Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita and CNS Calcification
Cognitive Impairment in CNS Calcification Patients
Physical Therapy for Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
Research Advances in Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita Treatment
Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita⁚ Causes and Treatments
Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita (AMC) is a rare condition characterized by multiple joint contractures at birth‚ leading to limited movement․ The causes of AMC include genetic mutations affecting fetal movements‚ maternal infections during pregnancy‚ and environmental factors․
Treatment of AMC involves a multidisciplinary approach tailored to each individual․ Physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving joint mobility and muscle strength․ Occupational therapy helps in developing daily living skills‚ while speech therapy addresses any speech-related issues․
Orthopedic interventions such as splinting‚ casting‚ or surgery may be necessary to correct joint contractures․ Assistive devices like braces or wheelchairs can enhance mobility and independence․ In some cases‚ ongoing care by a team of specialists is essential to manage associated complications and provide long-term support․
Research into potential genetic therapies for AMC is promising‚ offering hope for more targeted treatments in the future․ Early detection and intervention play a key role in improving outcomes for individuals with AMC‚ emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive and coordinated treatment plan․
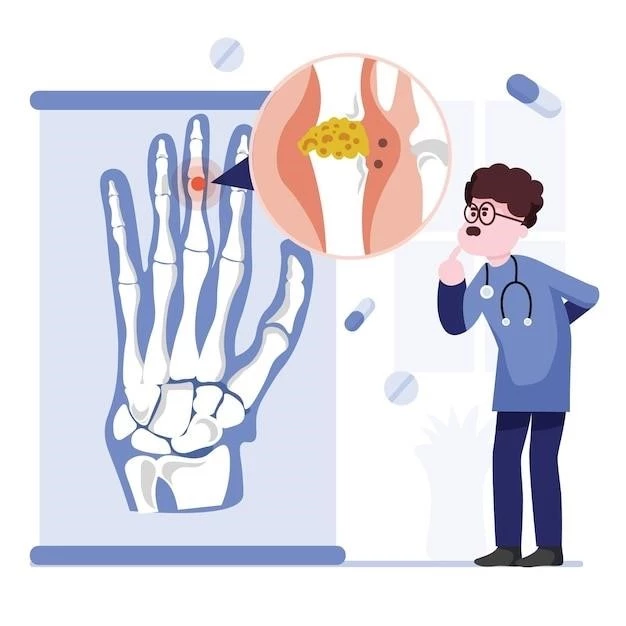
Understanding CNS Calcification⁚ Symptoms and Diagnosis
Central Nervous System (CNS) calcification refers to the accumulation of calcium deposits in the brain․ Symptoms of CNS calcification vary depending on the location and extent of calcification but may include headache‚ seizures‚ movement disorders‚ cognitive impairment‚ and neurological deficits․
Diagnosis of CNS calcification involves imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI to visualize the calcium deposits in the brain․ Blood tests to assess calcium levels and genetic testing may also be conducted to determine underlying causes of the calcification․
Management of CNS calcification focuses on symptom relief and addressing underlying conditions causing the calcification; Treatment may involve medications to control seizures‚ physical therapy to manage movement disorders‚ and cognitive therapy to address any cognitive impairments․
Monitoring of CNS calcification is crucial to track progression and adjust treatment plans accordingly․ Research into the mechanisms of CNS calcification and potential targeted therapies is ongoing‚ with the aim of improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by this condition․
Management of Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita in Children
Managing Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita (AMC) in children requires a comprehensive approach to address the physical and developmental challenges associated with the condition․ Early intervention is key in promoting optimal growth and mobility․
Physical therapy plays a central role in the management of AMC in children․ Therapists work to improve joint range of motion‚ muscle strength‚ and coordination through targeted exercises and stretching routines․ Occupational therapy helps children learn valuable skills for daily activities and enhances their independence․
Orthopedic interventions such as serial casting‚ splinting‚ and surgery may be recommended to address joint contractures and deformities․ Bracing and assistive devices can provide additional support and aid in mobility․ Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed․
Educational support is crucial for children with AMC to ensure they receive appropriate accommodations and resources to optimize their learning potential․ Collaborating with a team of specialists‚ including orthopedic surgeons‚ physical therapists‚ occupational therapists‚ and educational professionals‚ is fundamental in providing holistic care for children with AMC․
Neurological Complications in Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
Neurological complications are common in individuals with Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita (AMC) due to the impact of joint contractures and muscle weakness on motor function․ These complications can vary in severity and may affect mobility‚ coordination‚ and overall quality of life․
One of the primary neurological complications of AMC is muscle weakness‚ which can lead to challenges in movement and coordination․ This weakness may result from underlying neuromuscular conditions or nerve abnormalities․ Individuals with AMC may also experience spasticity or hypertonia in affected limbs‚ further complicating motor function․
Orthopedic deformities resulting from joint contractures can put pressure on nerves and impede neural signaling‚ contributing to neurological complications․ Additionally‚ individuals with AMC may be at risk of developing spinal cord compression due to abnormal curvature of the spine‚ potentially leading to motor deficits․
Management of neurological complications in AMC often involves a multidisciplinary approach‚ including physical therapy to improve muscle strength and coordination‚ orthopedic interventions to correct deformities‚ and neurological assessments to monitor nerve function and address any issues promptly․
Surgical Interventions for Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
Surgical interventions play a vital role in the management of Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita (AMC) to address joint contractures‚ deformities‚ and improve overall function and quality of life for affected individuals․ The decision to proceed with surgery is typically based on the severity of joint involvement and functional limitations․
Common surgical procedures for AMC include tendon releases‚ joint reconstructions‚ and osteotomies to correct malalignments․ Tendon lengthening surgeries can help improve joint mobility by releasing tight tendons‚ allowing for better range of motion and functionality․
Orthopedic surgeons may also perform soft tissue releases or transfers to rebalance muscles around affected joints and optimize alignment․ In severe cases of AMC‚ joint fusion surgeries may be considered to stabilize joints and prevent further contractures․
Post-surgical rehabilitation is crucial to maximize the benefits of these interventions․ Physical therapy and occupational therapy are essential components of the recovery process to restore strength‚ flexibility‚ and functional abilities following surgery․ Close follow-up care with healthcare providers is important to monitor progress and address any post-operative challenges that may arise․