome.
